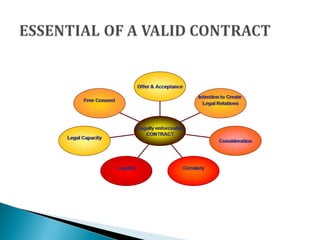
The document discusses the essential elements of a valid contract according to Indian contract law. It states that for a valid contract there must be 1) a lawful offer and acceptance, 2) lawful consideration, 3) capacity of parties to contract, 4) free consent, 5) lawful object, 6) possibility of performance, 7) certainty of meaning, and 8) not expressly declared void. It provides examples of agreements that do not constitute legally enforceable contracts, such as social engagements or domestic arrangements between husband and wife.