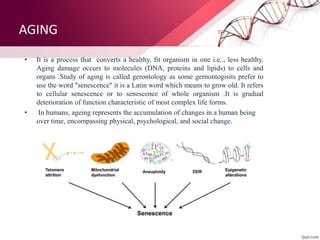
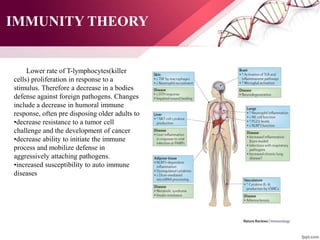
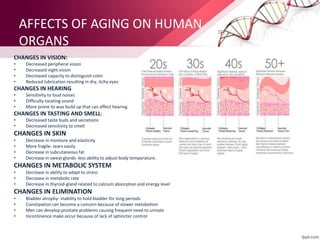
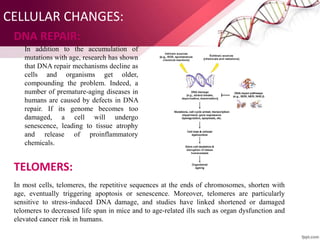
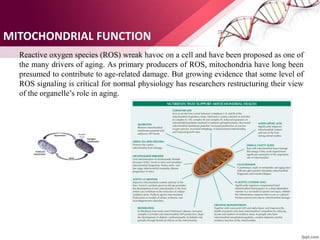
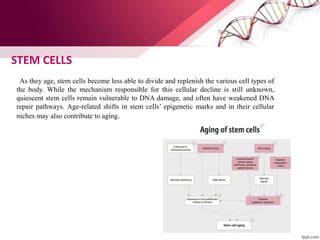
The document discusses the concept of rejuvenation, detailing historical myths and various theories of aging, including biological, sociological, and psychological perspectives. It explains the mechanisms behind aging processes such as DNA damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and hormonal changes, while exploring potential methods for life extension like stem cell therapy and hormone replacement. It concludes with insights on emerging research aims to counteract the effects of aging and promote rejuvenation.