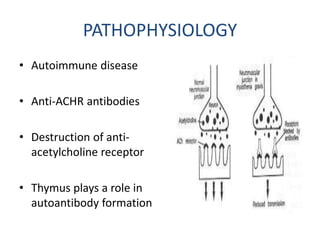
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigability, primarily affecting women aged 20-30 and men aged 50-60. Key diagnostic methods include antibody testing, electrodiagnostic tests, and the ice-pack test, while treatment options encompass anticholinesterase medications, thymectomy, immunosuppression, and plasmapheresis. The condition often presents with cycles of exacerbation and remission and may involve ocular and proximal muscle weakness.