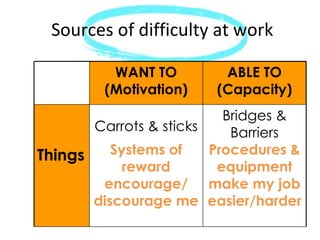
The document discusses the importance of feedback and coaching in maximizing alignment between individual work and organizational requirements, while promoting intrinsic motivation. It categorizes feedback into relational, observational, positive reinforcement, and redirective types, with a focus on the positive-to-negative feedback ratio for high-performance teams. Additionally, it notes the impact of motivational factors and attachment styles on workplace dynamics and provides insights into managing conflicts and promoting effective communication.