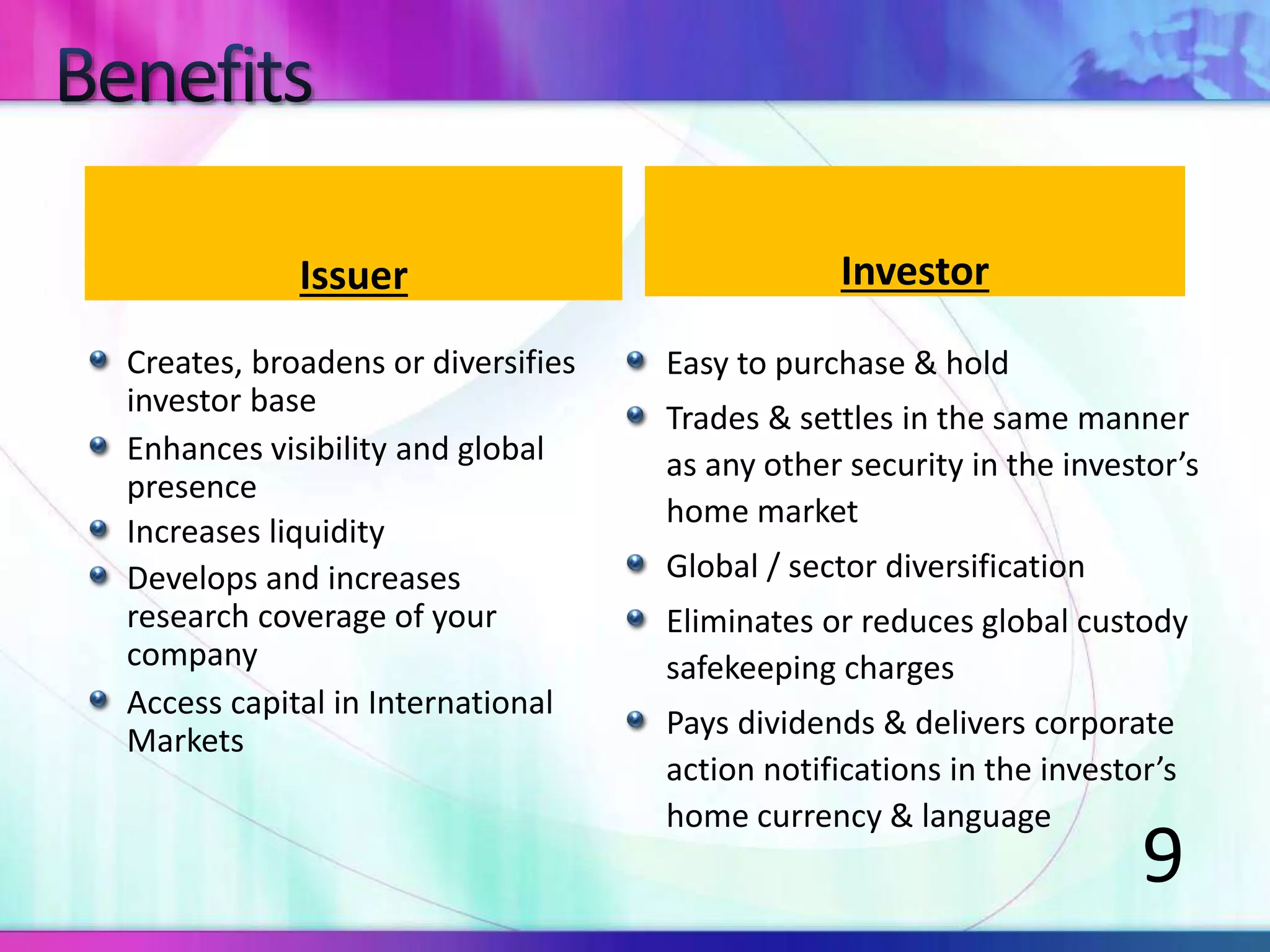
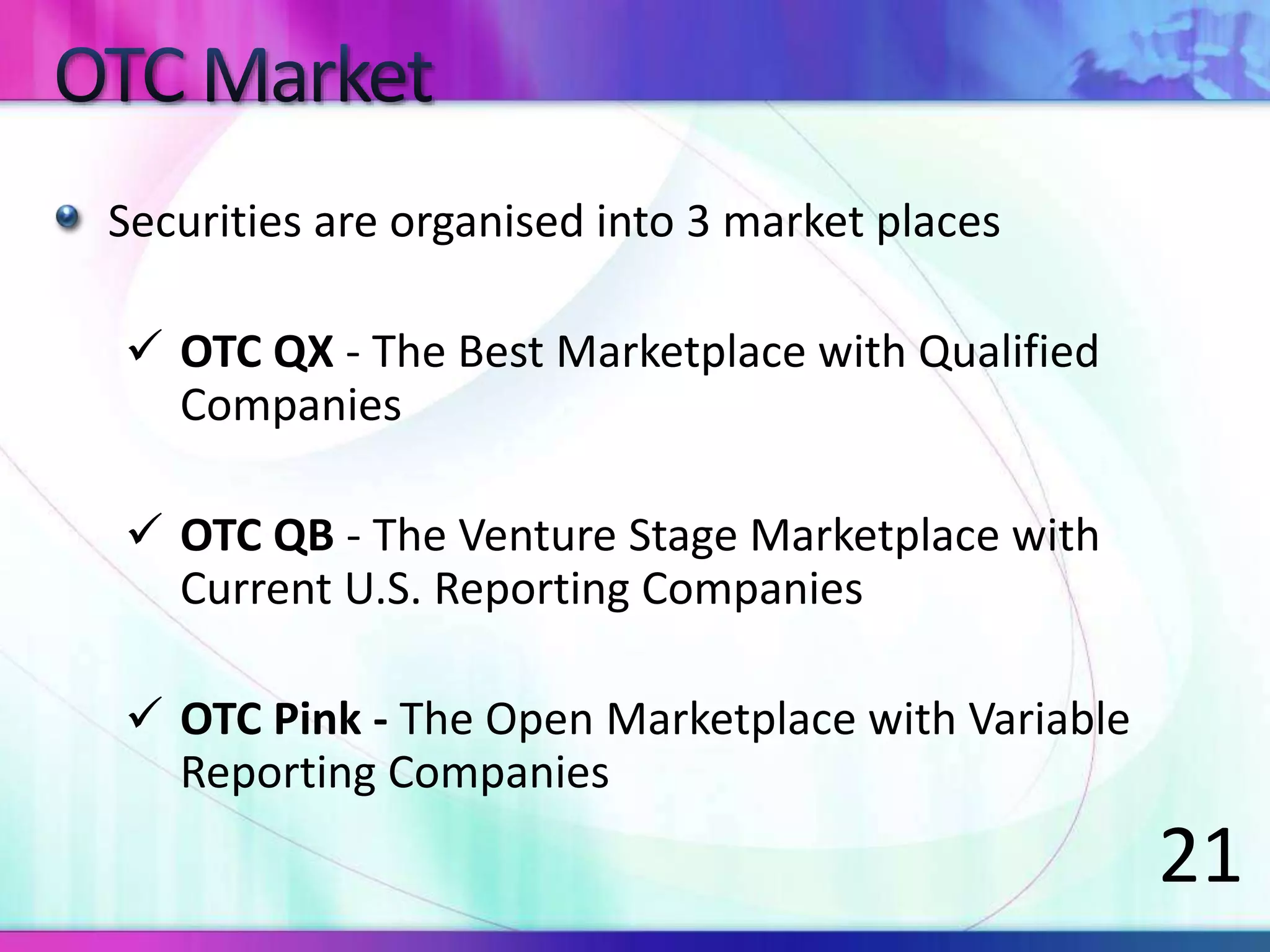
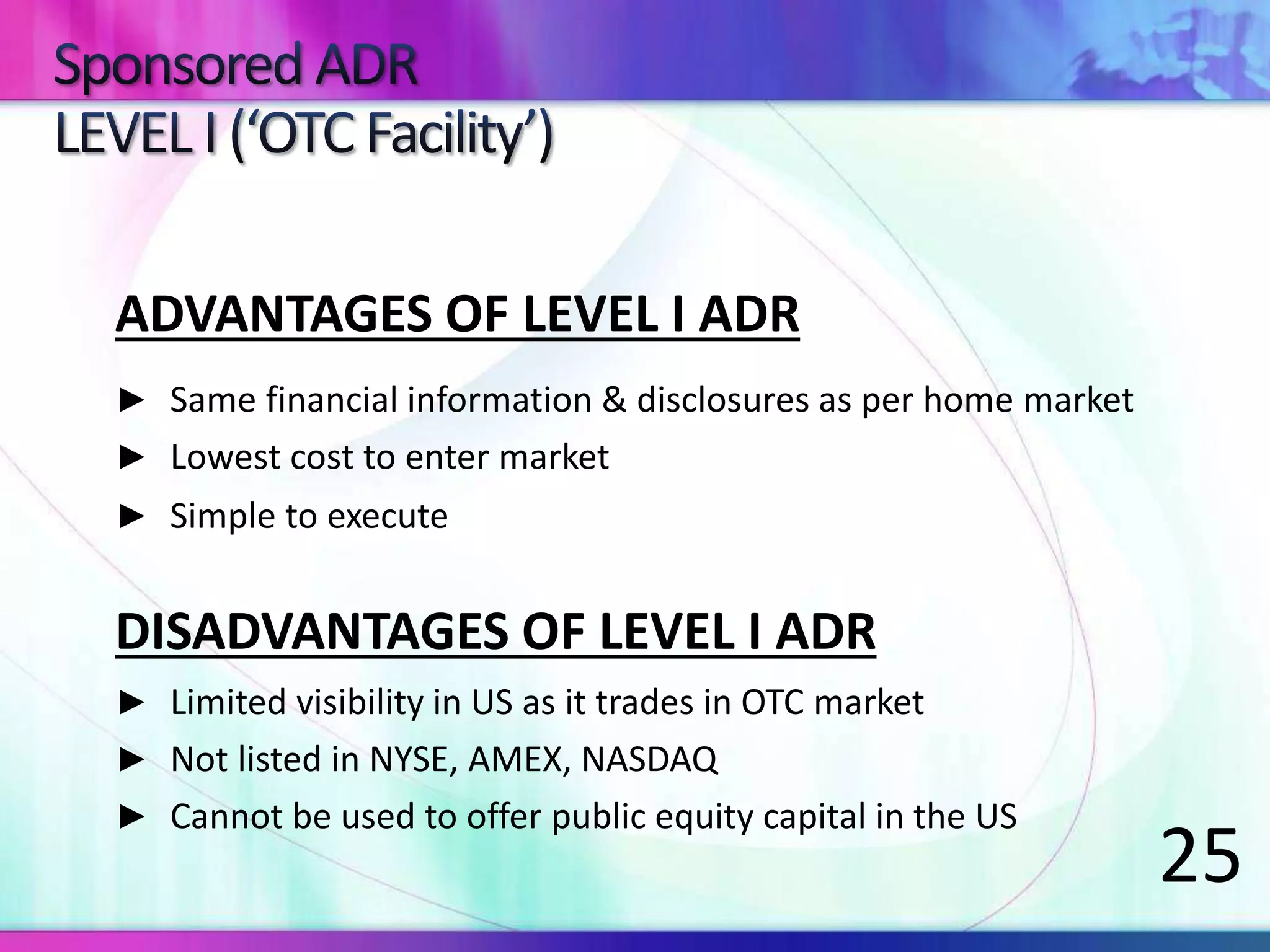
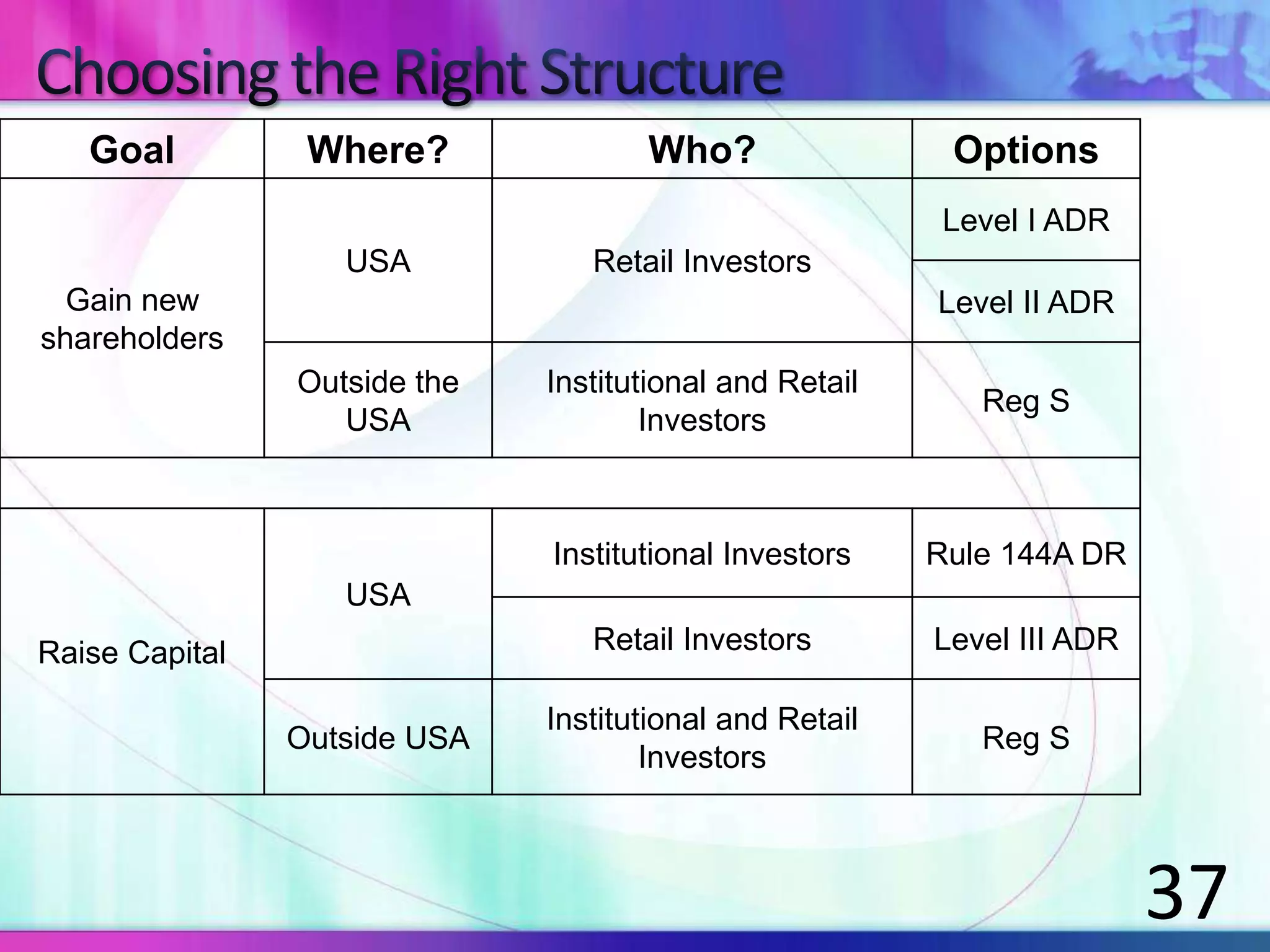
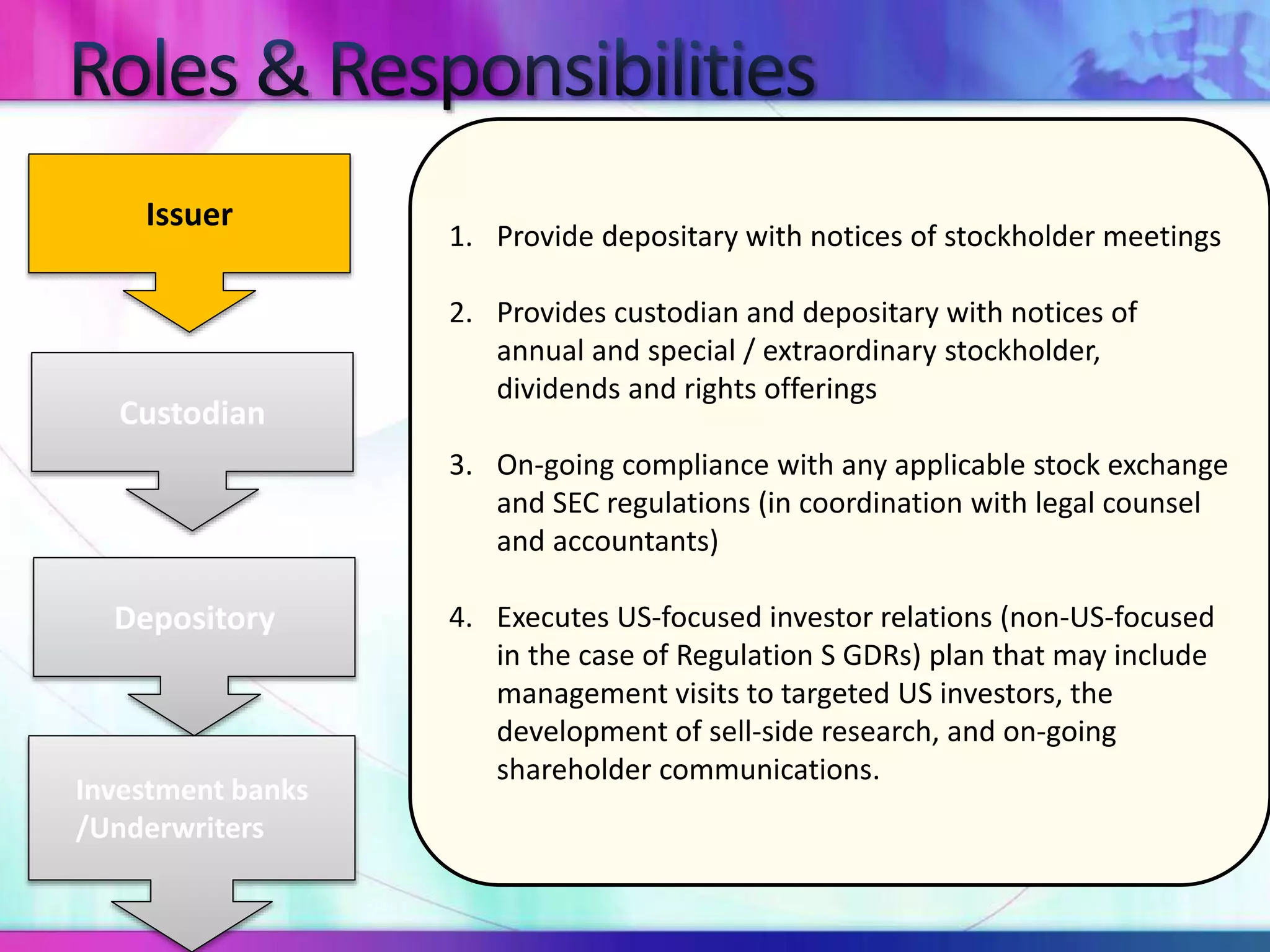
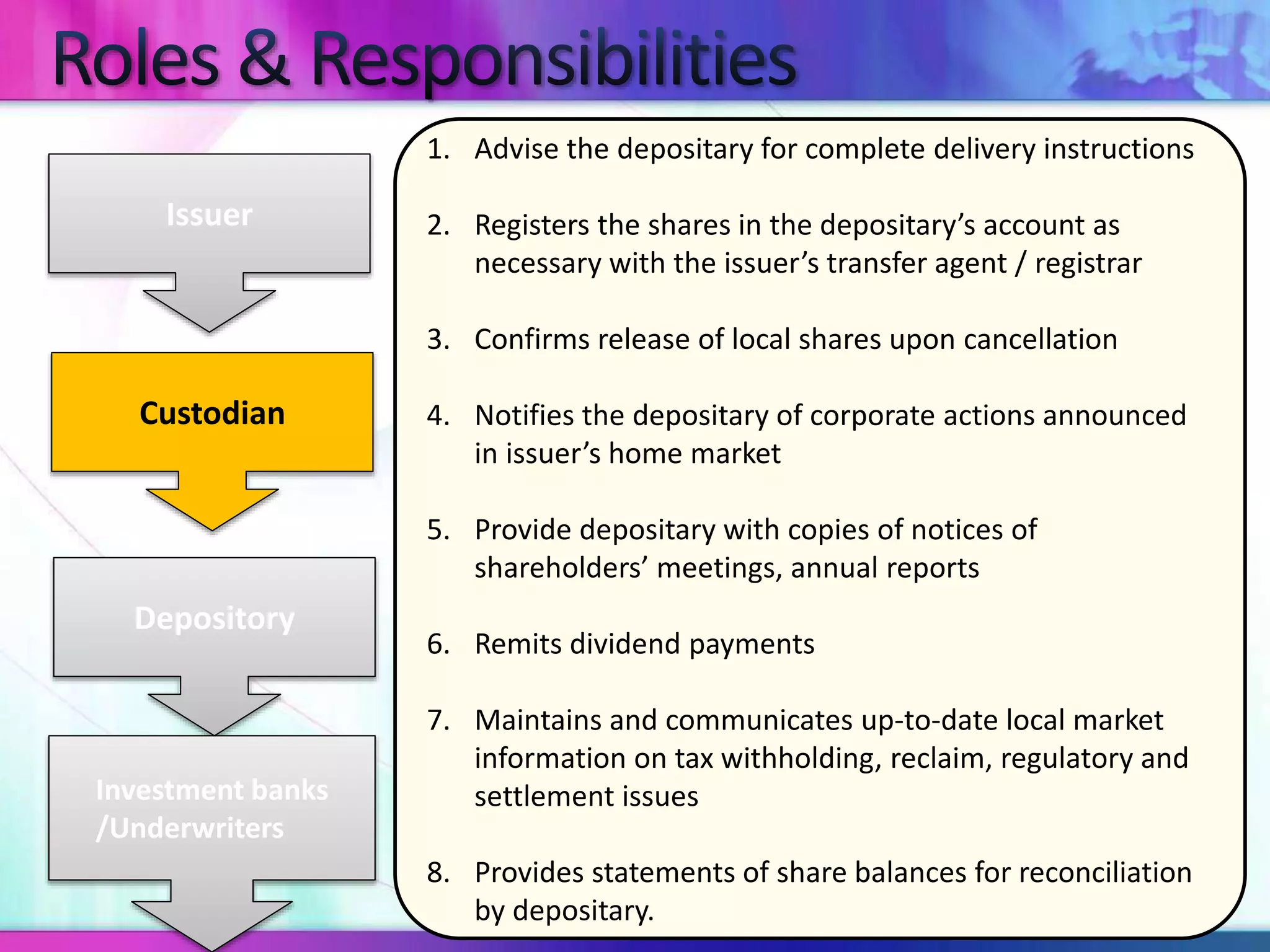
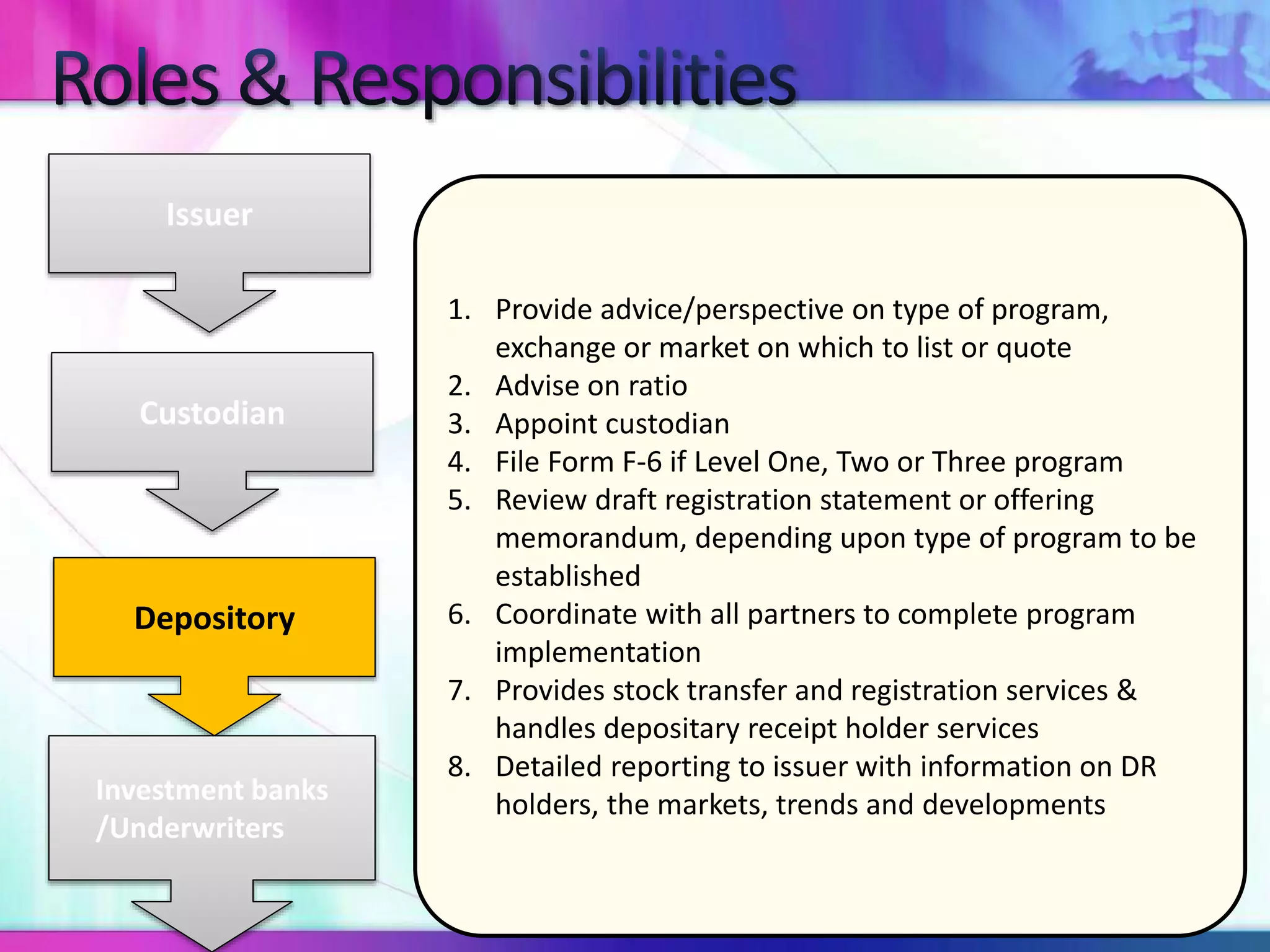
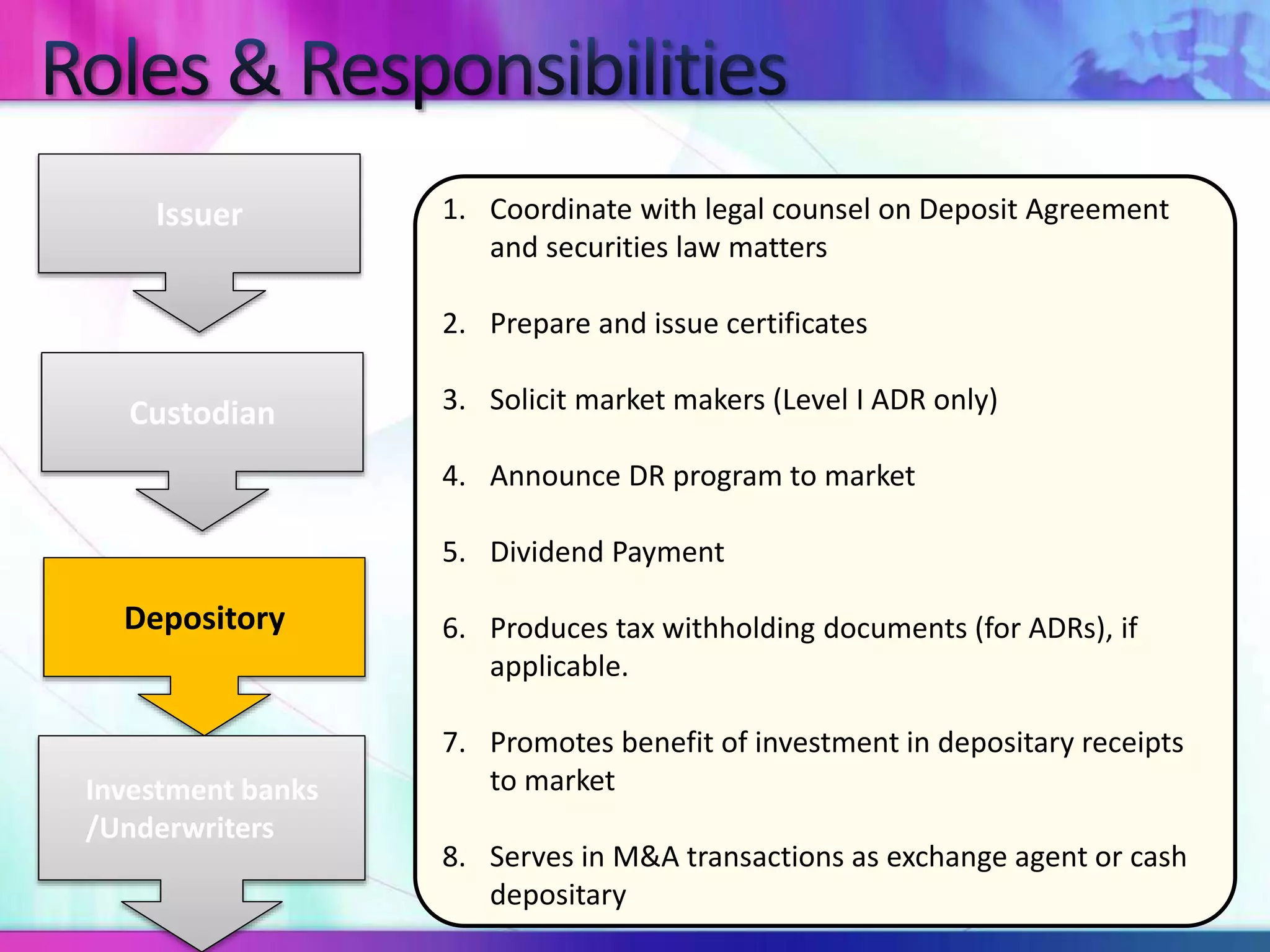
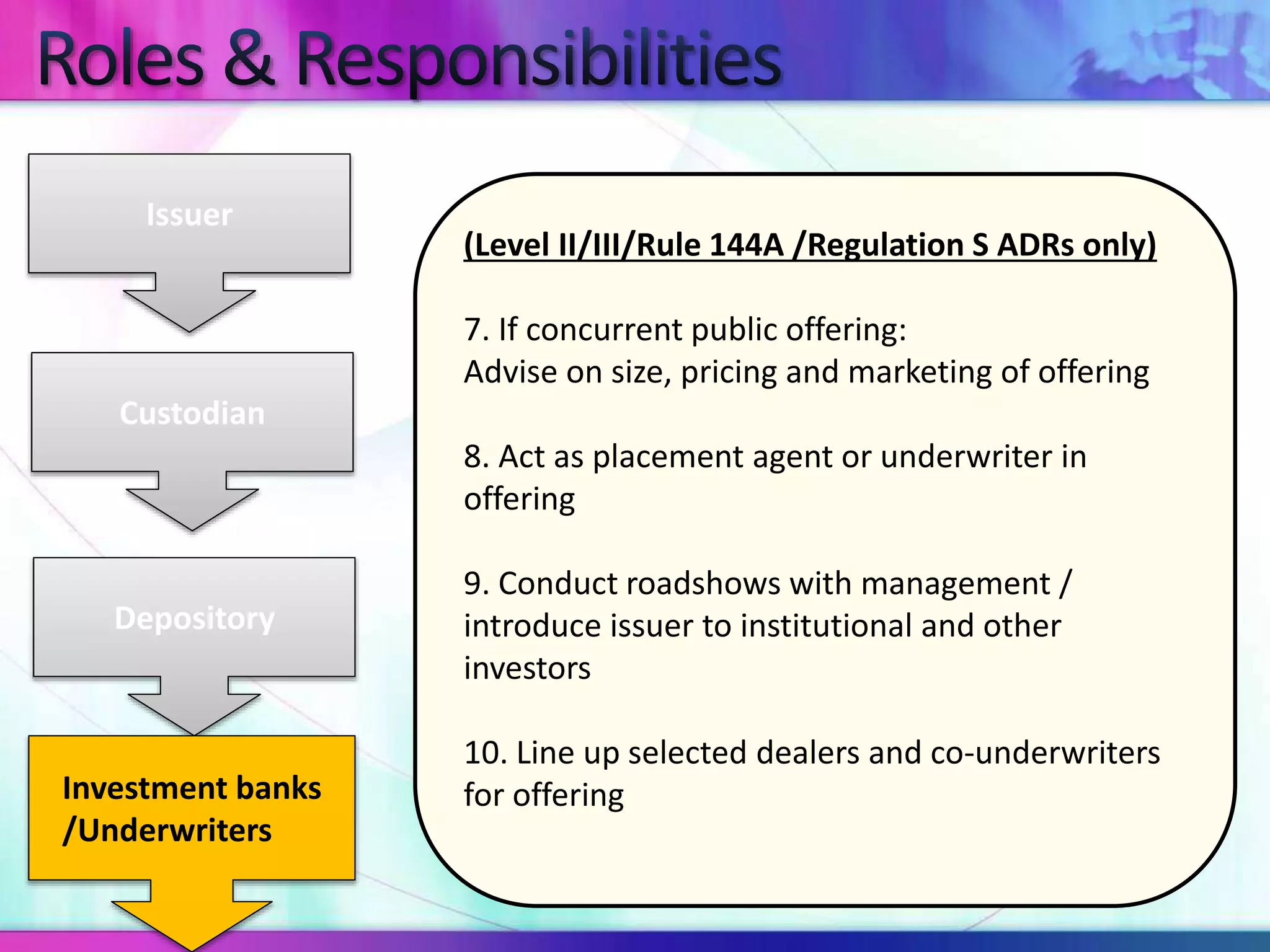
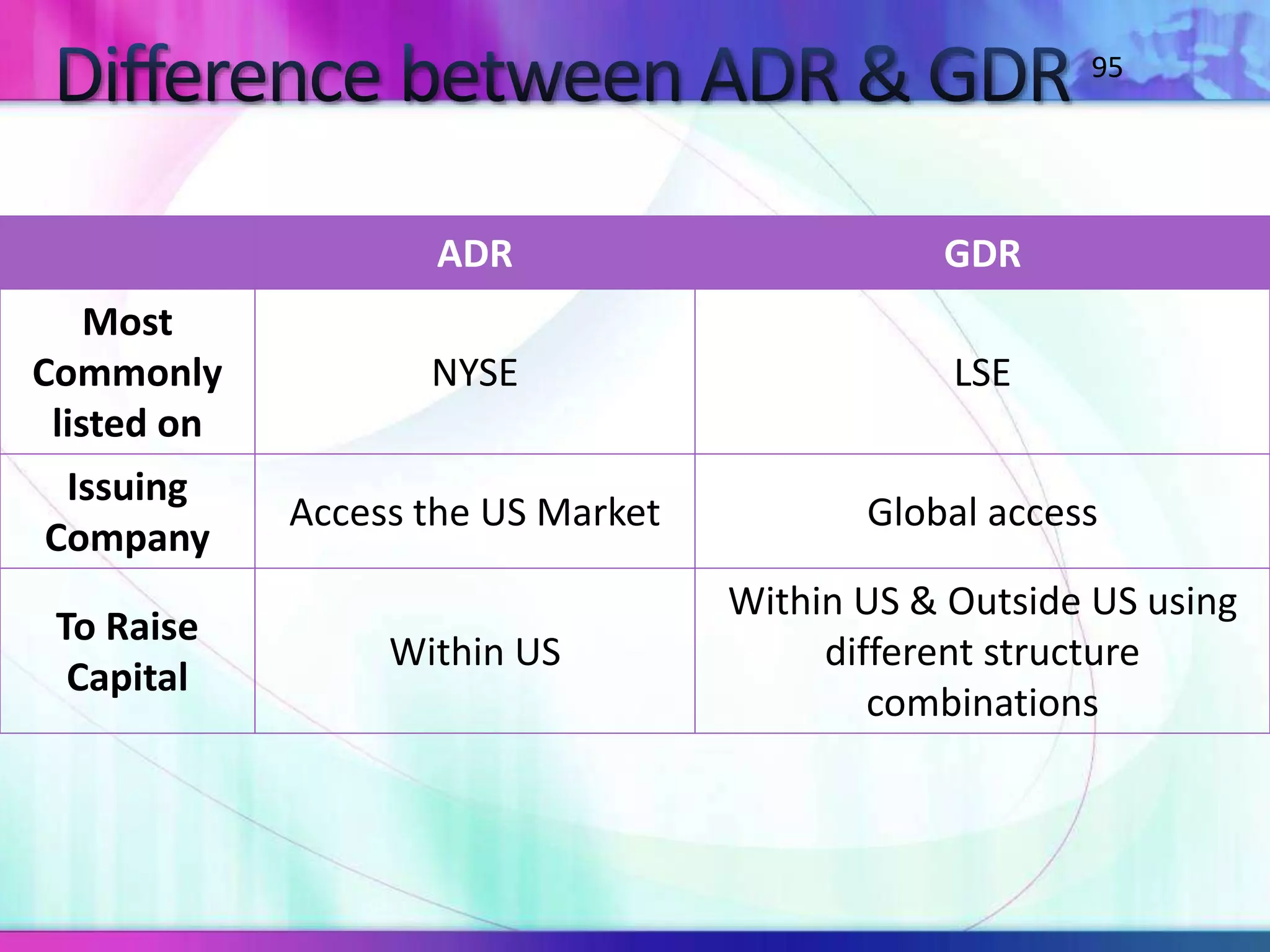
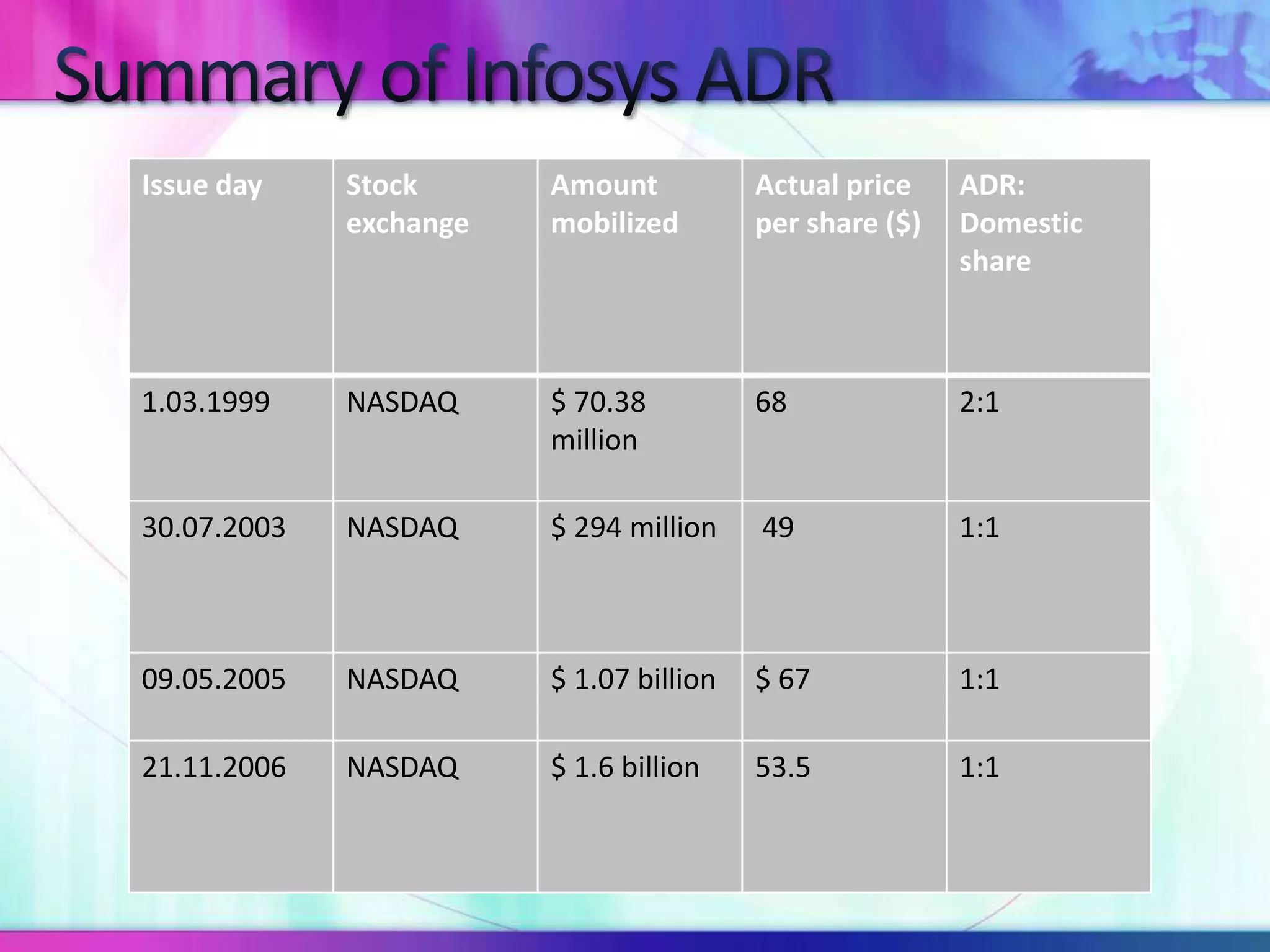
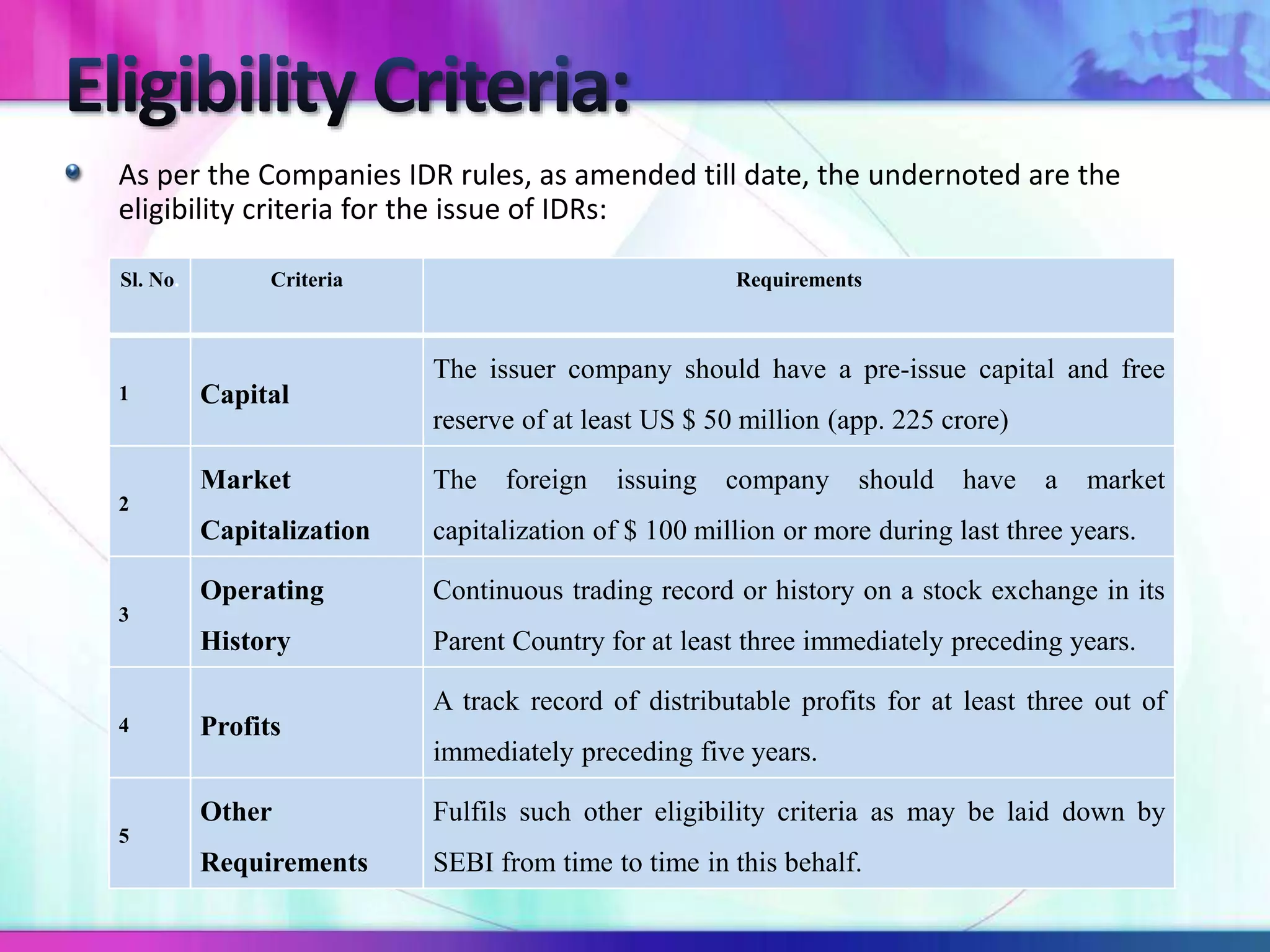
The document discusses various types of depository receipts (DRs) such as American Depository Receipts (ADRs) and Global Depository Receipts (GDRs). It explains that a DR allows investors to hold shares of foreign companies that trade on a local exchange. The document outlines the key parties involved in issuing DRs, including the issuer, depository, custodian bank and underwriters. It also describes the approval process for issuing DRs and the ongoing roles and responsibilities of each party.