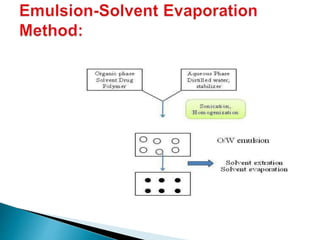
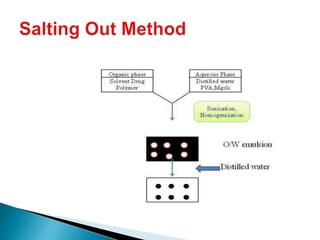
This document discusses nanoparticles and their uses in drug delivery. It defines nanoparticles as particulate dispersions between 10-1000nm in size. Nanoparticles are classified based on their method of preparation into nanocapsules and nanospheres. Some common types of nanoparticles discussed are solid lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, ceramic nanoparticles, and hydrogel nanoparticles. The document outlines advantages like increased shelf stability and ability to control drug release. Evaluation parameters for nanoparticles include particle size, molecular weight and in vitro drug release. Finally, applications like targeted drug delivery to the brain and topical formulations are mentioned.