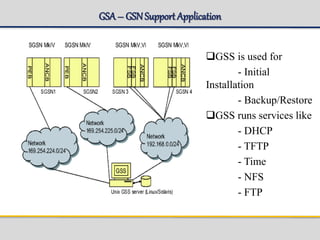
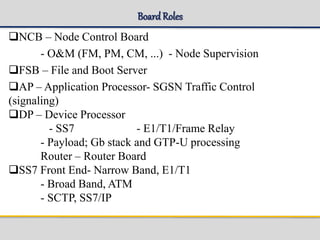
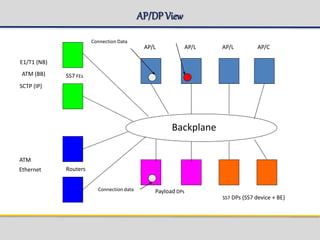
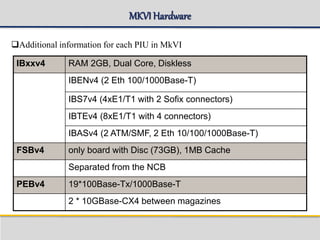
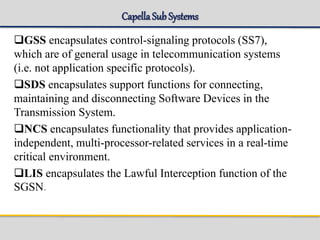
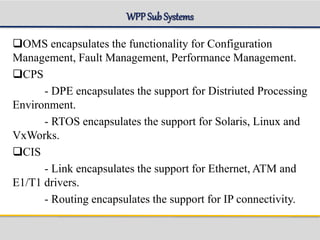
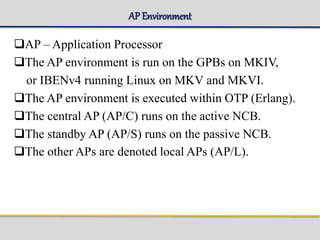
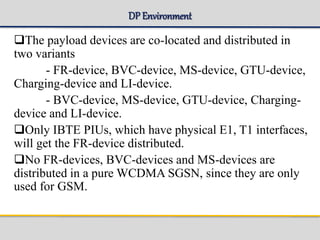
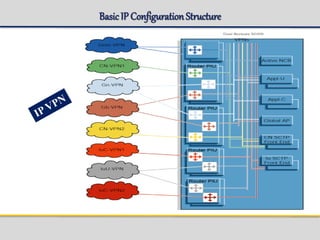
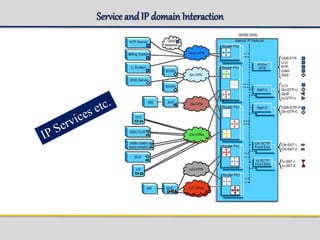
The document outlines the architecture and components of the SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) MKVI, detailing hardware, board roles, subsystems, and configuration. Key topics include communication protocols, processor assignments, subsystem functions, and subscriber commands for managing connections. It emphasizes the dual-file server setup for redundancy and the functionality of various application processors in handling telecommunications tasks.




![ConfigurationBreakdown
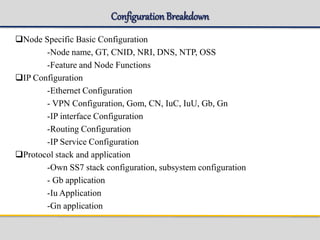
Interface configuration
-Gr interface [sigtran]
-IuC interface [Sigtran]
-Gb interface [dynamic]
-RNC configuration
Routing Area
-GSM Routing Area [manual+auto]
-WCDMA Routing Area [
-Coopeating Routing Area
Nodeproperties Parameter and Other services
-Node properties
- CDR properties
-EBM
-Gtrule & IMSI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sgsn-servinggprssupportnode-class02presented-conf-excluded-170721211808/85/SGSN-serving-gprs-support-node-Platform-HW-SW-and-CLI-29-320.jpg)
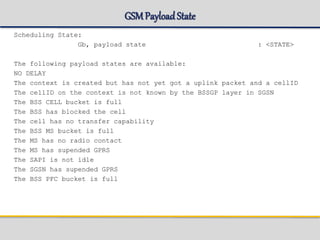
![Get_subscriber
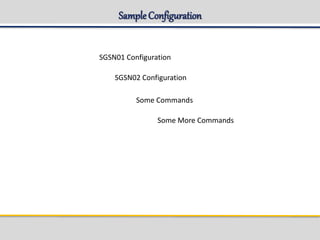
CLI command get_subsriber in gsh shell:
Usage:
get_subscriber -imsi Imsi [-dl 1 | 2]
get_subscriber -msisdn Msisdn [-dl 1 | 2]
get_subscriber -imei Imei [-dl 1 | 2]
get_subscriber -ptmsi Ptmsi [-dl 1 | 2]
get_subscriber -tlli Tlli [-dl 1 | 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sgsn-servinggprssupportnode-class02presented-conf-excluded-170721211808/85/SGSN-serving-gprs-support-node-Platform-HW-SW-and-CLI-32-320.jpg)
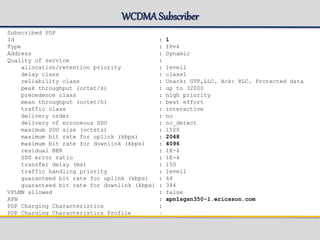
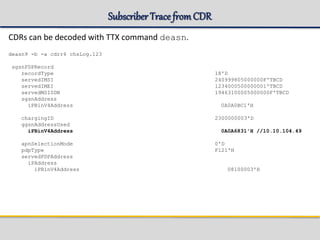
![WCDMASubscriber
=== sysadm@eqm01s14p2 ANCB ~ # gsh get_subscriber -imsi 240999800000000 -dl 2
Subscriber Data
----------------------------------------------------------------------
IMSI : 240999800000000
Mobile Subscriber ISDN No. : 463100000000000
IMEI : 123400000000000
Roaming Status : Home
HLR Address : 46990000001
Home PLMN APN Operator Id : mnc021.mcc123.gprs
Subscribed Teleservices : MO/MT SMS
Network Access Mode : Packet/Circuit Switched
Radio Access Technology : UMTS
Mobility Management State : PMM-CONNECTED/PMM-IDLE
Paging Proceed Flag : Set
Routing Area [RAI] : 123-021-5303-30
P-TMSI : 3496595516 (#D069D03C)
MSC/VLR Address : Not Gs connected
Location Confirmed in HLR : true
Data Confirmed by HLR : true
Charging Characteristics :
Charging Characteristics Profile :
Ciphering Algorithm : uea1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sgsn-servinggprssupportnode-class02presented-conf-excluded-170721211808/85/SGSN-serving-gprs-support-node-Platform-HW-SW-and-CLI-33-320.jpg)

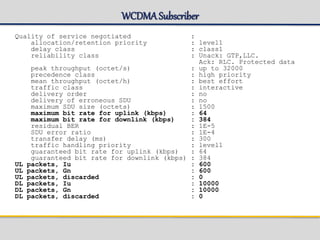
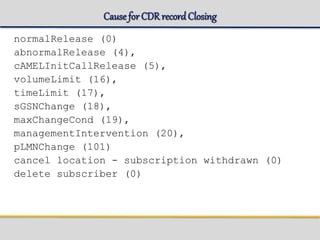
![GSMSubscriber
=== sysadm@eqm01s14p2 ANCB ~ # gsh get_subscriber -imsi 240999805000000 -dl 2
Subscriber Data
----------------------------------------------------------------------
IMSI : 240999805000000
Mobile Subscriber ISDN No. : 463100005000000
IMEI : 123400050000000
Roaming Status : Home
HLR Address : 46990000001
Home PLMN APN Operator Id : mnc021.mcc123.gprs
Subscribed Teleservices : MO/MT SMS
Network Access Mode : Packet/Circuit Switched
Radio Access Technology : GSM
Mobility Management State : Ready/Standby
Paging Proceed Flag : Set
Routing Area [RAI] : 123-021-5201-20
Cell [CGI] : 123-021-5201-1000
P-TMSI : 4041822746 (#F0E9521A)
MSC/VLR Address : Not Gs connected
Location Confirmed in HLR : true
Data Confirmed by HLR : true
Charging Characteristics :
Charging Characteristics Profile :
Ciphering Algorithm : gea3
NSEI : 4201
BVCI : 1000
MS Bucket :
MS Bucket Counter (octets) : 1519
MS Bucket Level (percent) : 3
MS Bucket Leak Rate (octets/sec) : 256000
BVC Bucket :
BVC Bucket Counter (octets) : 1519
BVC Bucket Level (percent) : 3
BVC Bucket Leak Rate (octets/sec) : 768000
Default MS Bucket Size (octets) : 50000 octets
Default MS Bucket Leak Rate (octets/sec) : 256000 octets/sec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sgsn-servinggprssupportnode-class02presented-conf-excluded-170721211808/85/SGSN-serving-gprs-support-node-Platform-HW-SW-and-CLI-37-320.jpg)


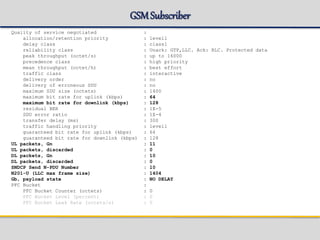




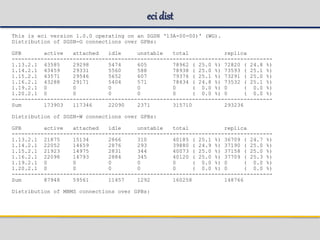
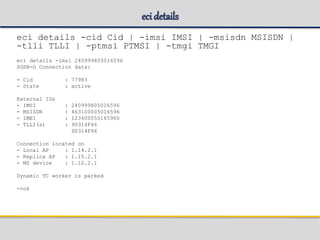
![eci list
eci list [-l Limit| -all] [-idle|-attached|-active
eci list -all -idle > idle.txt
eci list -all -attached > attach.txt
eci list -all -active > active.txt
eci list -all -unstable > unstable.txt
eci list -l 500 -active > active.txt
SGSN-G connection details:
IMSI MSISDN TLLI(s) State Cid Local AP Replica AP DP
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
240999805007295 463100005007295 8031A179 active 82755 1.15.2.1 1.13.2.1 1.12.2.1
+ C031A179
SGSN-W connection details:
IMSI MSISDN P-TMSI State Cid Local AP Replica AP DP
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
240999800001174 463100000001174 F0918F01 active 73502 1.16.2.1 1.15.2.1 1.11.2.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sgsn-servinggprssupportnode-class02presented-conf-excluded-170721211808/85/SGSN-serving-gprs-support-node-Platform-HW-SW-and-CLI-49-320.jpg)