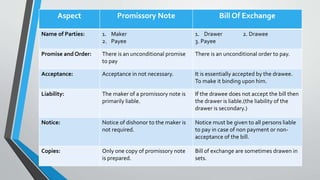
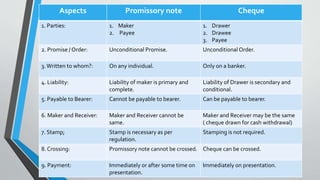
This document defines and explains the key characteristics of negotiable instruments including bills of exchange, promissory notes, and cheques. It states that a negotiable instrument is a device for transferring debt from one person to another and includes any document where ownership can be transferred through simple delivery. The document then outlines the essential elements and parties involved in promissory notes, bills of exchange, and cheques. It provides comparisons of their characteristics and differences between the instruments.