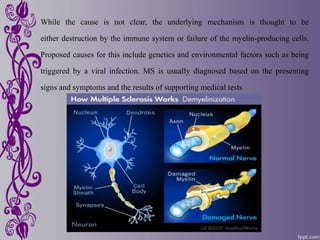
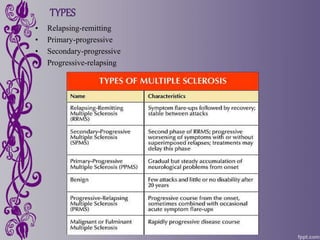
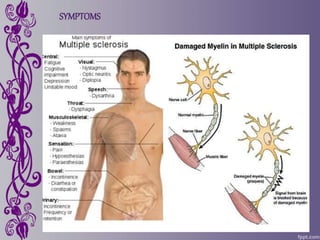
Multiple sclerosis is a disease that damages the myelin sheath surrounding nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. This damage disrupts communication between nerves and causes a variety of physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric symptoms. While the exact cause is unknown, it is considered an immune-mediated disease involving both genetic and environmental factors. There is no known cure, but treatments aim to relieve symptoms or slow progression, including drug therapies and complementary approaches like acupuncture, herbal medicine, yoga, and relaxation techniques.