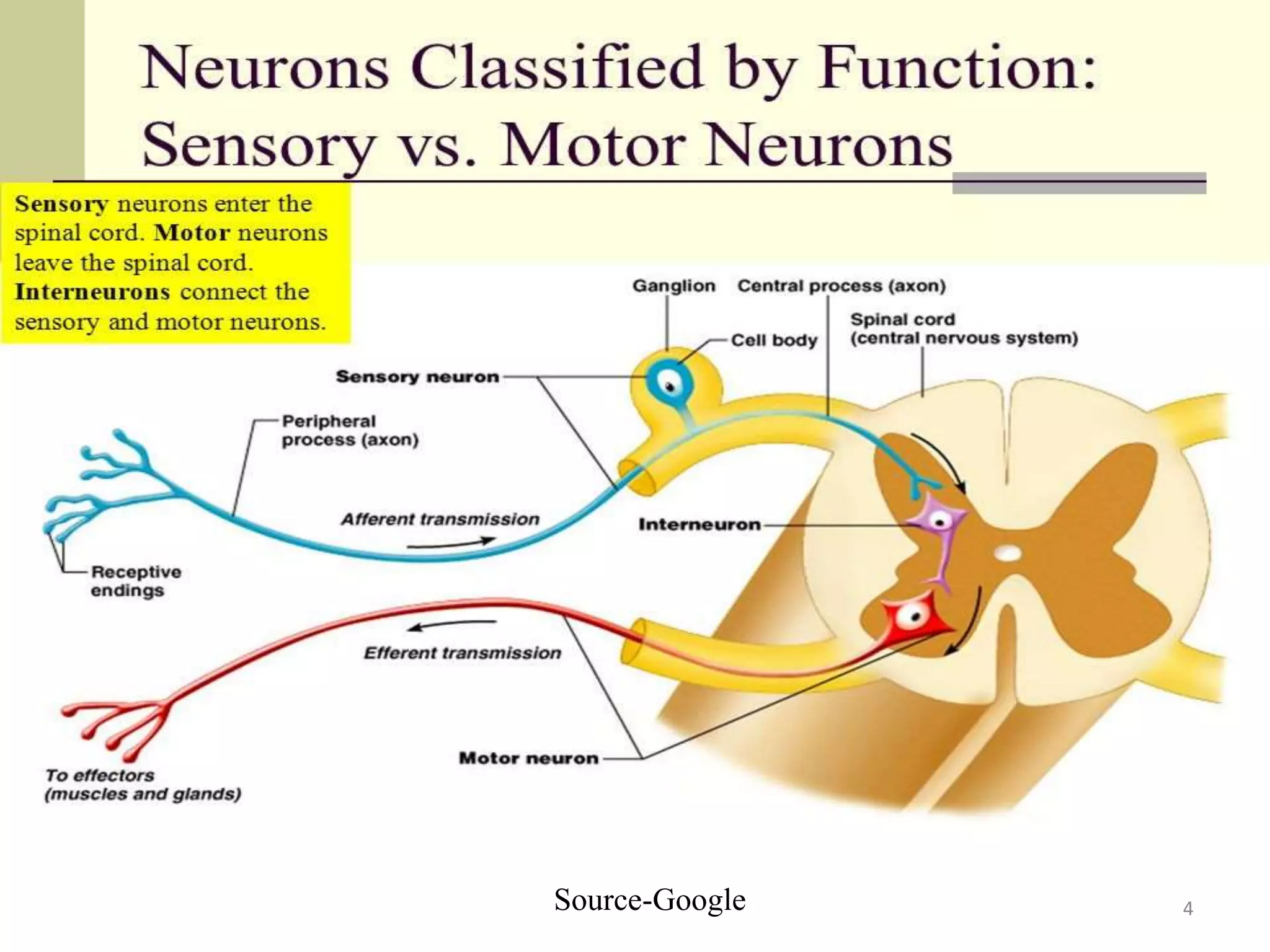
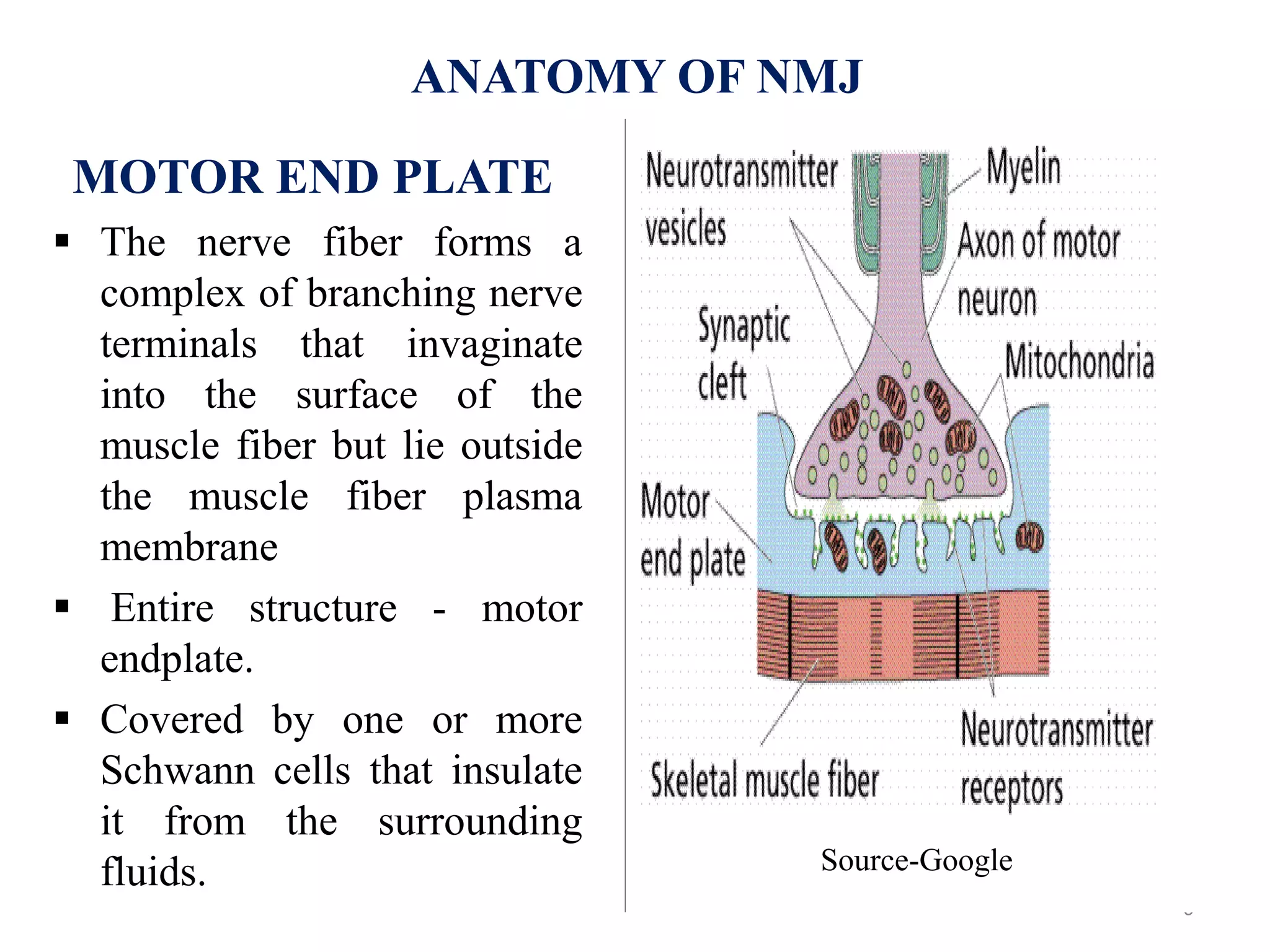
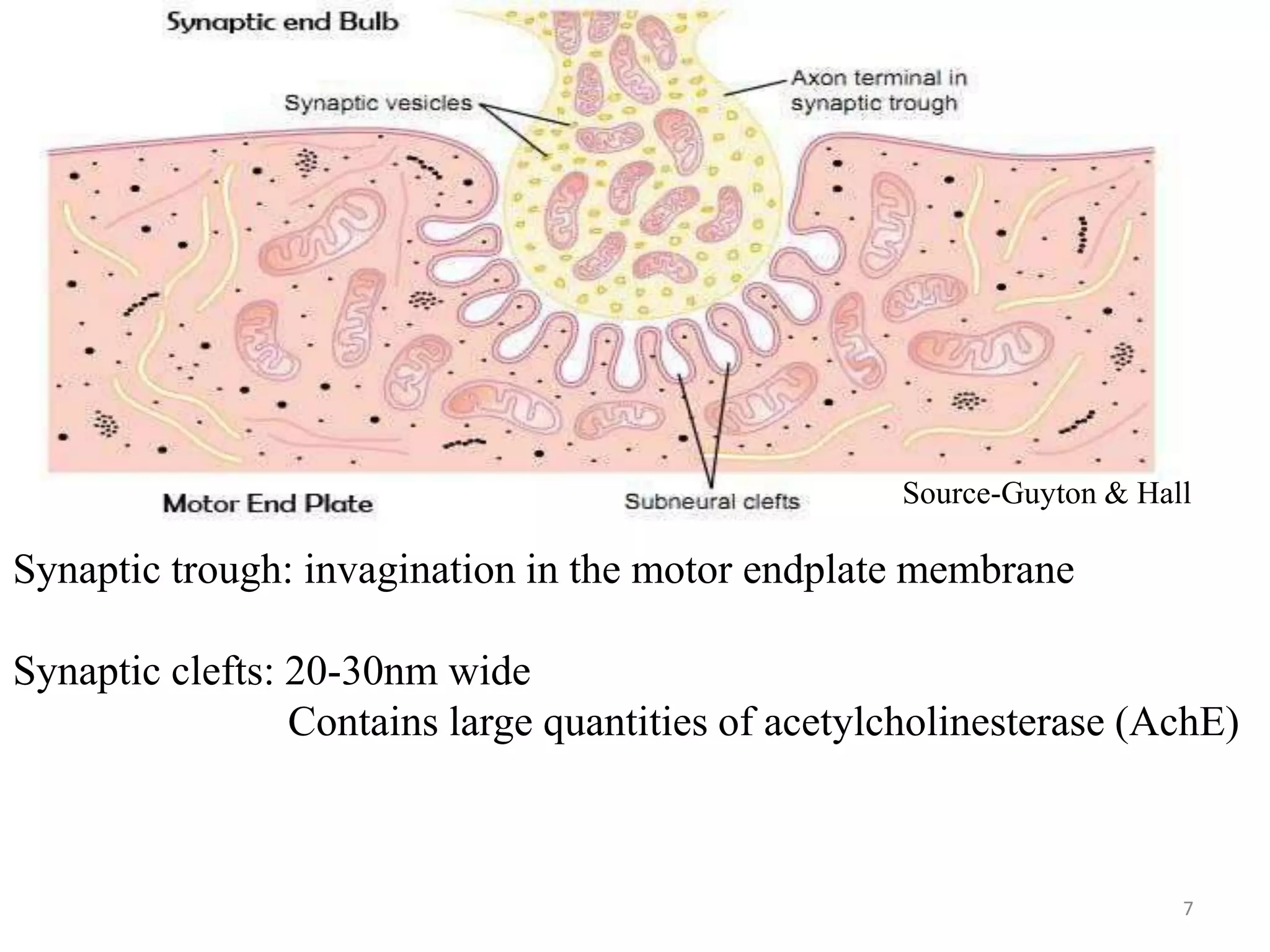
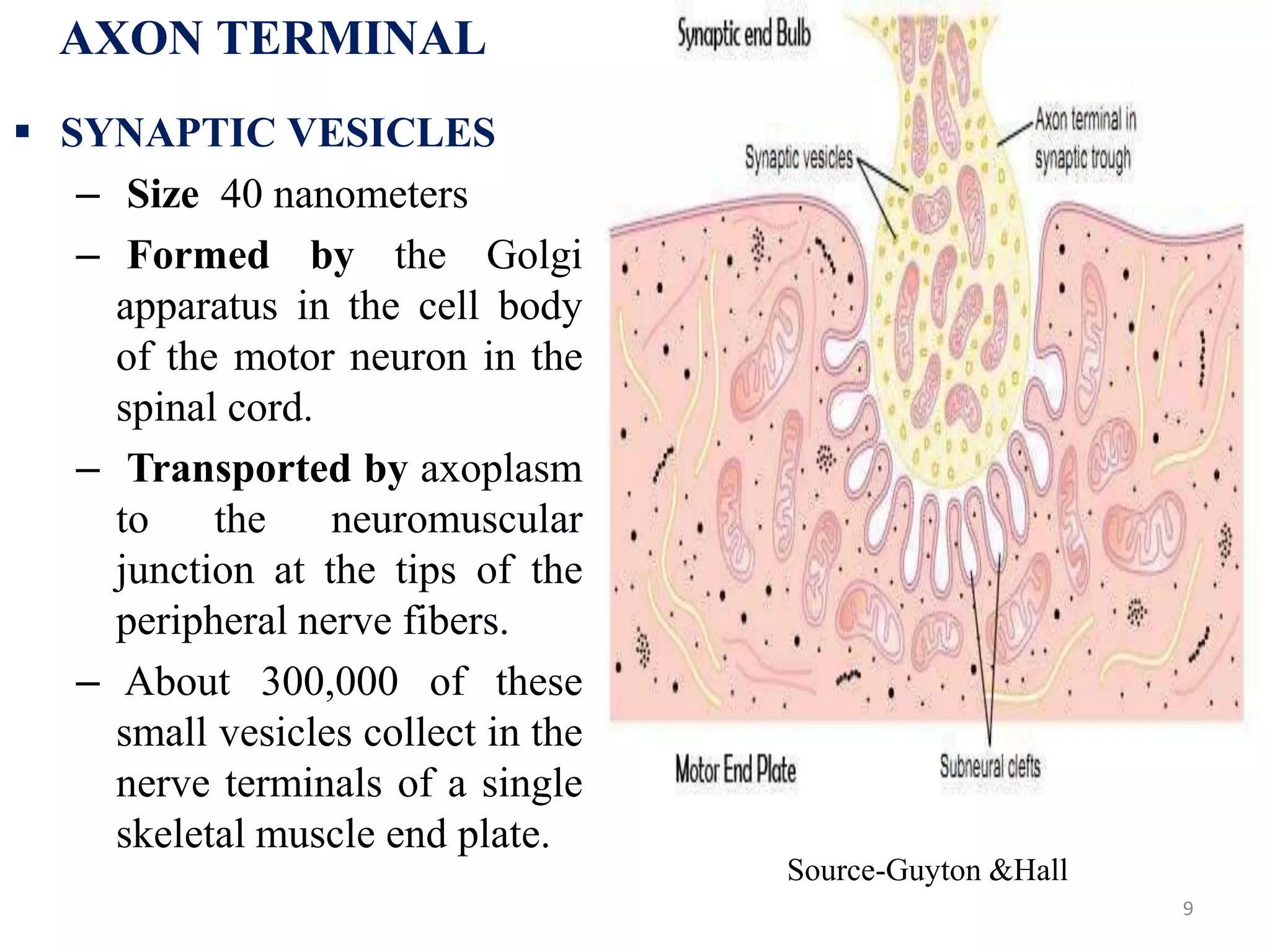
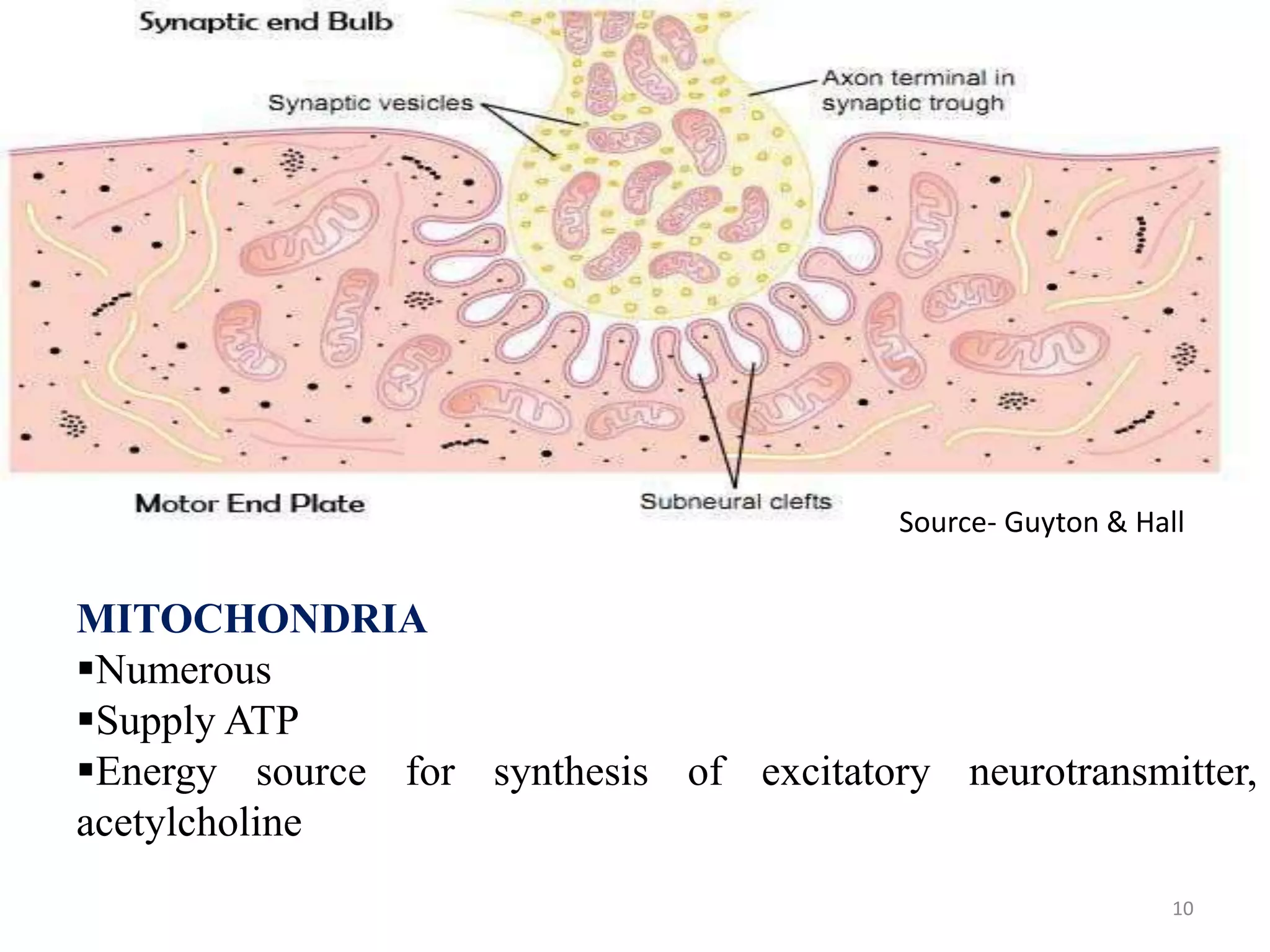
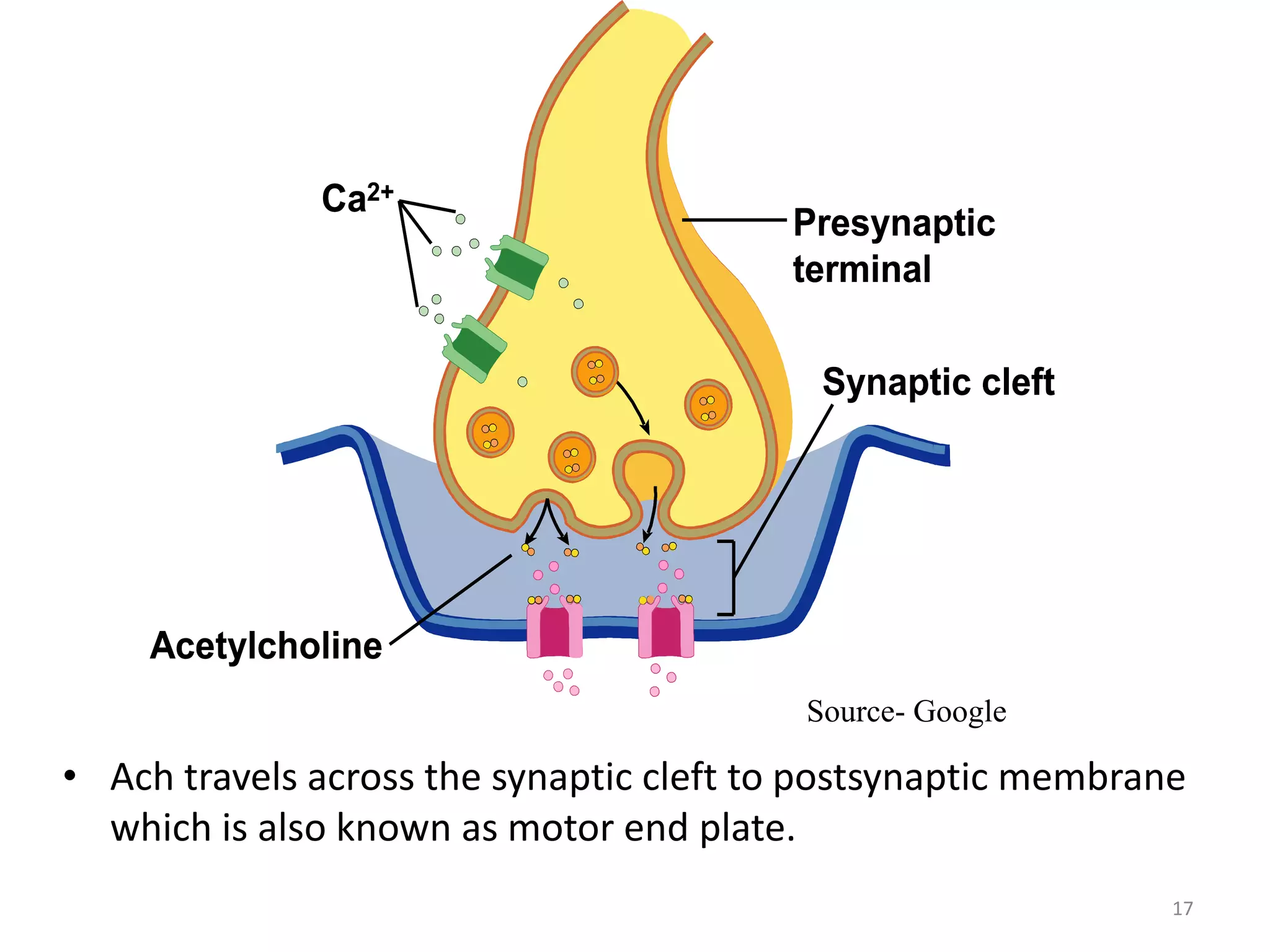
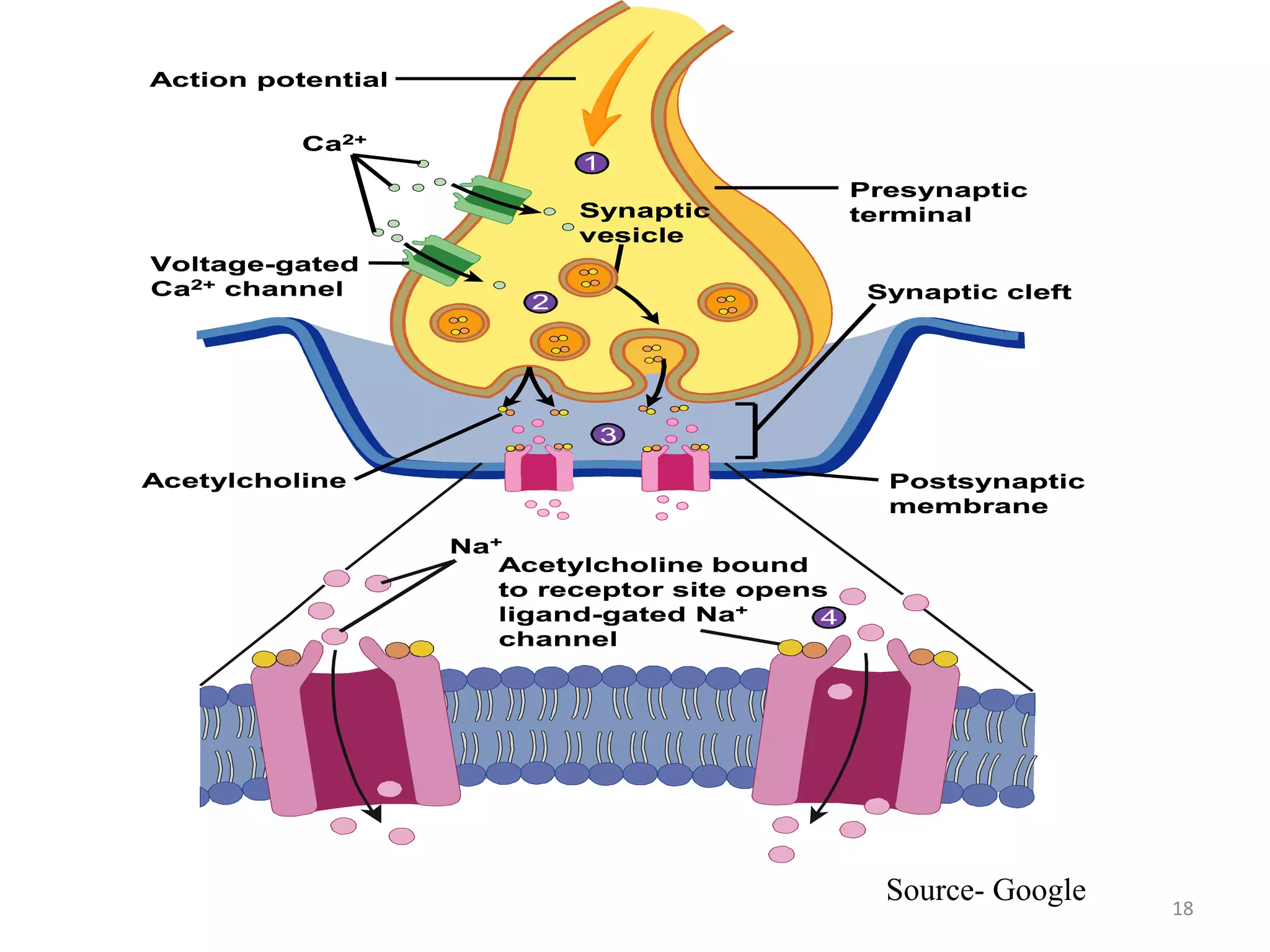
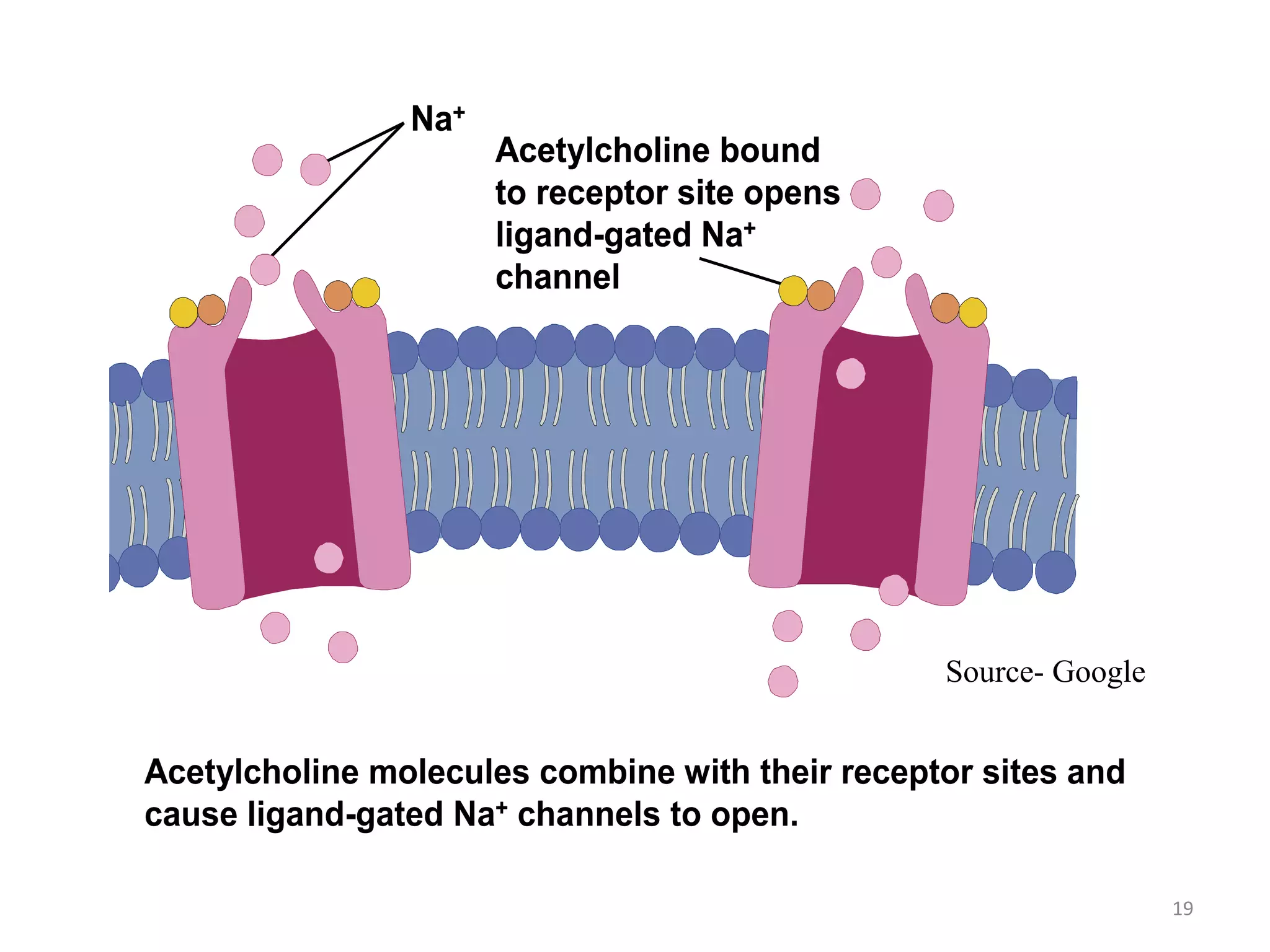
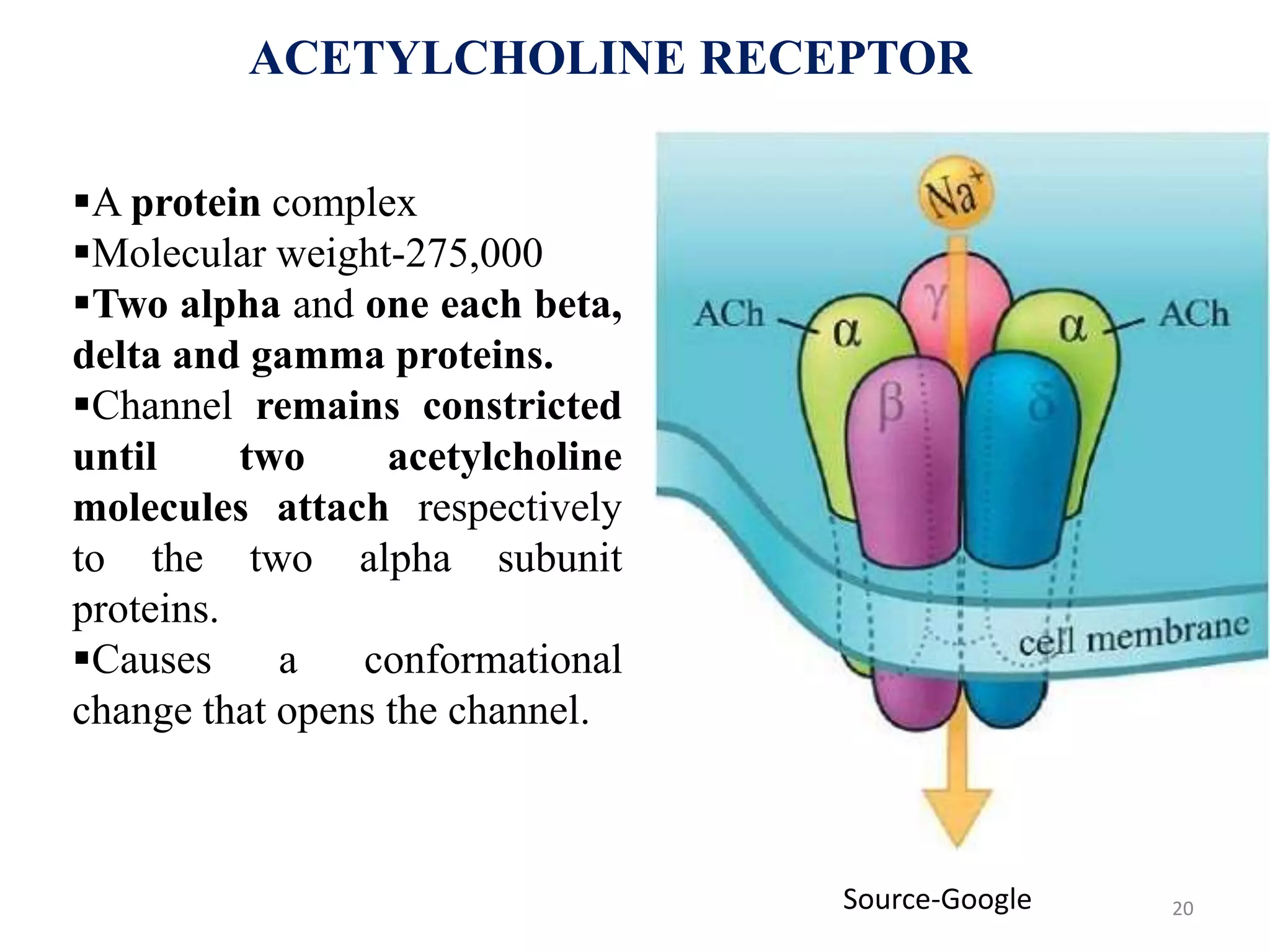
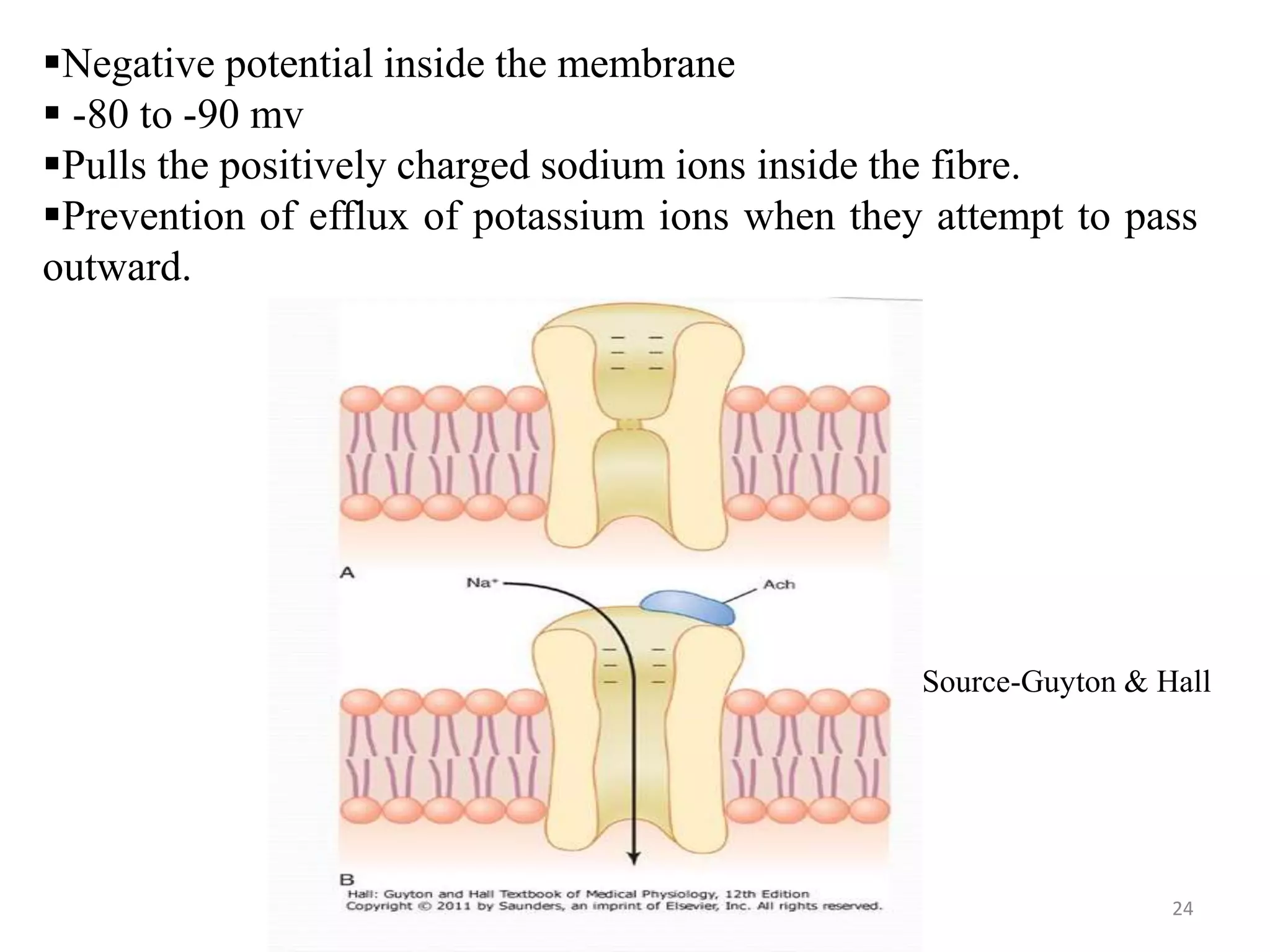
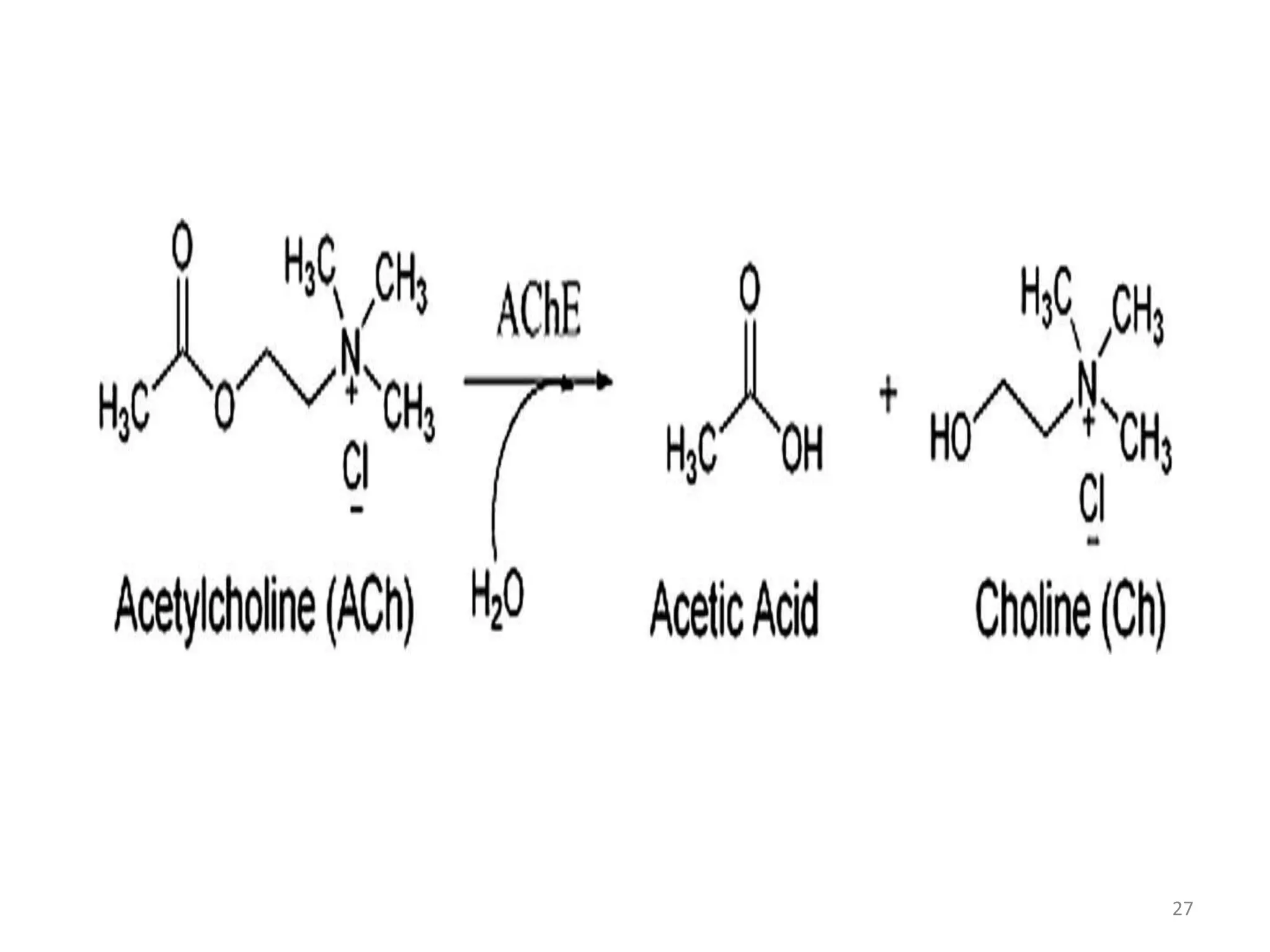
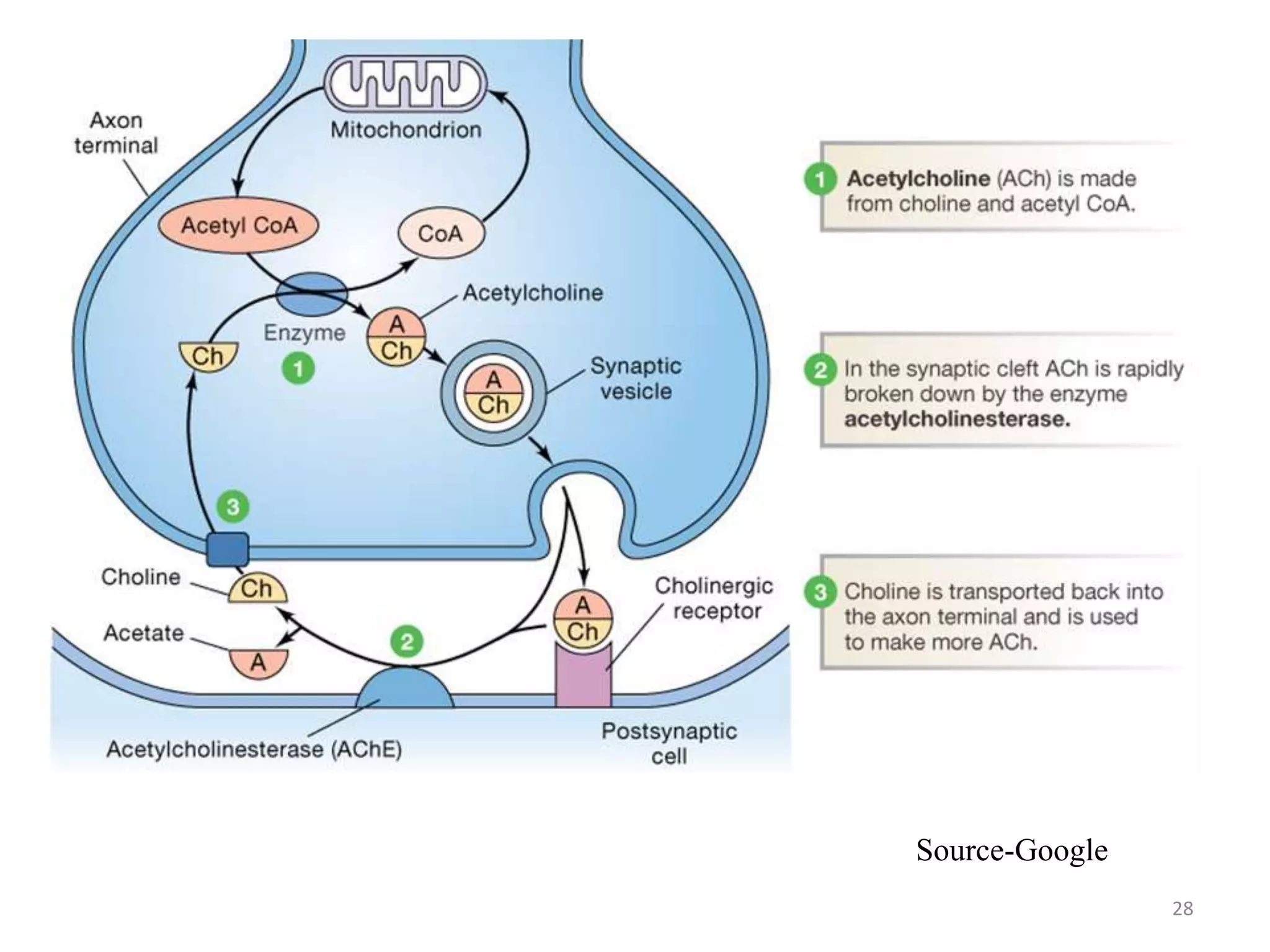
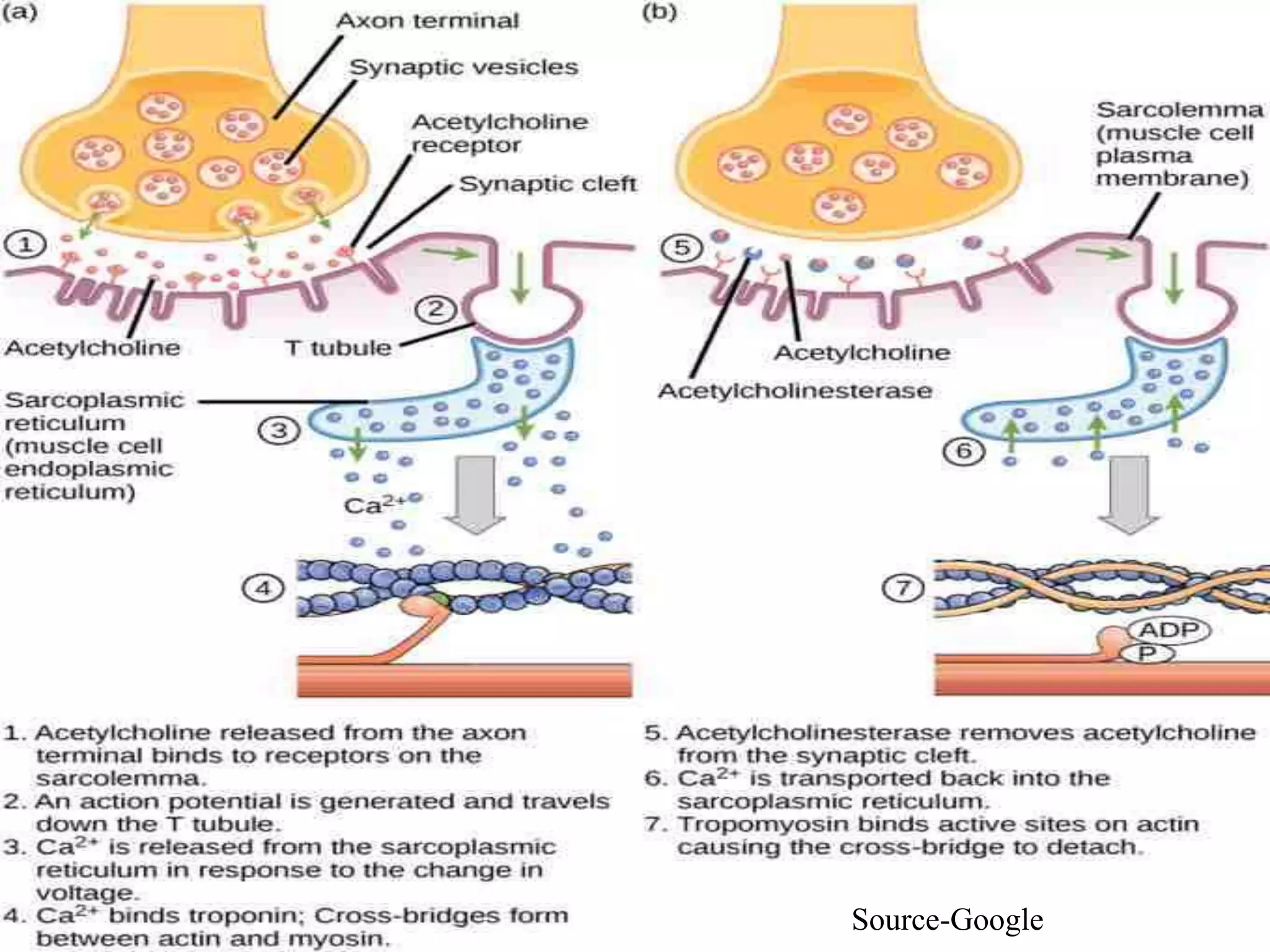
The neuromuscular junction is the chemical synapse between a motor neuron and muscle fiber. When an action potential reaches the motor neuron terminal, calcium ions enter and cause vesicles to release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft. Acetylcholine then binds to nicotinic receptors on the muscle fiber, opening sodium channels and causing an endplate potential that generates an action potential in the muscle fiber, leading to muscle contraction. Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine to terminate the signal and allow muscle relaxation.