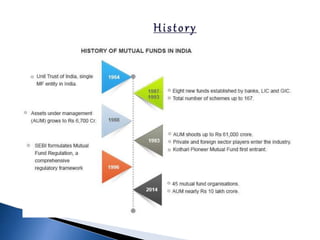
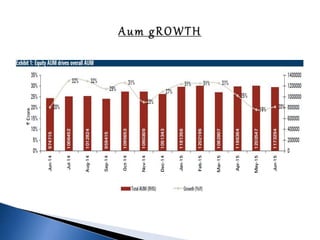
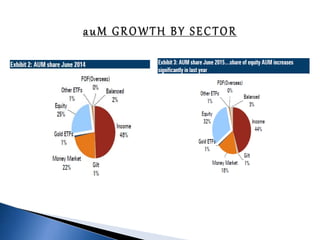
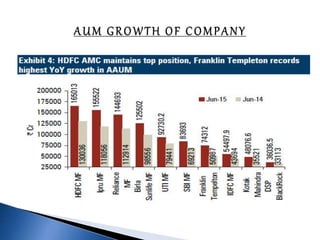
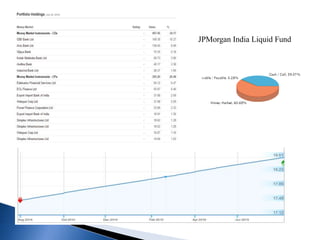
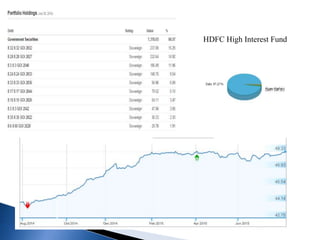
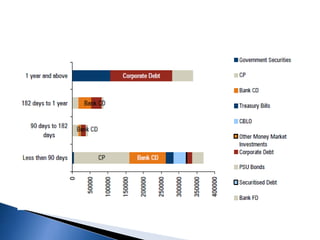
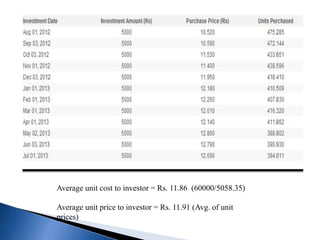
The document provides an overview of mutual funds in India, including their history, structure, guidelines, terms, types of funds, ratios, taxation, and future outlook. Some key points:
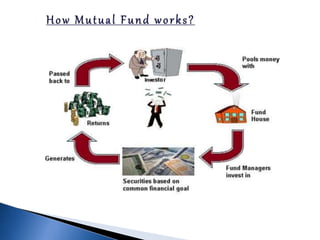
- A mutual fund pools money from investors and invests it in stocks, bonds, and other securities to generate returns. Returns and capital appreciation are shared proportionally by unit holders.
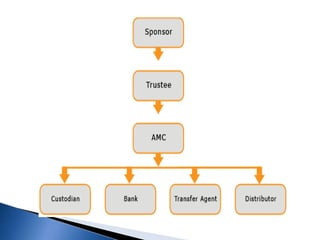
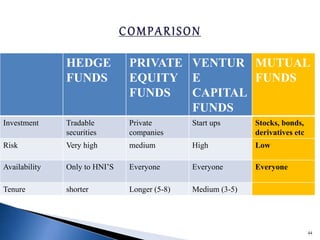
- SEBI regulates the mutual fund industry and has established a three-tier structure of sponsors, trustees, and asset management companies.
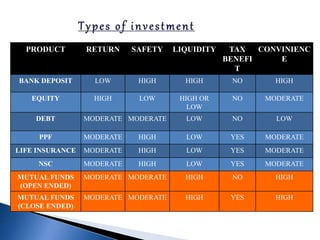
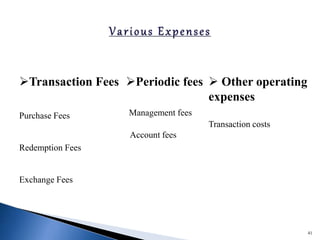
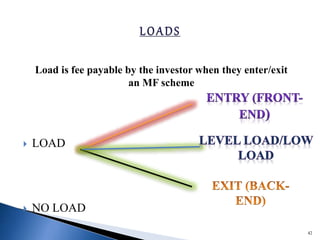
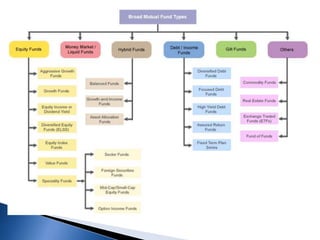
- There are various types of mutual funds that invest in different asset classes like equity, debt, hybrid, and money market instruments. Expense ratios, loads, and taxation vary across fund types.





































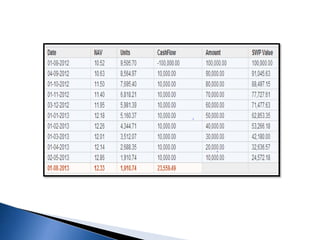







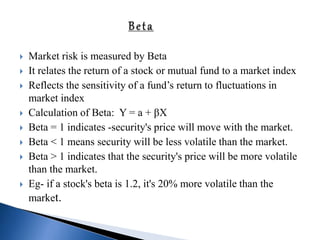
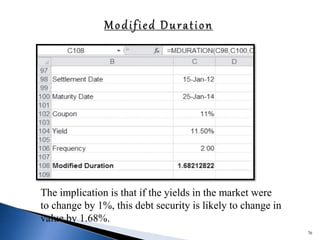
![ It is rate of return for the period of holding
Also known as total return or point to point returns.
HPR = {[INCOME+(END PRICE – BEGINNING
PRICE)]*BEGINNING PRICE}*100
HPR ={ [2+(12-10)]/10}*100 = 40%
DIVIDEND 2 HPR 40%
BEG.PRICE 10
ENDPRICE 12
HOLDINGPERIOD 1YEAR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group1mutual-fund-160218173559/85/mutual-fund-66-320.jpg)
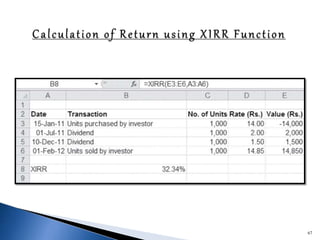
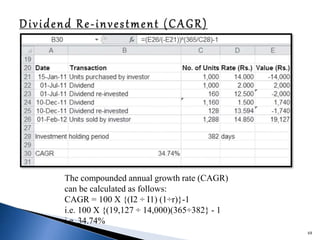



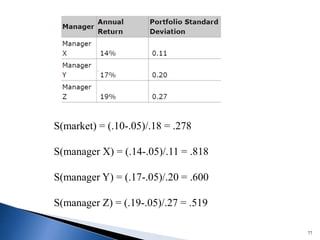

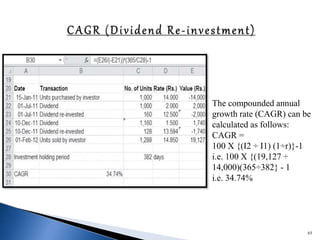
![Alpha is the risk-adjusted return on an investment
Alpha demonstrates whether your investment
outperformed or underperformed a risk-related
benchmark
The formula for alpha is expressed as follows:
a = Rp – [Rf + (Rm – Rf) ß]
Where:
Rp = Realized return of portfolio
Rm = Market return
Rf = risk-free rate
80](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group1mutual-fund-160218173559/85/mutual-fund-80-320.jpg)




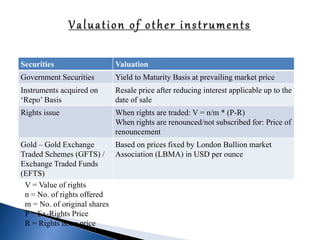

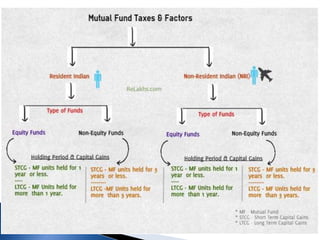

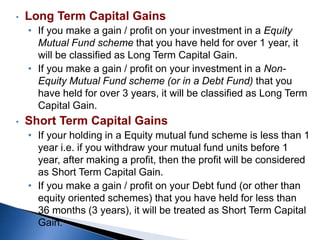
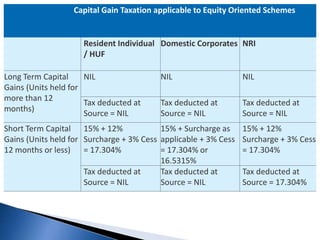
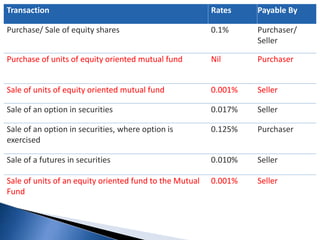
![Capital Gain Taxation applicable to Schemes other than equity oriented
schemes
Resident Individual /
HUF
Domestic
Corporates
NRI
Long Term Capital Gains
[Units held for more than
36 months] (Listed Units)
20% with indexation + 12%
Surcharge + 3% Cess
= 23.072%
20% with indexation +
Surcharge as applicable +
3% Cess
= 22.042% or 23.072%
20% with indexation +
12% Surcharge + 3%
Cess
= 23.072%
Tax deducted at Source =
NIL
Tax deducted at Source =
NIL
Tax deducted at Source
= 23.072%
Long Term Capital Gains
[Units held for more than
36 months] (Unlisted
Units)
20% with indexation + 12%
Surcharge + 3% Cess
= 23.072%
20% with indexation +
Surcharge as applicable +
3% Cess
= 22.042% or 23.072%
10% without indexation
+ 12% Surcharge + 3%
Cess
= 11.536%
Tax deducted at Source =
NIL
Tax deducted at Source =
NIL
Tax deducted at Source
= 11.536%
Short Term Capital Gains
(Units held for less than 36
months)
30%^ + 12% Surcharge +
3% Cess = 34.608%
30% + Surcharge as
applicable + 3% Cess =
34.608% or 33.063%
30%^ + 12% Surcharge
+ 3% Cess = 34.608%
Tax deducted at Source =
NIL
Tax deducted at Source =
NIL
Tax deducted at Source
= 34.608% (Listed and
Unlisted) ^](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group1mutual-fund-160218173559/85/mutual-fund-91-320.jpg)