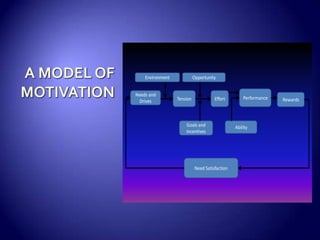
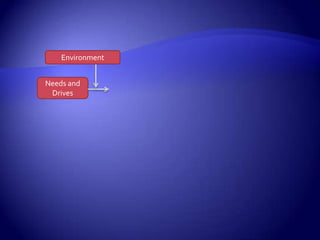
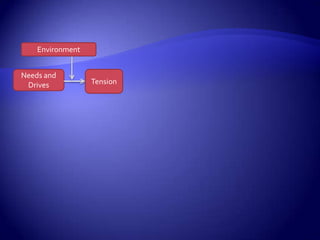
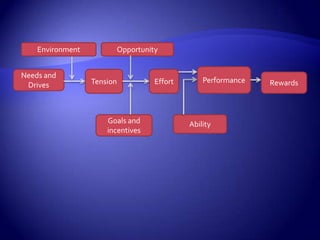
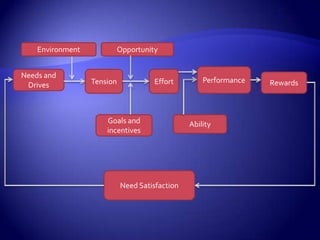
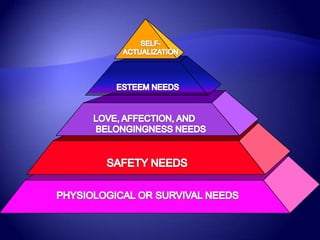
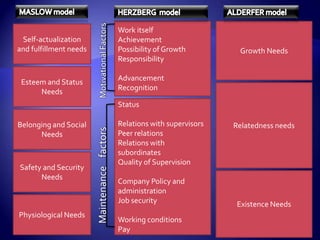
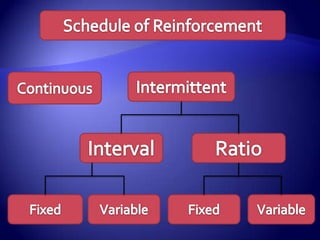
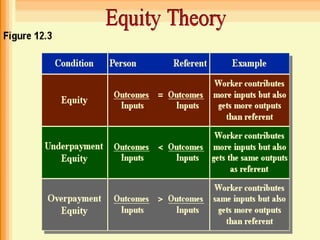
Work motivation is driven by internal and external forces that influence employee behavior, focused in three key areas: direction, effort level, and persistence. A model of motivation involves the interaction between an individual's needs/drives and the work environment. Needs range from basic physical needs to higher-level social and psychological needs. Motivational drives include achievement, affiliation, and power. When needs and drives are met through opportunities, performance, and rewards in the work environment, employees experience satisfaction and are motivated to continue their efforts. Behavior modification uses principles of reinforcement to encourage desirable behaviors and discourage undesirable ones through consequences in the workplace. The equity model also motivates through fair treatment and perceptions of fair outcomes relative to inputs.