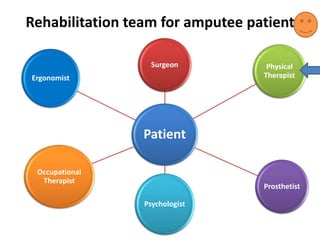
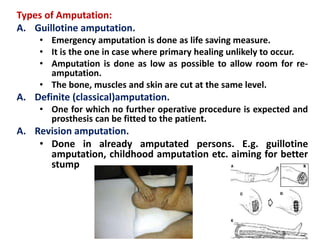
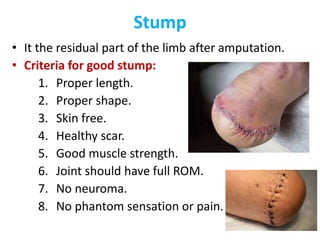
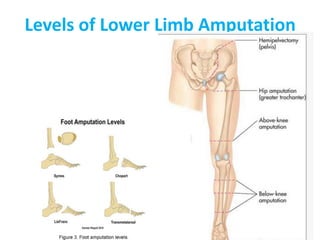
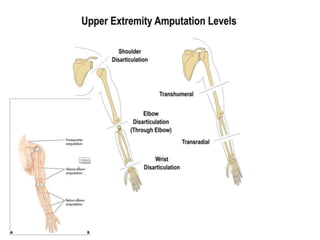
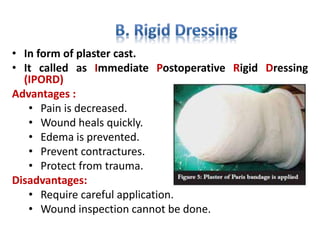
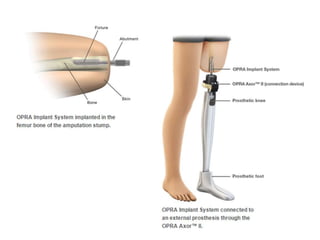
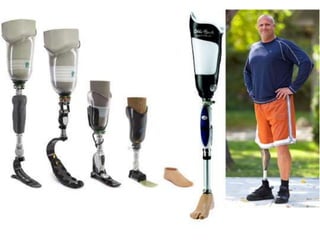
This document defines key terms related to orthotics and prosthetics. It describes different causes of amputation including trauma, vascular issues, infections, and tumors. The stages of rehabilitation for an amputee are outlined, including pre-amputation counseling, surgery, post-operative care, prosthetic training, and reintegration. Different levels of extremity amputation and criteria for a good stump are also defined. The roles of an interdisciplinary rehabilitation team are emphasized.