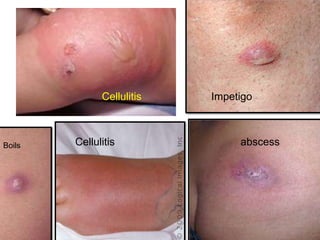
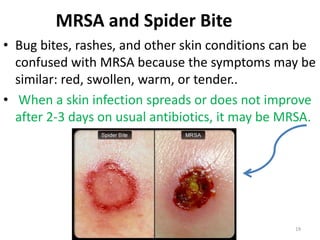
MRSA is a bacteria that is resistant to methicillin and other antibiotics such as penicillin. It can cause dangerous infections in humans. MRSA spreads through direct contact with infected individuals or surfaces and is a concern in healthcare settings. Symptoms of MRSA infection vary depending on the site of infection but may include boils, abscesses, or cellulitis. Treatment involves draining infections and administering antibiotics, with more serious cases requiring hospitalization. Preventing the spread of MRSA requires good hand hygiene and avoiding sharing personal items.