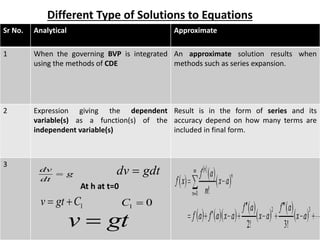
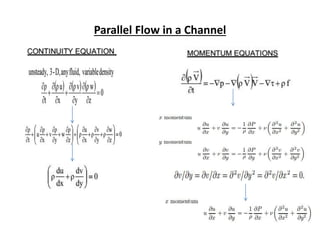
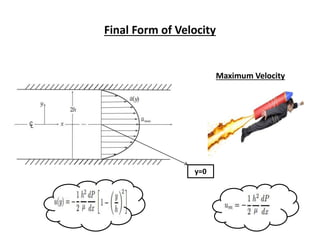
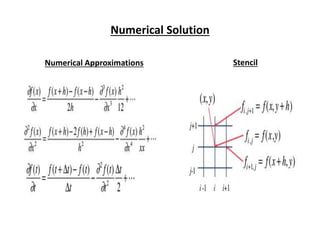
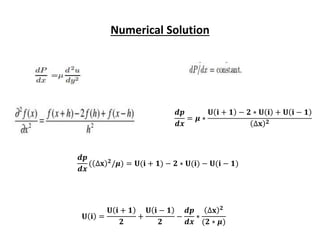
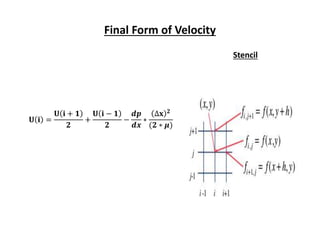
The document discusses analytical and numerical solutions for parallel flow in a channel. Analytical solutions are obtained by integrating the governing boundary value problem using methods like series expansion, resulting in an approximate solution. The solution is expressed as a function of the independent variables in a series form, with accuracy depending on the number of terms included. Numerical solutions involve approximating derivatives using finite differences on a grid, resulting in an equation relating the velocity at neighboring points that can be solved iteratively.