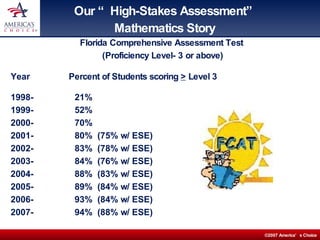
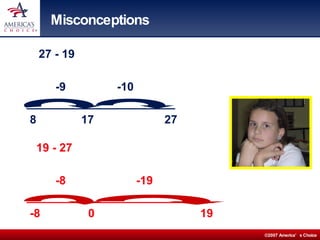
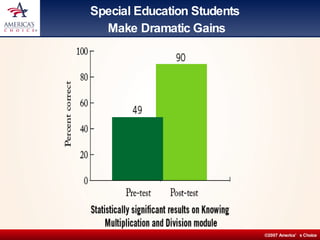
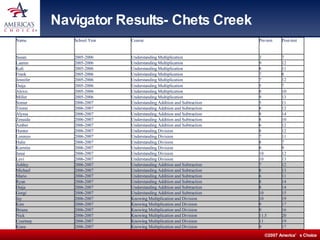
The document describes Chets Creek Elementary School, an A+ rated school in Florida. It discusses the school's approach to math intervention using a program called Math Navigator. Math Navigator uses modular instruction to target specific concepts and remedies for common student misconceptions. It also provides professional development for teachers. The school has seen dramatic test score gains, including among special education students using this approach.