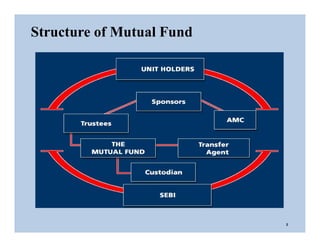
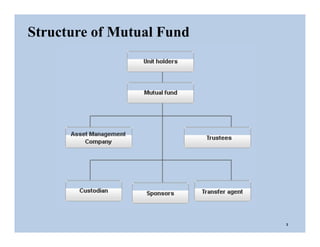
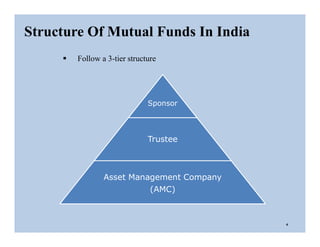
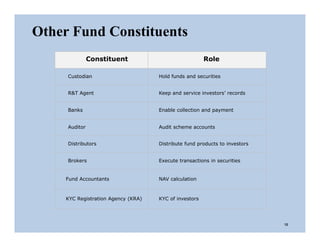
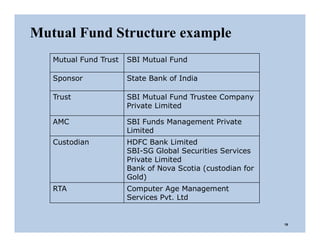
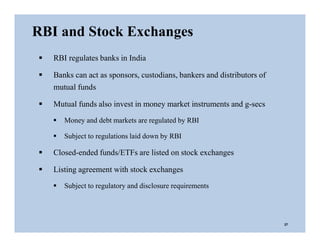
The document discusses the structure and legal environment of mutual funds in India. It describes the key constituents of a mutual fund which follow a 3-tier structure including sponsors, trustees, asset management companies (AMCs), custodians and other service providers. The roles and responsibilities of each constituent are explained. Regulatory authorities that oversee mutual funds like SEBI, RBI and AMFI are also summarized along with their functions. The grievance redressal process for investors is outlined.