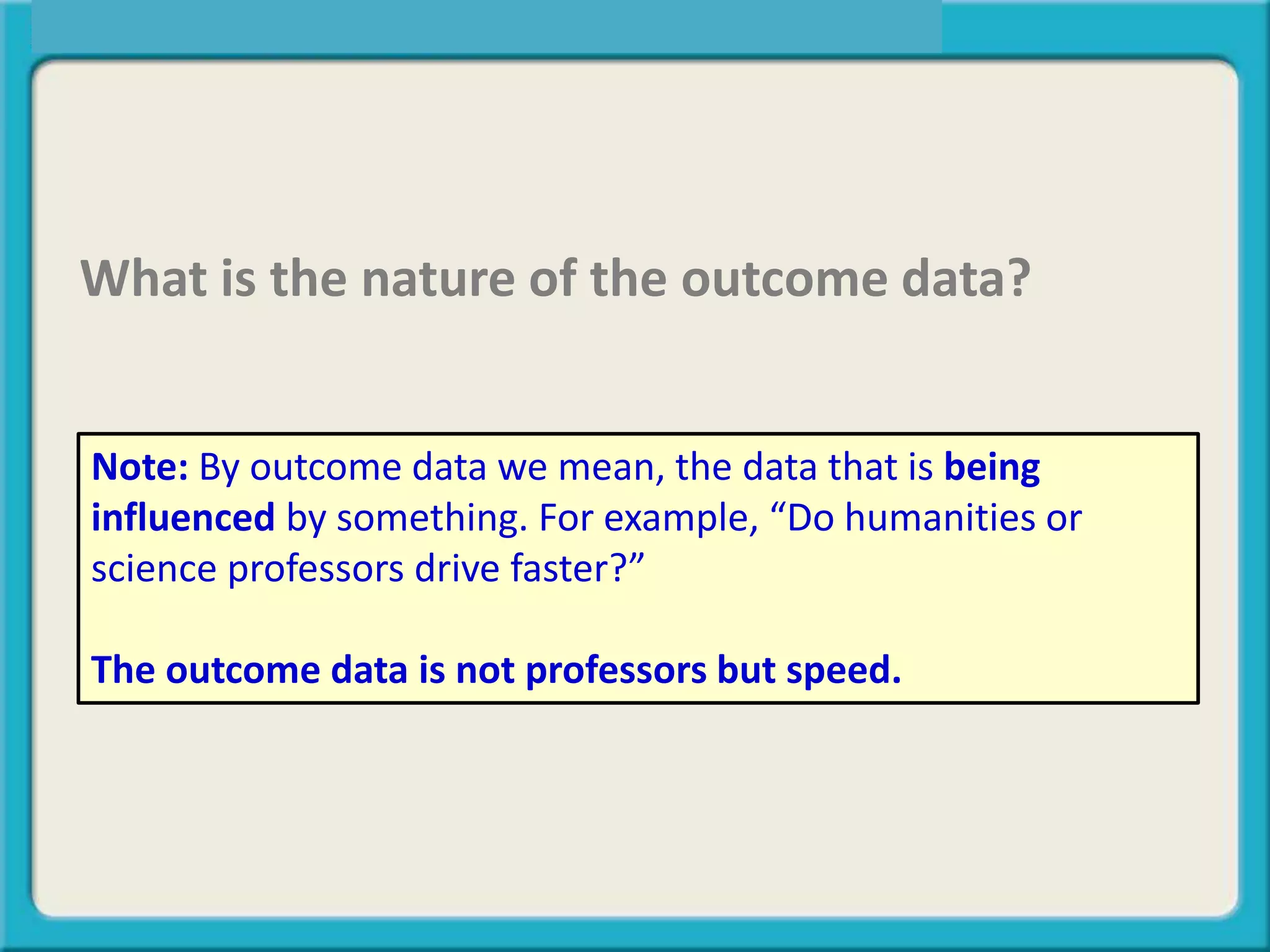
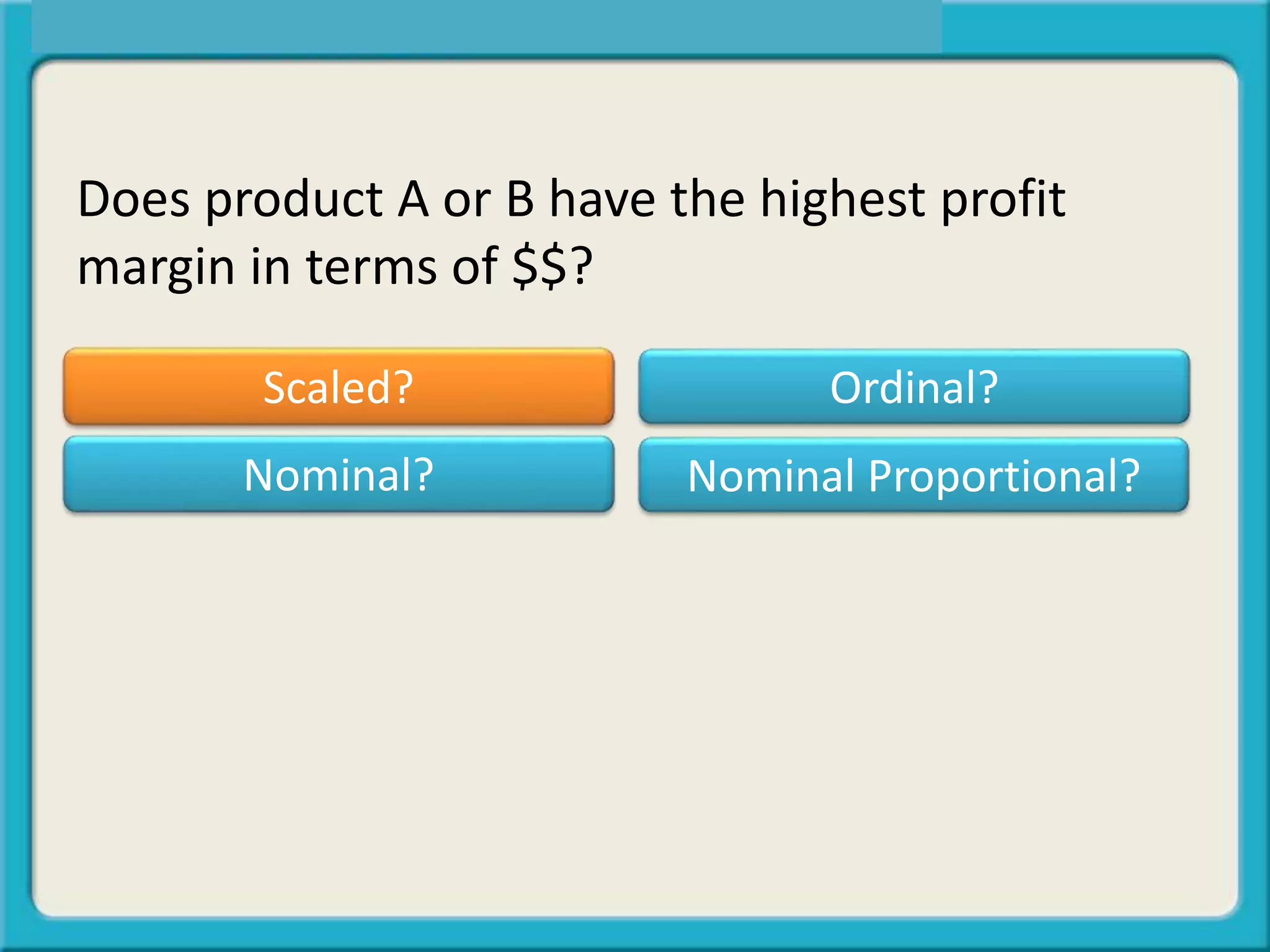
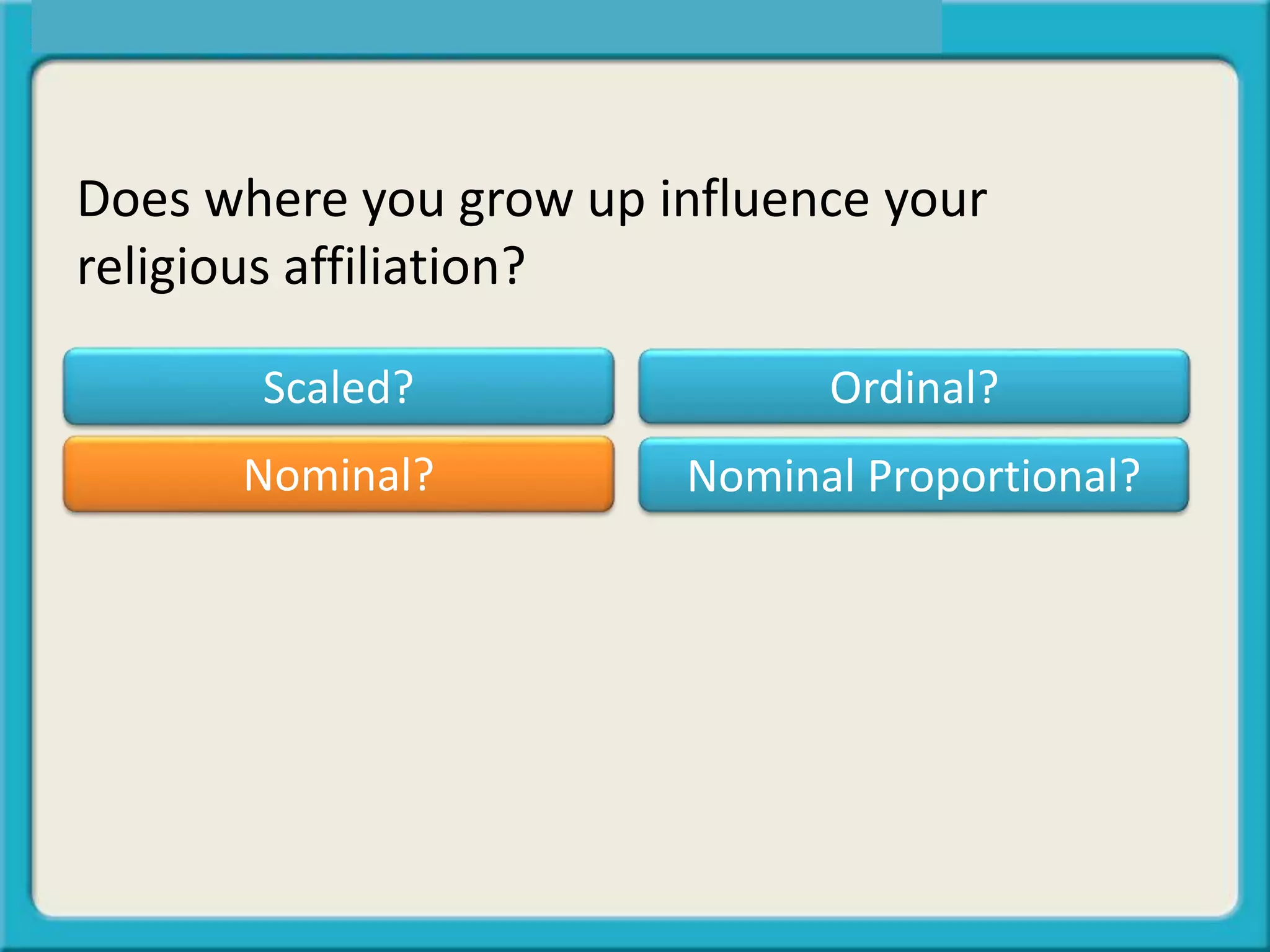
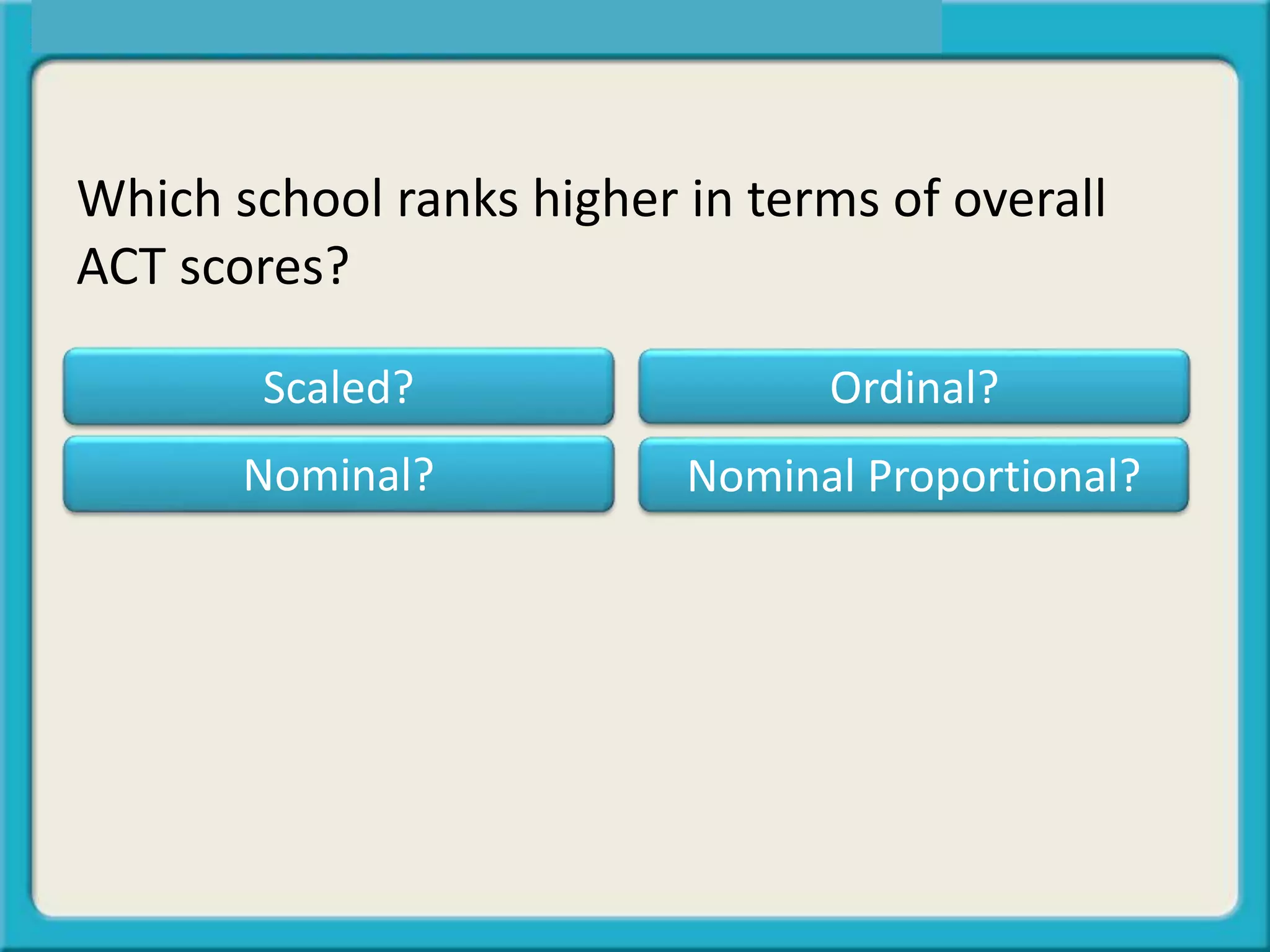
The document discusses different types of data:
- Scaled data provides exact amounts like miles per hour.
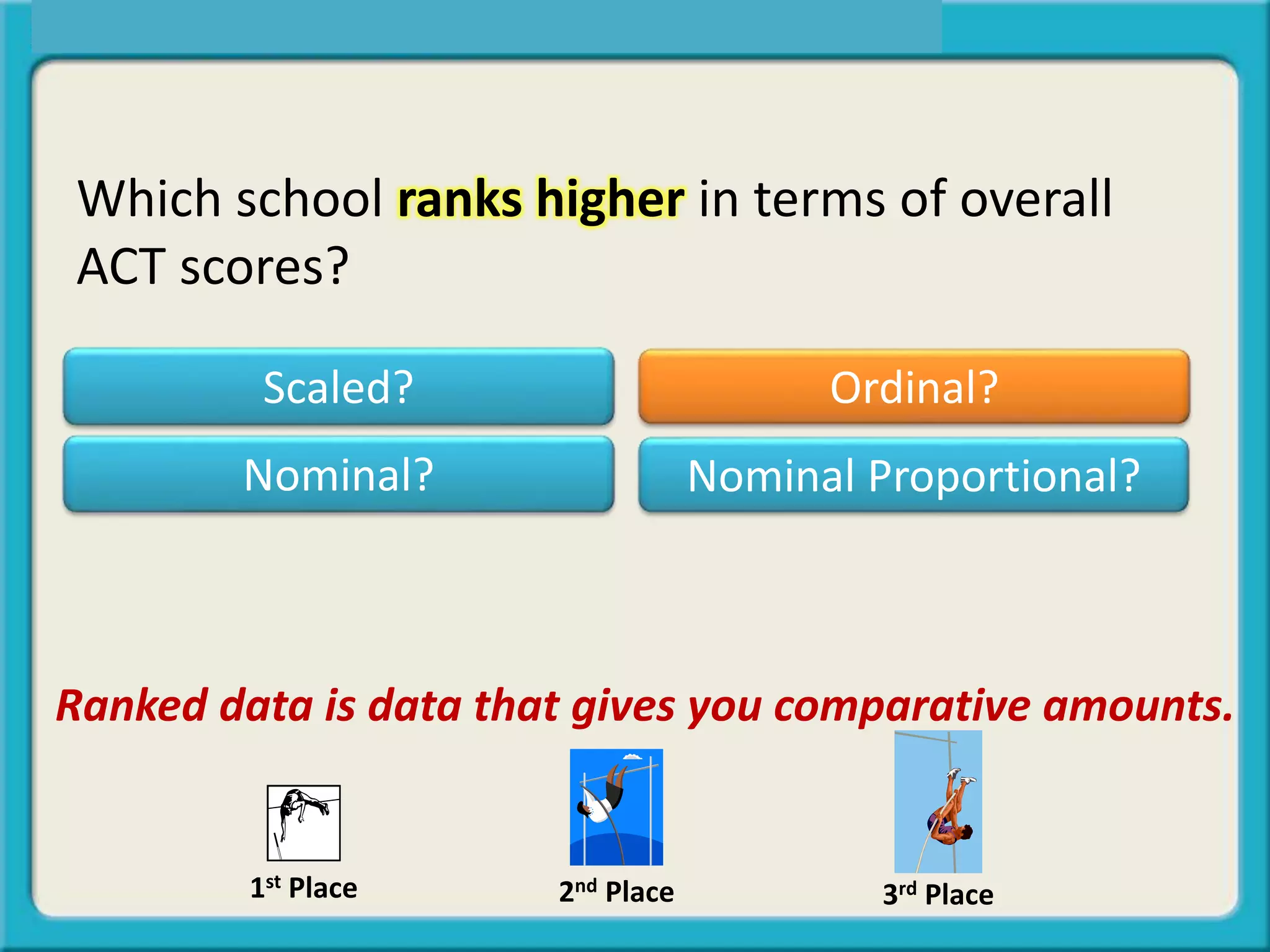
- Ordinal or ranked data provides comparative amounts like 1st, 2nd, 3rd place.
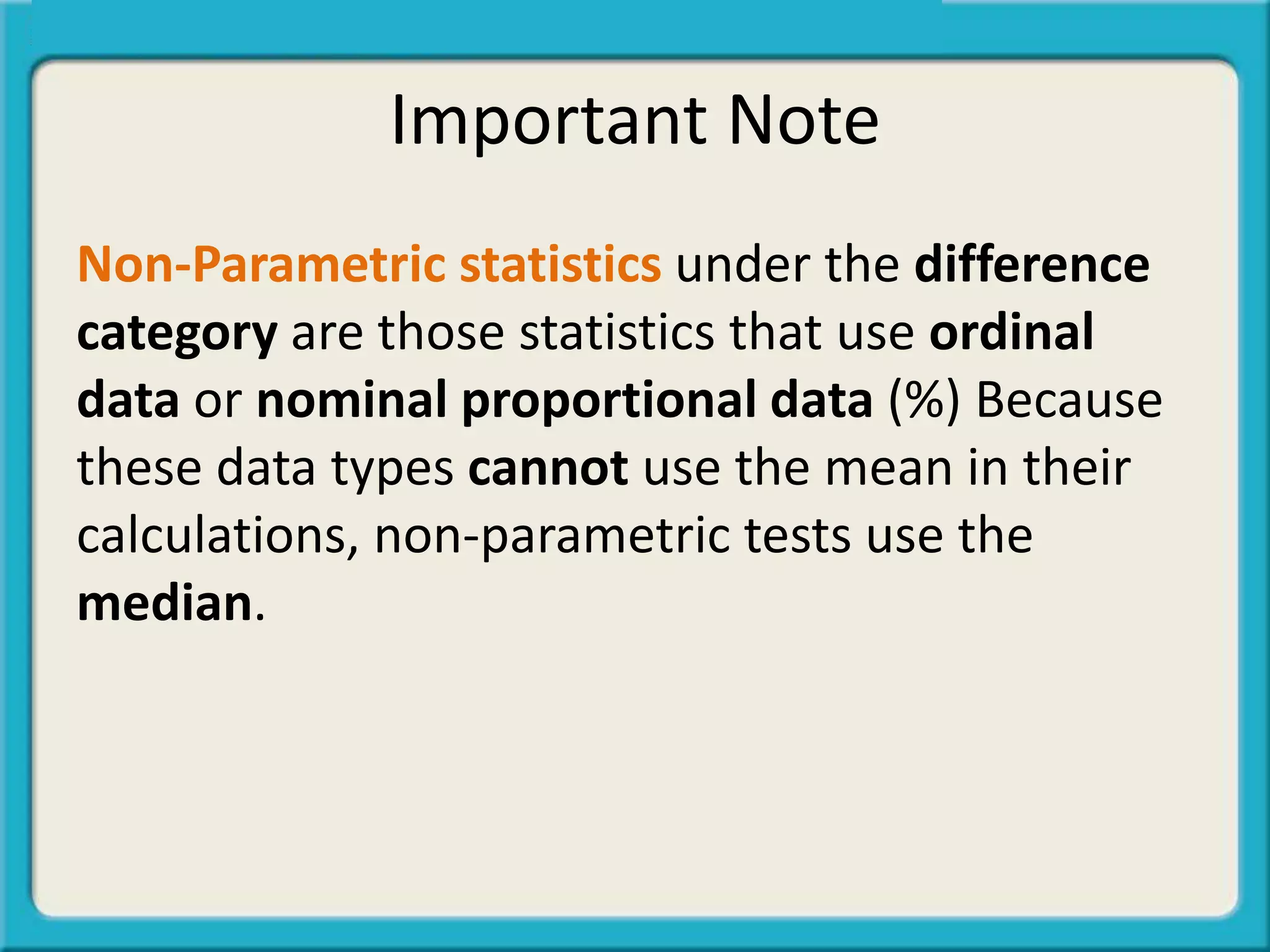
- Nominal data names or categorizes values like Republican or Democrat.
- Nominal proportional data are percentages like 45% Republican, 55% Democrat.
The key is determining what type of data is being influenced or is the "outcome" in questions being analyzed.