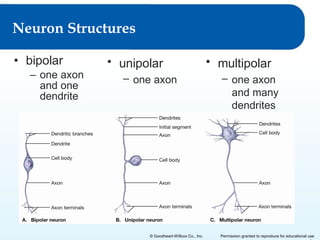
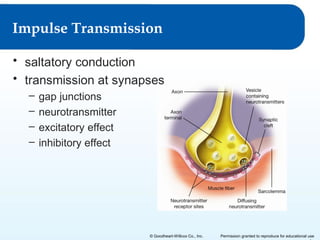
The document provides an overview of the nervous system including:
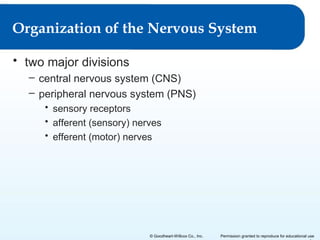
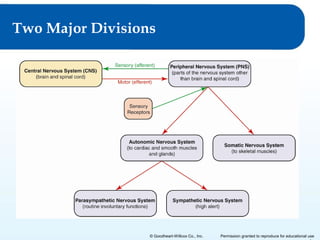
1) It describes the two major divisions of the nervous system - the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
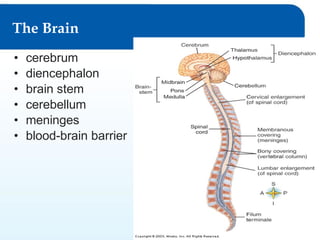
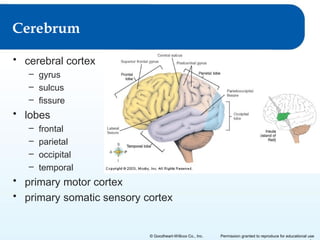
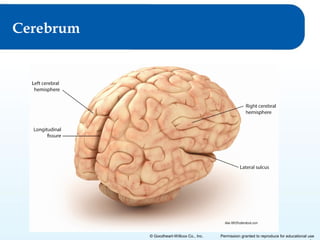
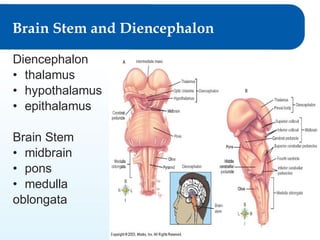
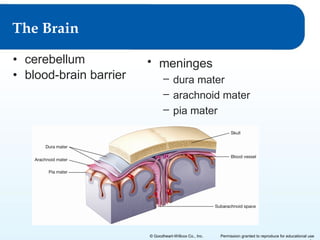
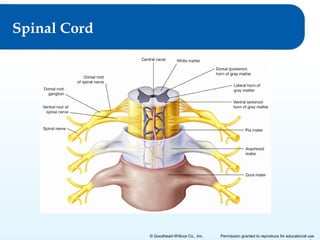
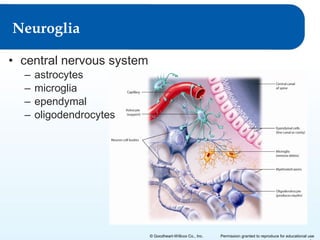
2) It explains the functional anatomy of the CNS including structures like the brain, spinal cord, and various parts of the brain.
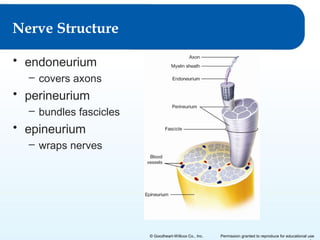
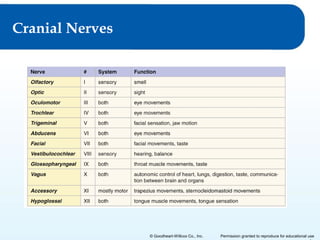
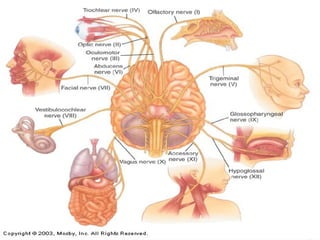
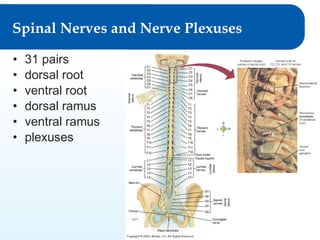
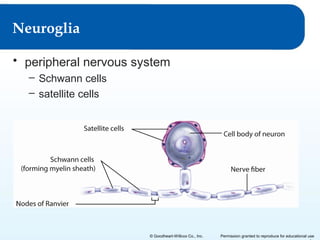
3) It details the functional anatomy of the PNS including cranial nerves, spinal nerves, nerve plexuses, and the autonomic nervous system.