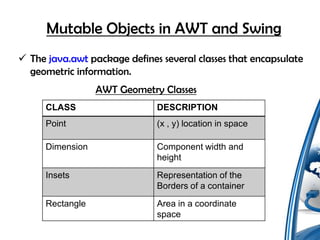
The document discusses the differences between mutable and immutable classes in Java, with mutable classes having methods that can modify object state after creation while immutable classes cannot be modified after creation, and provides examples of both types of classes including Strings, Date, and StringBuffer. It also covers cloning mutable objects and ensuring independent copies are made rather than references to the original objects.




![Sample Program
Class Pro1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "WELCOME";
System.out.println(str);
str.toLowerCase(); //Doesn’t impact on original content of Str
System.out.println(str); Output
} WELCOME
} WELCOME](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutableandimmutableclasses-120903114312-phpapp02/85/Mutable-and-immutable-classes-6-320.jpg)
![Modified Program
class Pro1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = “WELCOME";
System.out.println(str);
String str1 = str.toLower();
System.out.println(str1); Output
} WELCOME
} welcome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutableandimmutableclasses-120903114312-phpapp02/85/Mutable-and-immutable-classes-7-320.jpg)