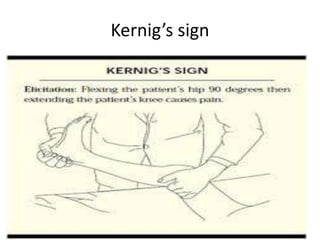
Meningitis is a medical emergency caused by various bacterial and viral pathogens. Early recognition through symptoms like fever, neck stiffness, and altered mental status is important as mortality can be 100% if untreated. A lumbar puncture allows examination of cerebrospinal fluid which typically shows elevated white blood cells and normal glucose/protein levels in bacterial meningitis. Diagnosis involves blood and CSF cultures along with CT scan. Treatment involves empiric antibiotics targeting the most common organisms based on patient age, with adjunctive steroids to reduce inflammation. Proper antibiotic selection, timing and duration of treatment are key to successful management of this potentially fatal condition.