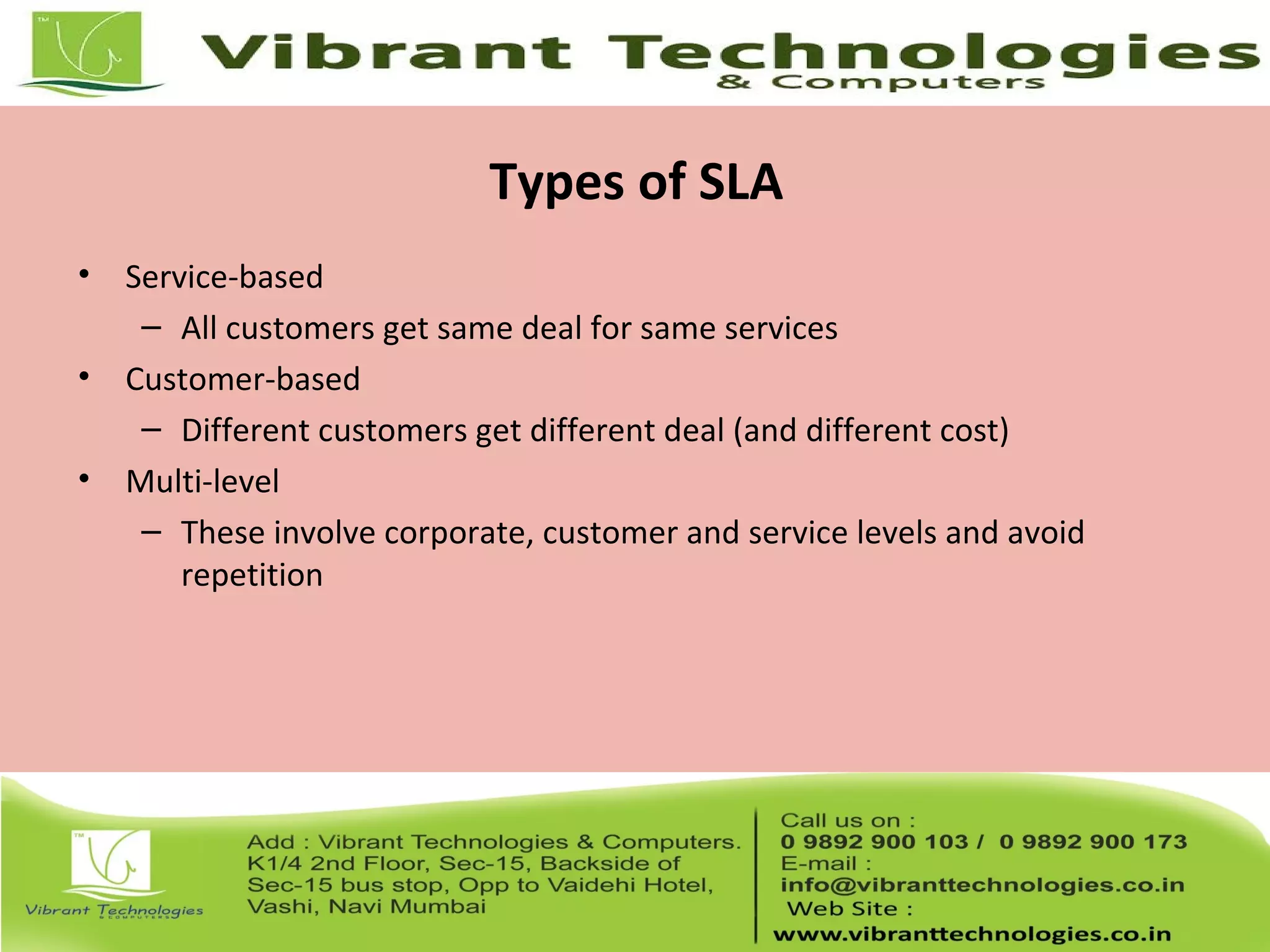
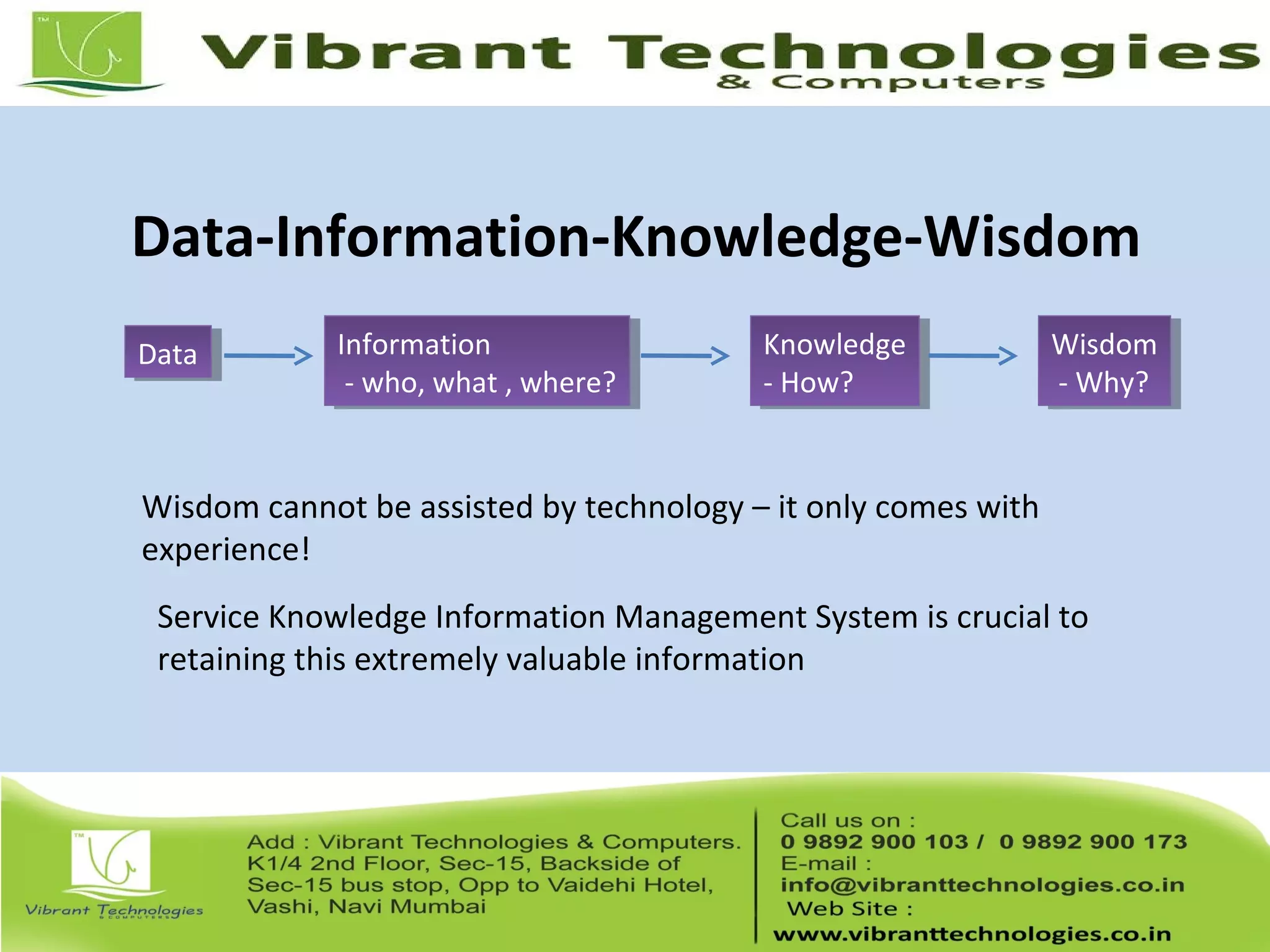
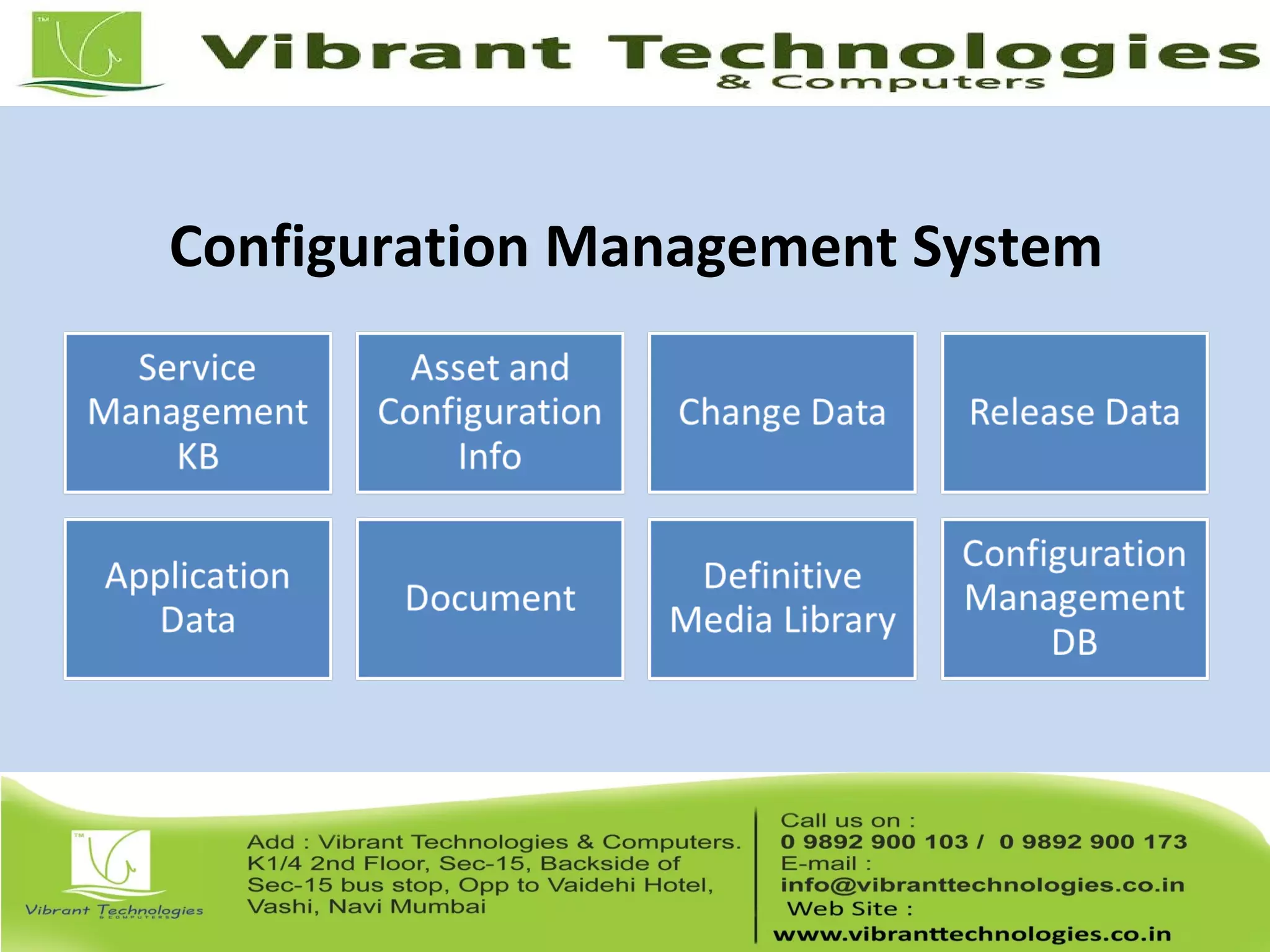
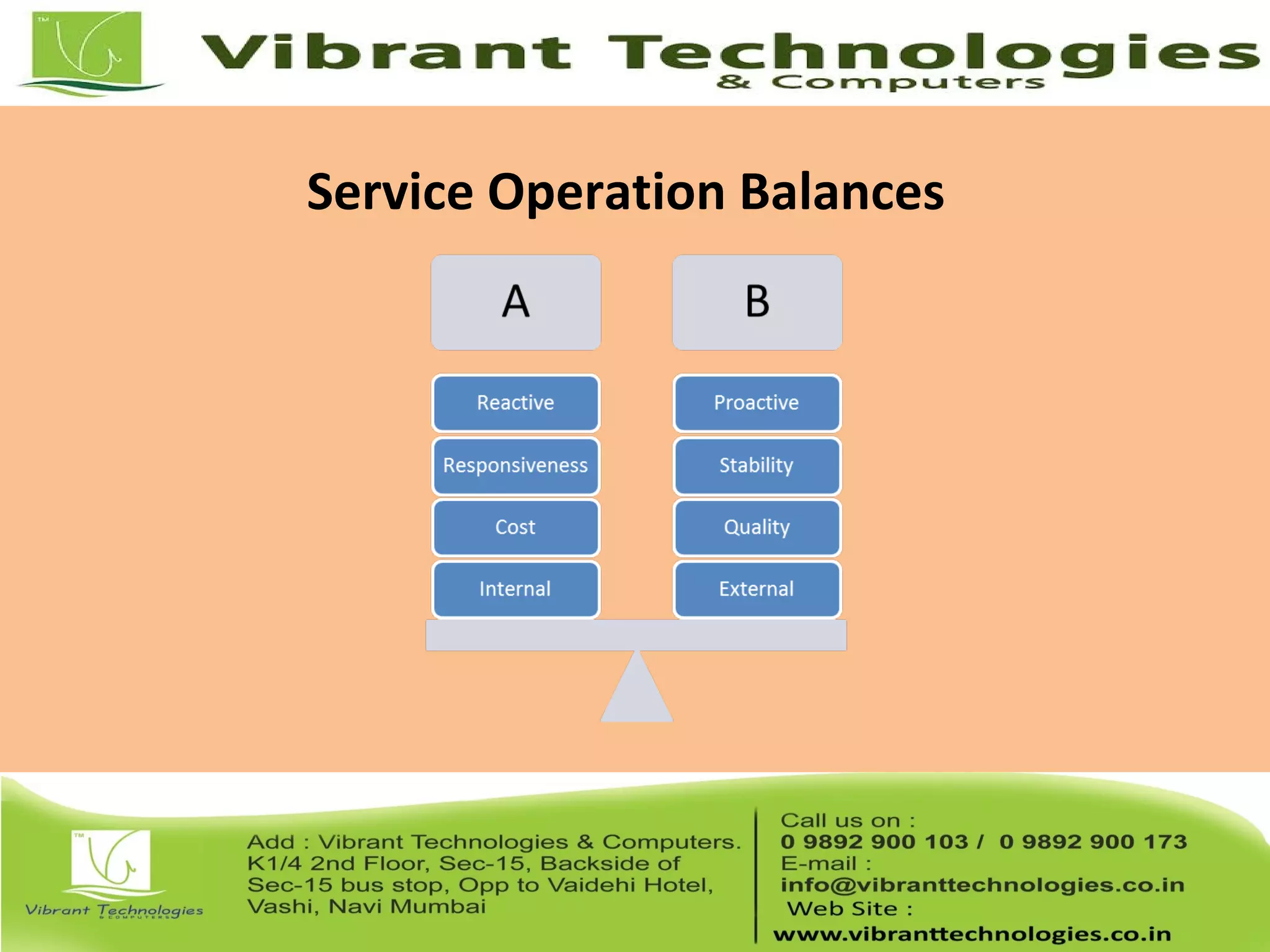
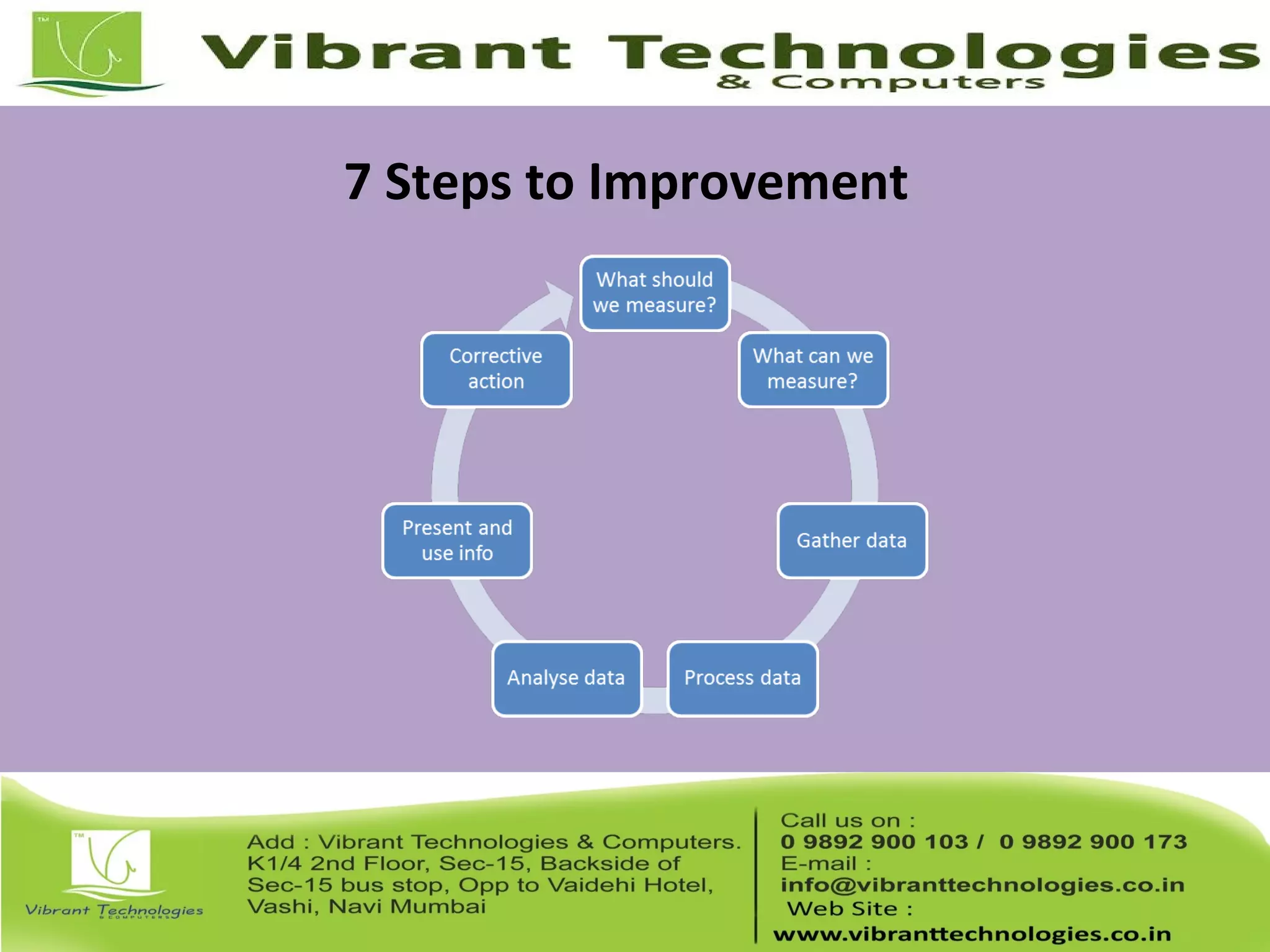
This document provides an introduction to ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), covering its history, key concepts, and the service lifecycle. It outlines the transition from earlier versions to ITIL v3, highlighting the simplified structure and enhanced focus on strategic guidance. Additionally, it discusses various aspects of service management, including service delivery strategies, roles, functions, and further learning opportunities.