Embed presentation










Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) can be used to measure knowledge management performance and objectives. When identifying KPIs, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. KPIs can measure the overall KM program, projects, activities, and systems at the organizational, team and personal levels. Examples of KPIs include the number of knowledge assets created, the percentage of staff contributing or accessing documents, and the number of searches. Relating KPIs to what matters most to the audience, such as financial results or performance, helps make the metrics more meaningful.












Importance of measuring KM performance for evidence, progress monitoring, and learning.
Factors affecting the choice of measurement tools like surveys and activity reports.
KPIs are metrics to quantify objectives reflecting strategic performance, both financial and non-financial.
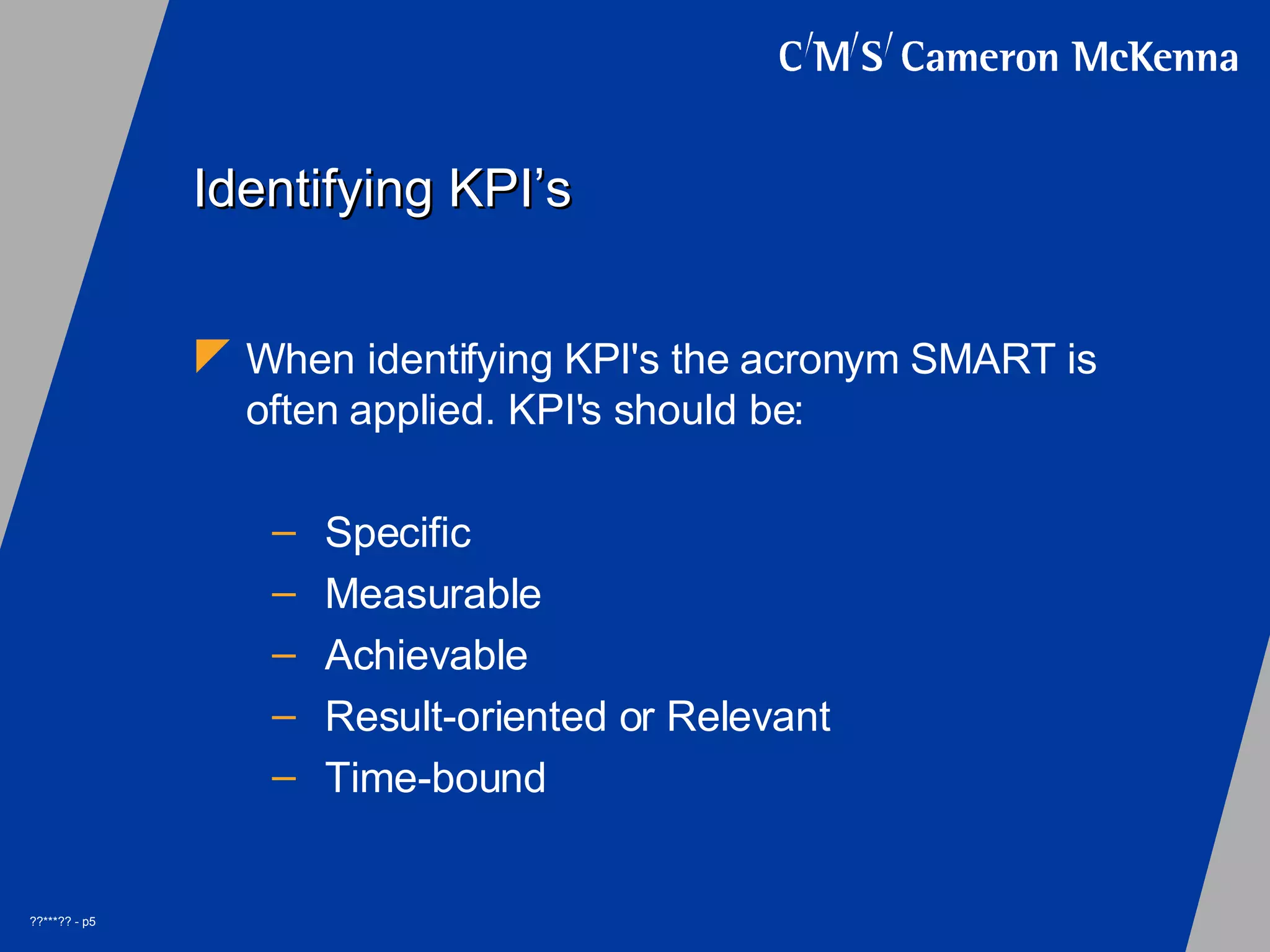
KPI identification using SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
KPIs used to evaluate KM programs, projects, activities, and systems within organizations.
KPI levels include organizational, team linkage to goals, and personal competencies.
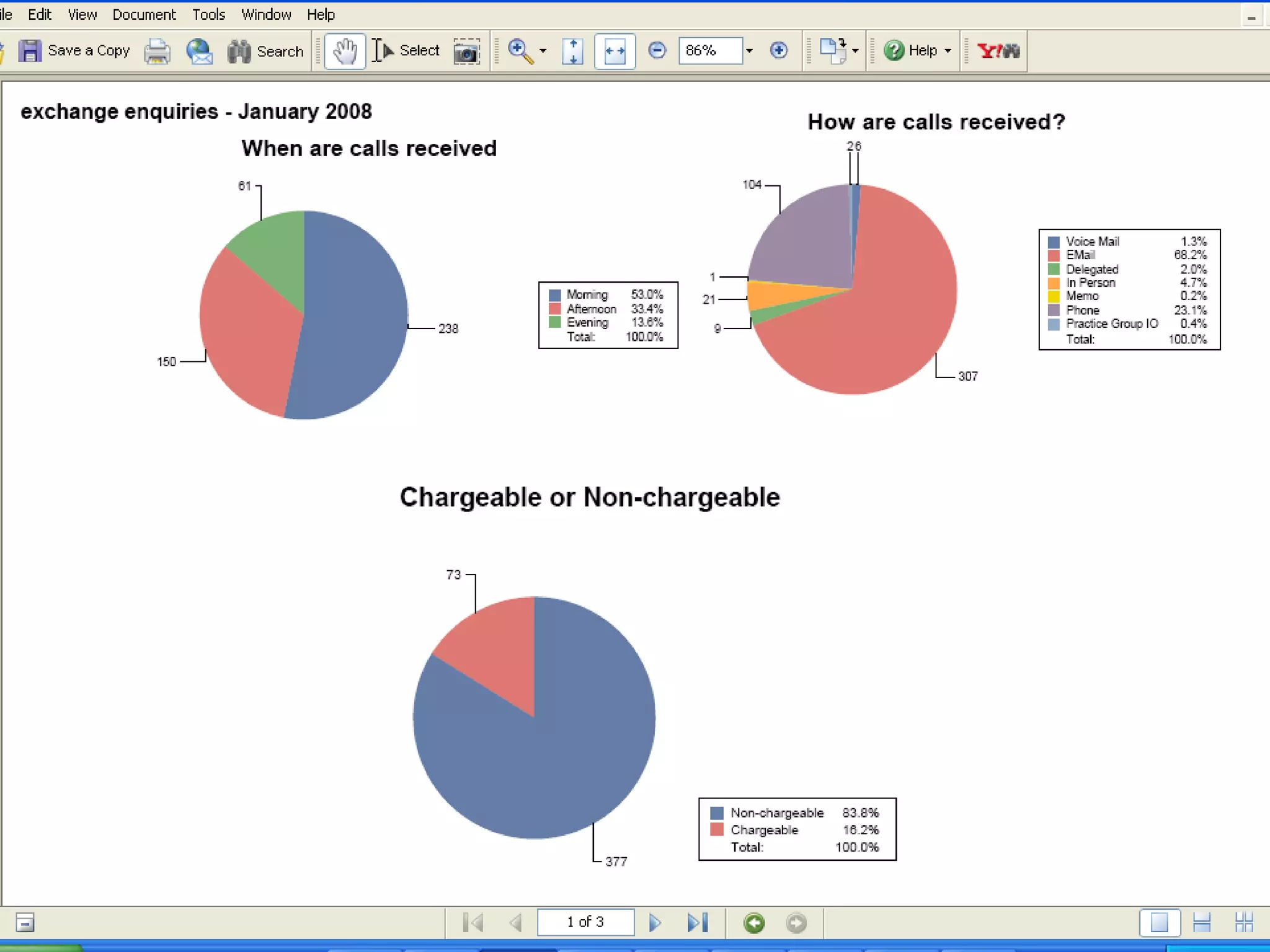
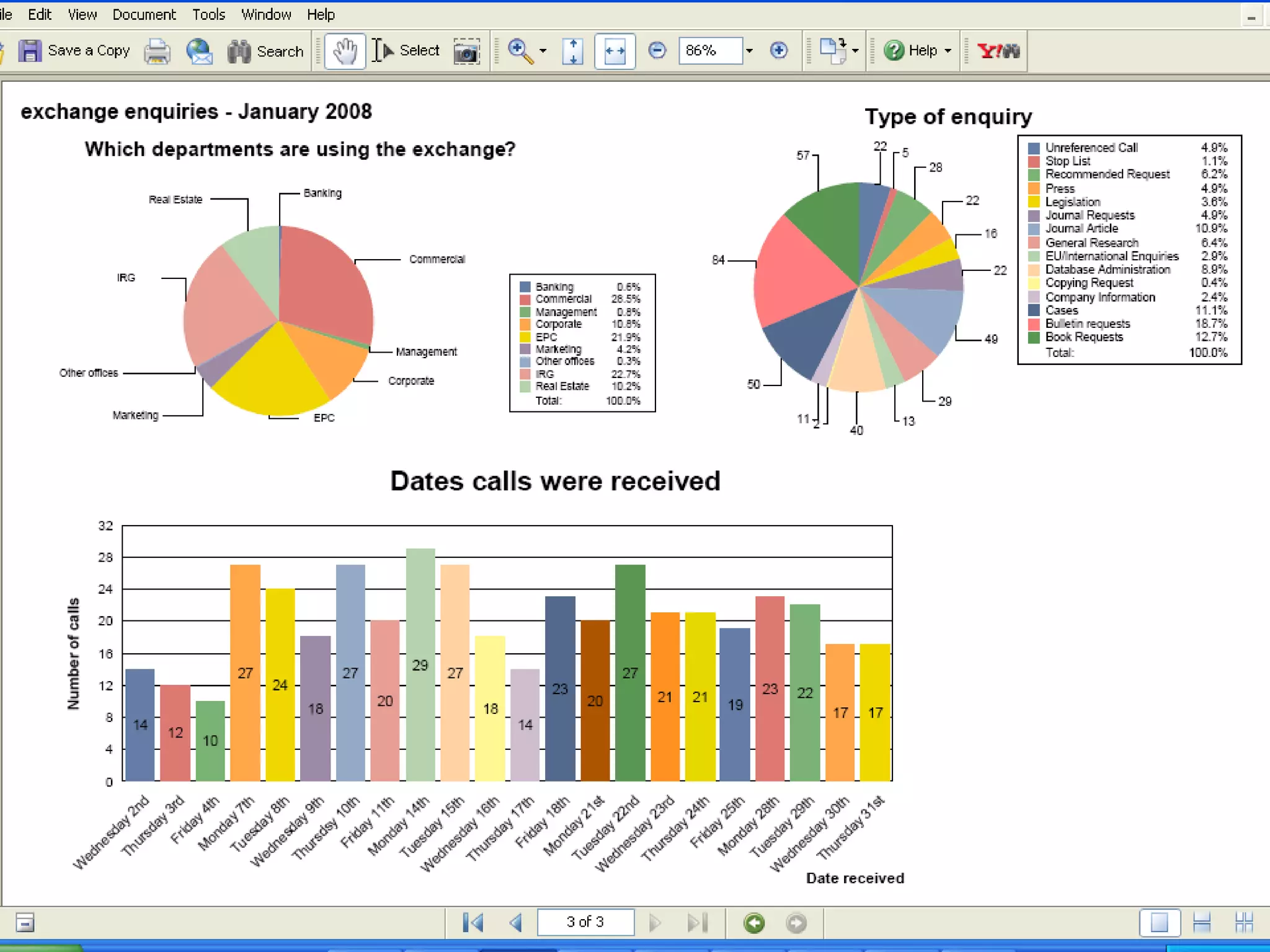
Examples of KM activity KPIs like knowledge assets created and staff contributions and accesses.
Importance of tying metrics to financial results, appraisals, and overall performance.
Inviting audience experiences related to previous discussions on KM performance.