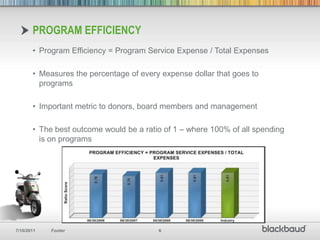
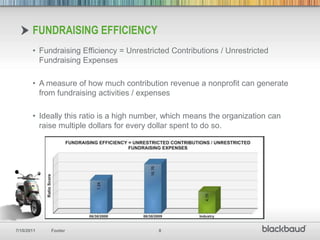
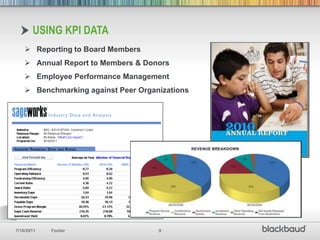
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential quantifiable measures for nonprofits, used for transparency, accountability, and demonstrating success in meeting goals. Important financial ratios discussed include program efficiency, operating reliance, and fundraising efficiency, which help assess an organization's performance compared to peers. Using KPI data can improve reporting to stakeholders and aid in financial decision-making, while exploring these ratios fosters meaningful discussions about organizational health.