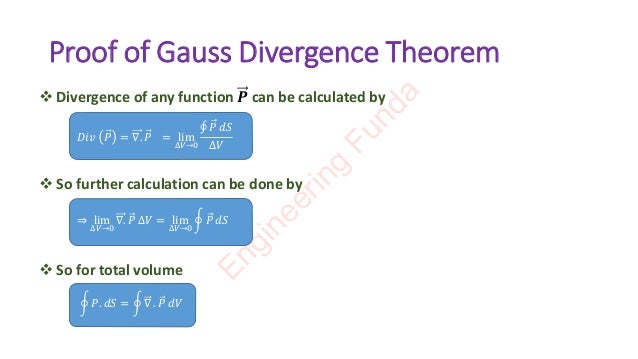
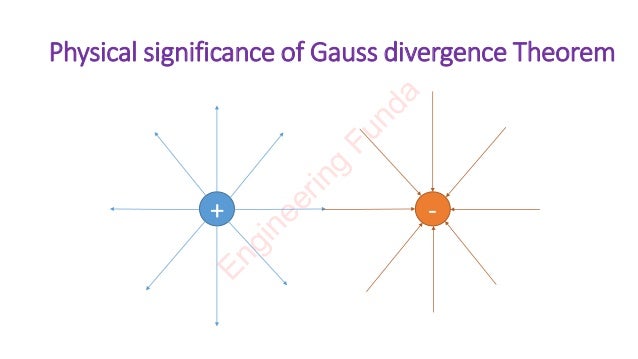
The Gauss divergence theorem explains the relationship between volume and surface integration. It states that the flux of a vector field out of a closed surface is equal to the total divergence of that field over the volume enclosed by the surface. The theorem can be used to understand electromagnetics, fluid mechanics, fields like gravity and electromagnetism, and aerodynamics. It also helps explain the location of sources and sinks of a vector field and the rate of change of a function with respect to position.