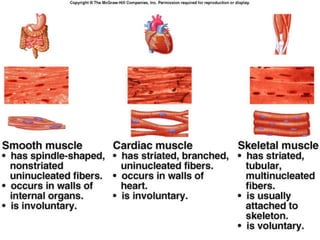
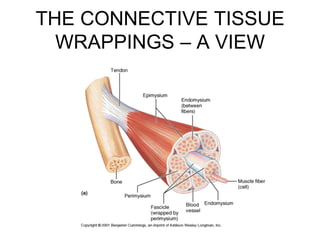
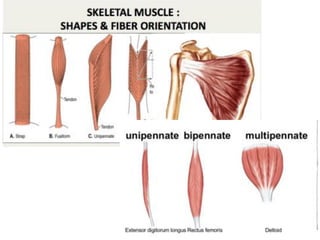
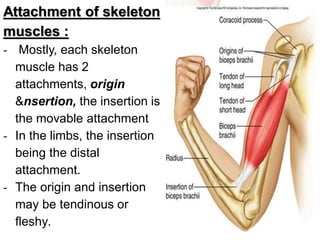
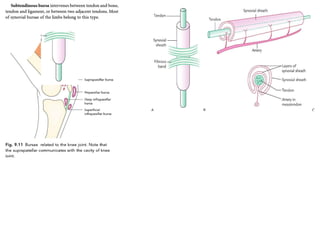
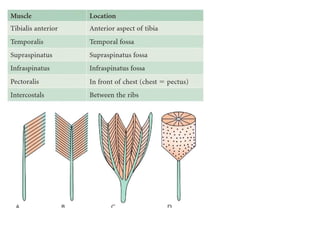
This document provides an overview of general myology (the study of muscles). It discusses the three main types of muscles - smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles that are attached to bones and have bundles of fibers. The document describes the layers of connective tissue (epimysium, perimysium, endomysium) that surround skeletal muscle fibers. It also discusses the arrangements of skeletal muscle fibers, their attachments via tendons, and associated structures like tendon sheaths and bursae.