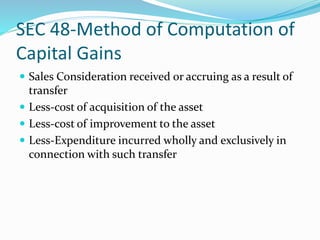
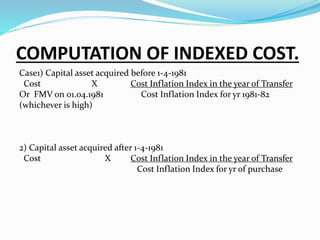
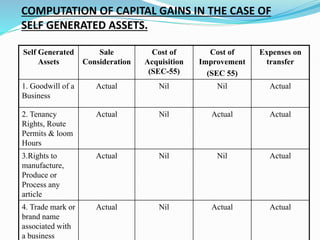
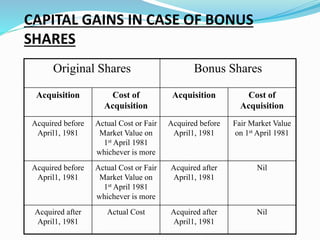
Capital gains tax is levied on profits arising from the transfer of a capital asset. For gains to be taxed under capital gains, there must be a capital asset that is transferred, resulting in profits. Any profits exempted under sections 54-54G are not taxed. Capital assets include all property except certain exceptions like stock-in-trade. Short term capital gains arise from assets held for 36 months or less, while long term gains are for assets held longer. Indexation of cost is used to arrive at capital gains for long term assets by factoring inflation. Profits are taxed differently based on whether the gain is short term or long term.










![• Transfer Includes
• Sale
• Exchange
• Relinquishment
• Extinguishment
• Compulsory Acquisition
• Conversion of Capital Asset Into Stock in Trade[sec(45(2)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![•Distribution of Assets to Its Shareholder on Its Liquidation
[Sec46(1)]
•Distribution of Capital Assets in HUF to Its Member at the Time
of Total or Partial Partition [Sec 47(1)]
•Transfer of a Capital Asset Under a Will or an Irrevocable Trust or
a Gift [Sec 47(iii)]
• Transfer of a Capital Asset by a Company to Its Wholly Owned
Indian Subsidiary Company [Sec 47(iv)]
• Transfer of a Capital Asset by a Wholly Owned Subsidiary
Company to Its Indian Holding Company [Sec 47(v)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-12-320.jpg)

![•Transfer in Case of Amalgamation Sec[47(vi)]
•Transfer in Case of Demerger Sec[47(vi B)]
•Transfer of Agricultural Land in India Effected Before March 1, 1970
[Sec 47(viii)]
• Transfer of a Capital Asset , Being Any Work of Art ,Scientific or Art
Collection, Book, Drawing, painting, photograph Etc [Sec47(ix)]
•Transfer by Way of Conversion of Bonds or Debenture of a Company
Into Shares or Debenture of That Company [ Sec 47(x)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-15-320.jpg)



















![CAPITAL GAINS ON CONVERSION OF DEBENTURES
INTO SHARES [SEC 49(2A)]:
1) Any transfer by way of conversion of debentures,
debenture – stock, or deposit certificates in any form, of a
Co. into shares or debentures of that co. is not regarded as a
transfer giving rise to Capital gains.
2) Cost of Acquisition will be the cost of debentures,
debentures – stock or deposit certificates which has been
appropriated towards to shares or debentures in case there
is sale of above transferred assets giving rise to capital
gains.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-36-320.jpg)
![CAPITAL GAINS ON CONVERSION OF DEBENTURES
INTO SHARES
[SEC 49(2A)]:
In case of conversion of debentures into Shares:
1) Cost of Debentures will be the Cost of acquisition
of shares.
2) To find out whether or not shares are LTCA or
STCA, the period of holding shall be determined
from date of allotment of shares.
3) The indexation will start from the date of
conversion of debentures into shares.
4) Not applicable for preference shares converted into
equity shares.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-37-320.jpg)
![CAPITAL GAINS ON TRANSFER OF SECURITY BY
DEPOSITORY
[ SEC 45(2A) ]
1) Any beneficial will be chargeable to Income tax, if in
PY he has had
any profits or gains by virtue of transferring of any
securities through
depository or participant of such beneficial interest.
2) It shall not be income of the depository.
3) Cost of Acquisitions and the period of holding of any
securities shall be determined on the basis of the First
– In – First – Out (FIFO)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-38-320.jpg)

![CAPITAL GAINS IN CASE OF COMPULSORY
ACQUISITION OF AN ASSET [SEC 45(5)]
Applicability :
Transfer of capital asset by way of compulsory acquisition
under any law.
Capital asset is transferred (not by way of compulsory
acquisition), & consideration is approved or determined by
central Gov. or RBI.
Chargeability :
Initial Compensation is full value of consideration.
Charged in the year in which first Initial Compensation is
received
Enhanced Compensation-Taxable in the year in which it is
received by the assessee.
*Nature of capital gains shall be the same as the nature of capital
gain with reference to original compensation.
*COA= nil](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-43-320.jpg)


![OTHER SPECIAL PROVISIONS
Capital Gains in case of Depreciable Assets ( Sec 50 )
Buy Back of Shares
Transfer of Land & Bldg ( Sec 50 [c])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/capital-gainsppt-180105192411/85/Capital-gains-ppt-46-320.jpg)











