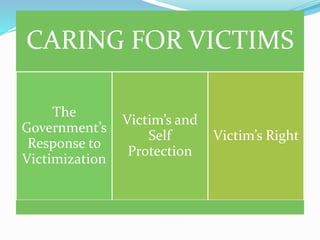
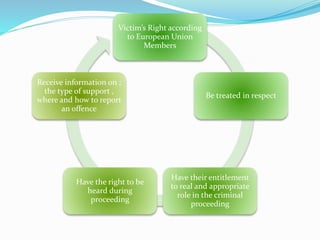
This document summarizes information about victimization from a criminology course. It discusses the social ecology and characteristics of victimizations, as well as theories of victimization. The key points are:
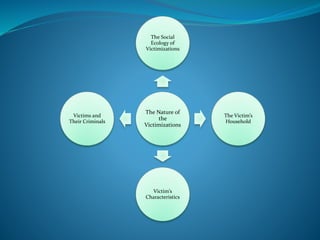
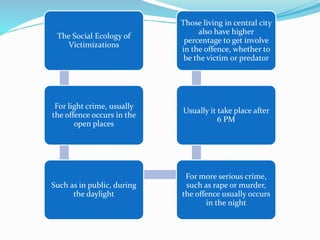
1) Victimization risk varies based on location (e.g. public vs. private), gender, age, social status, and other demographic factors.
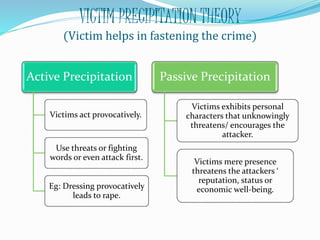
2) Theories of victimization like lifestyle theory and routine activities theory suggest victimization risk increases through behaviors like frequenting risky locations, having valuable possessions, and lacking capable guardians.
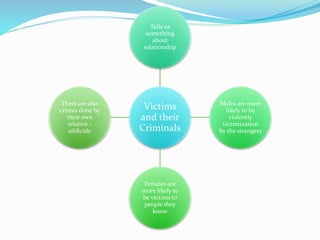
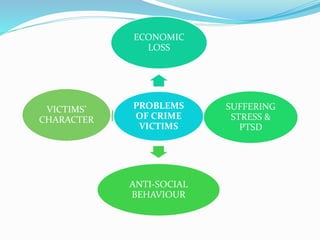
3) Victimization can cause economic losses, suffering, stress, PTSD and increased risk of anti-social behavior in victims.







![ECONOMIC LOSS
COSTS OF
GOODS
PRODUCTIVITY
LOSS
COSTS OF
VICTIMIZATION
A] SYSTEM COSTS B] INDIVIDUAL
COSTS
Criminologists use this below method which is similar to determine
civil damages, to estimate the costs of victimization:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/victimfs-140620053728-phpapp02/85/Victimization-Criminology-15-320.jpg)
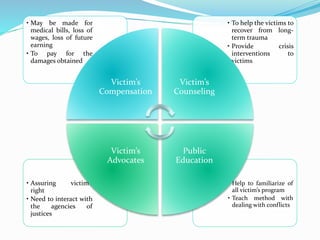
![A] SYSTEM COSTS
Effected party: Society at large, taxpayer, federal and
state government.
Cost incurred to:
• Early prevention program
• Organization to combat crimes
Reduce
crime
• Medical treatment for injuries
• Services for victims
• Loss wages, pain and suffering, also
reduced quality of life
Victims
• Legal costs
• Treatment costs
Justice
system
• Abused product
• Treatments and care centre
Social
costs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/victimfs-140620053728-phpapp02/85/Victimization-Criminology-16-320.jpg)
![B] INDIVIDUAL COSTS
Earning and occupational attainment affected.
If happen to have physical disabled during the
incidents of crime but victims had no
insurance financial devastating occur due to the
costs of special treatment.
Victims may bear psychological and physical ills
that may inhibit academic achievement and later
their economic and professional success.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/victimfs-140620053728-phpapp02/85/Victimization-Criminology-17-320.jpg)