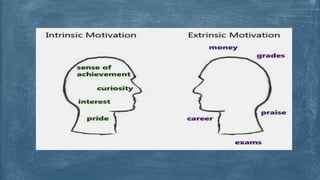
This document discusses different concepts and theories of motivation. It defines intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and explores drive theory, instinctual behavior theory, and cognitive approaches. Drive theory proposes that biological drives increase over time if not satisfied, motivating goal-directed actions. Instinctual behavior theory examines inborn tendencies and social instincts. Cognitive approaches emphasize expectations and subjective interpretations of reality in motivating behavior. Theories of motivation can be used to relate biology to behavior, account for variability, infer internal states, assign responsibility, and explain perseverance. Motivation is the internal force directing behavior and governing how people live.