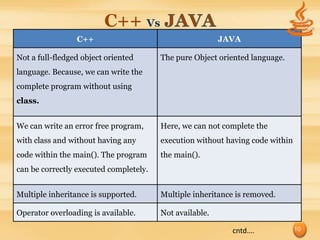
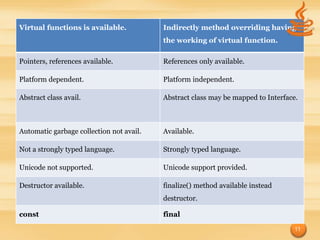
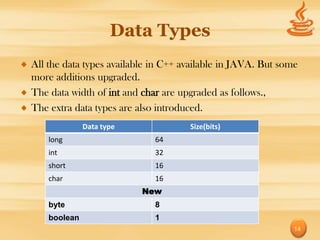
The document provides an overview of the Java programming language by discussing its origins, goals, features, data types, classes, and code examples. It began as a language called Oak that aimed to be platform independent. Key goals included using object-oriented methodology and allowing programs to run on multiple operating systems. Features include being simple, secure, portable, robust, and having automatic garbage collection. It also compares Java to C++, highlighting differences in inheritance, overloading, and memory management. Code examples demonstrate basic Java syntax and handling exceptions.







![Example code
public static int main(String[] a)
{
System.out.println(“n”+4+34);
return 0;
}
Output???
Error: Main method not found in class sample, please define the main method as:
public static void main(String[] args)
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-8-320.jpg)
![eg: cntd
public static void main(String[] a)
{
System.out.println(“n”+4+34);
System.out.println(34+2+"n");
return 0;
}
Output ??? 434
36
public static void main(String[] a)
{
System.out.println(4+34);
return 0;
}
Output ??? 38
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-9-320.jpg)


![for example
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
Integer g;
g=45;
System.out.println("ng : “+g);
}
Output
45
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-16-320.jpg)

![example…..
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
String fg=“PSG",gh=“Psg";
if((fg+=gh)==fg)
System.out.println("same....n");
else
System.out.println(“Not same....n");
}
Output:
same....
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-18-320.jpg)
![Example
public static void main(String[] arr)
{
int i1=45;
int i2=34;
System.out.println(“Ans is : “+i1+i2);
}
Output???
Ans is : 4534
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-19-320.jpg)
![General example
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
DataInputStream inp=new DataInputStream(System.in);
String mine=inp.readLine();
}
output???
Error: Un handled Exception IOException
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-20-320.jpg)
![Revised
public static void main(String[] arg) throws IOEception
{
DataInputStream inp=new DataInputStream(System.in);
String mine=inp.readLine();
System.out.println(“nString is : ”+mine);
float h=Float.parseFloat(inp.readLine());
System.out.println(“n Float values is : ” +h);
}
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-jun-2012-120903114059-phpapp01/85/14-jun-2012-21-320.jpg)

