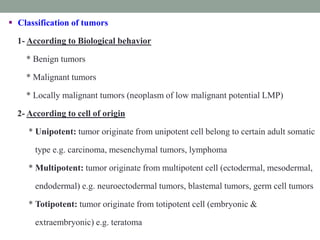
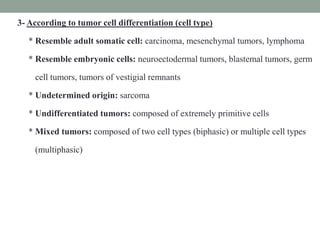
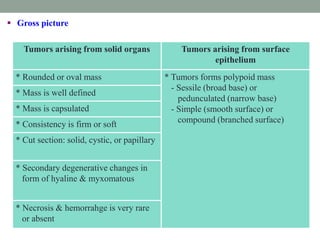
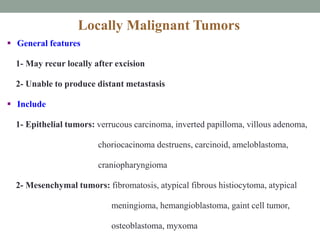
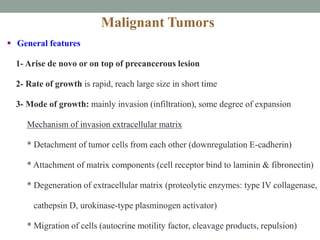
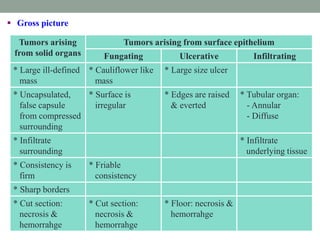
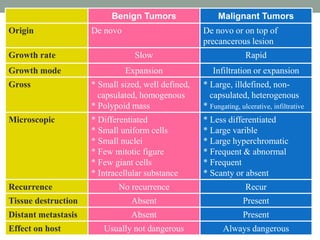
Neoplasia refers to abnormal tumor growth. There are two main types of tumors: benign tumors, which remain localized and do not recur after removal, and malignant tumors, which invade surrounding tissues and can metastasize to distant sites. Benign tumors are well-defined masses that grow slowly by expansion, while malignant tumors are poorly defined masses that grow rapidly by infiltration. Microscopically, benign tumor cells resemble normal cells and have few blood vessels and mitoses, whereas malignant tumor cells are poorly differentiated with irregular nuclei, frequent mitoses, and necrosis. Malignant tumors can recur after removal and are always a health risk.