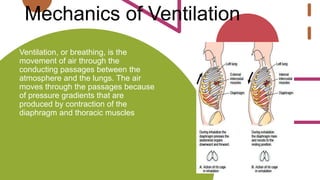
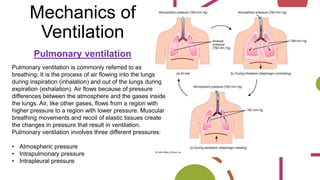
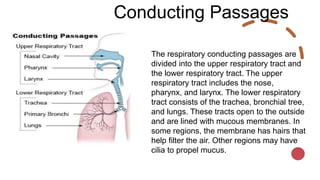
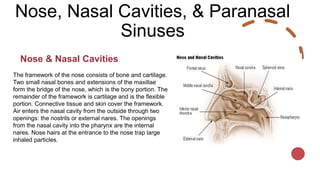
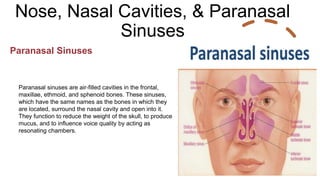
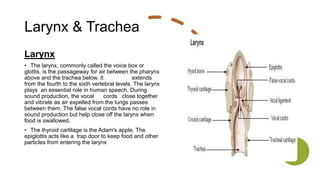
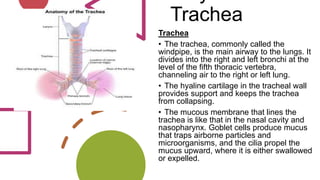
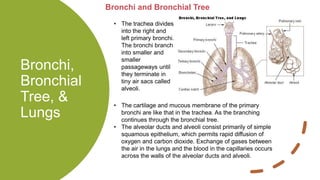
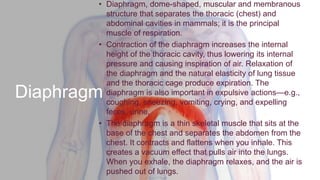
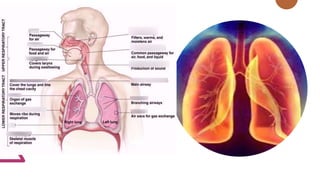
The respiratory system works to deliver oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. It includes the mouth, nose, pharynx, larynx, lungs, trachea, bronchi, and diaphragm. Air enters through the nose or mouth and travels down the trachea to the lungs, where oxygen passes into blood vessels and carbon dioxide is removed. The lungs, trachea, and bronchi form a branching tree structure ending in tiny air sacs called alveoli that facilitate gas exchange with blood in the pulmonary circulation. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles help drive breathing by expanding the lungs and lowering their pressure.