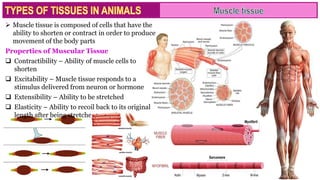
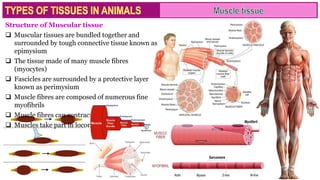
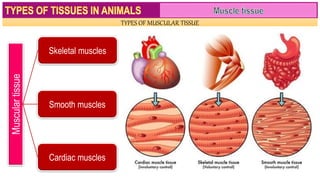
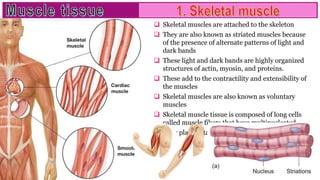
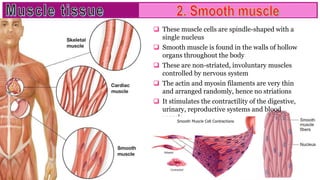
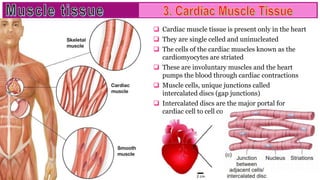
Muscle tissue is composed of contractile cells that facilitate body movement and is characterized by properties such as contractibility, excitability, extensibility, and elasticity. There are three types of muscular tissue: skeletal (striated and voluntary), smooth (non-striated and involuntary), and cardiac (striated and involuntary, found only in the heart). Each type has distinct structural features and roles, with skeletal muscles being multinucleated fibers attached to the skeleton, smooth muscles found in hollow organs, and cardiac muscle cells featuring unique intercalated discs for communication.