Embed presentation
Downloaded 68 times






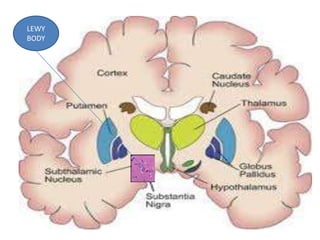
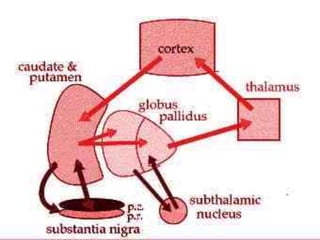
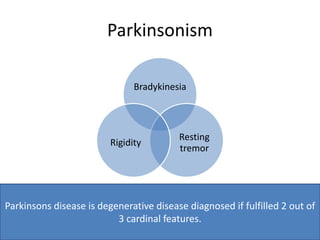






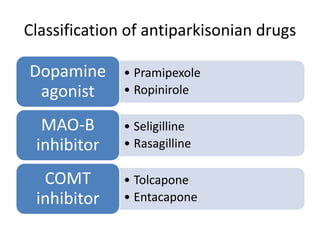
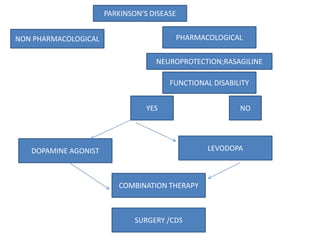
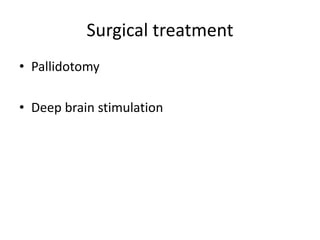
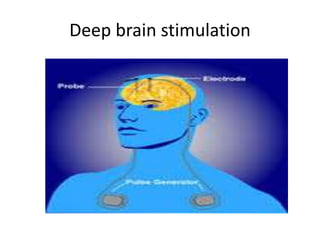


Parkinson's disease is the second most common degenerative disease of the central nervous system. It typically occurs in older adults around age 60 and is more common in males. The disease is characterized by degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain and presence of Lewy bodies. The main symptoms include bradykinesia, resting tremor, and rigidity. Levodopa is the most effective treatment for motor symptoms, but its long term use can cause dyskinesia and other side effects. Deep brain stimulation is an effective surgical treatment for some patients. Overall, Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder involving the extrapyramidal system.