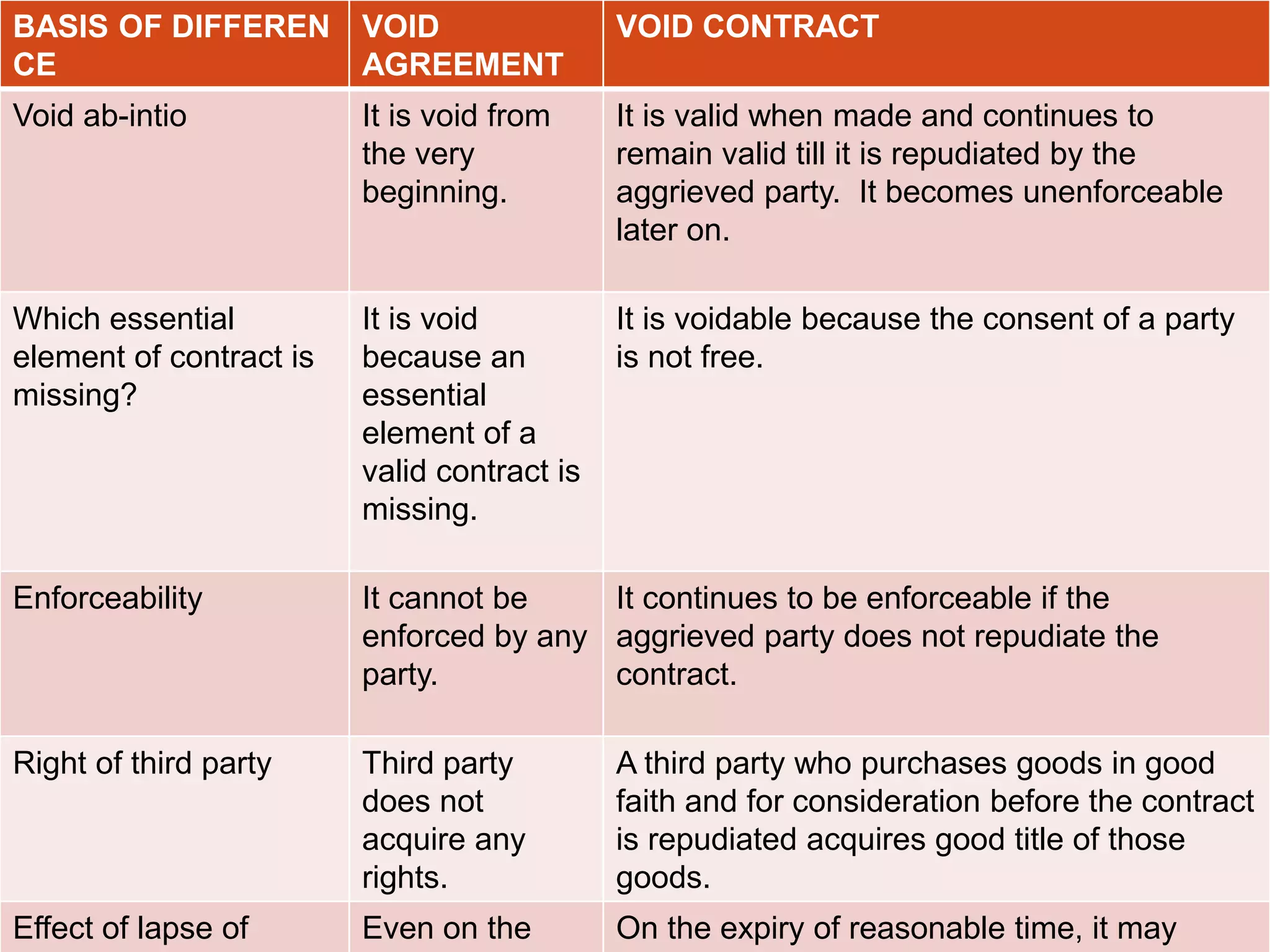
This document summarizes the key differences between void agreements and void contracts under Indian contract law. It explains that void agreements are not enforceable by law from the very beginning due to missing essential elements, like consideration or involving a minor. Void contracts, on the other hand, become unenforceable later due to supervening events, like outbreak of war preventing supply of goods. The document provides a table that outlines the main differences between void agreements and void contracts in terms of enforceability, rights of third parties, effects of lapse of time, treatment under the Indian Contract Act, and ability to claim damages.