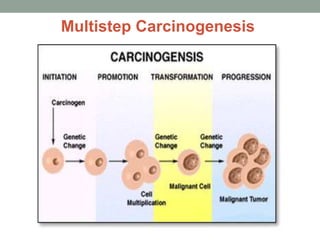
1) Carcinogenesis is a multistep process involving initiation, promotion, and progression. Initiation involves genetic mutations from environmental factors like smoking. Promotion involves clonal expansion driven by growth factors in a reversible stage. Progression results in irreversible aneuploidy and cellular anaplasia.
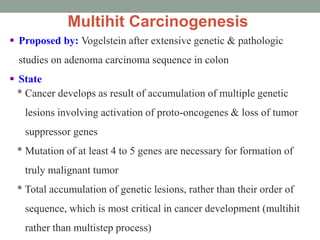
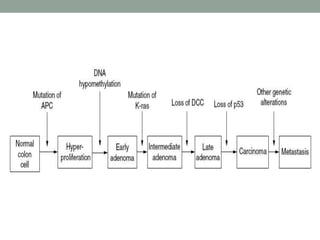
2) The multihit hypothesis proposes cancer develops through accumulation of multiple genetic mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, requiring 4-5 mutations for malignancy.
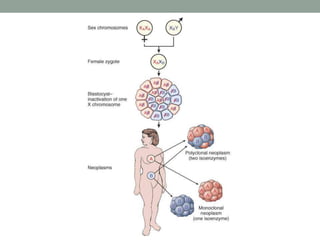
3) Cancers arise from a single cell of origin (monoclonal) that accumulates mutations over time, leading to intratumor heterogeneity as subclones evolve. Evidence for monoclonal origin includes single enzyme/immunoglob