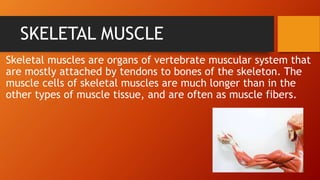
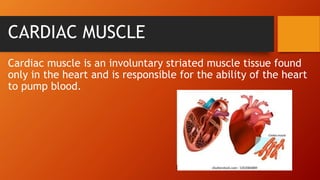
There are three main types of muscles in the human body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles that are attached to bones and enable movement. Smooth muscles are involuntary and are found in internal organs and passageways. Cardiac muscle is only found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.