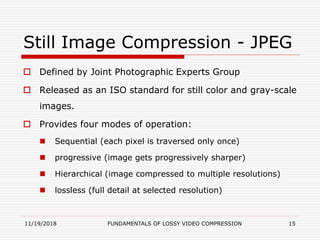
This document discusses fundamentals of lossy video compression. It introduces digital video and factors like frame rate, color resolution, and spatial resolution. It describes video compression standards including MPEG, JPEG, H.261, and H.263. MPEG standards like MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4 are discussed in detail regarding their applications and capabilities. The goals of video compression are to reduce file size while retaining quality for storing and transferring video efficiently.