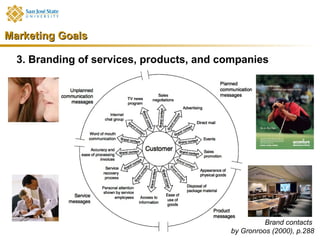
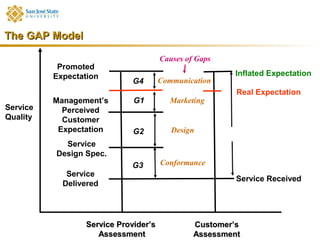
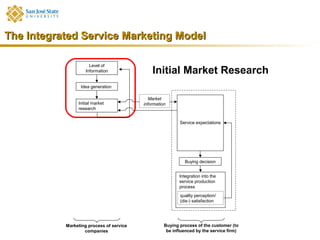
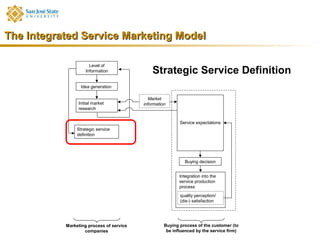
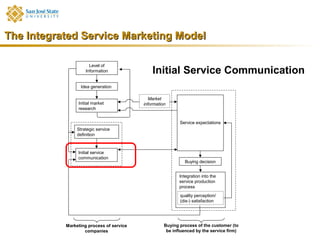
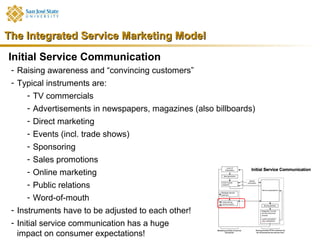
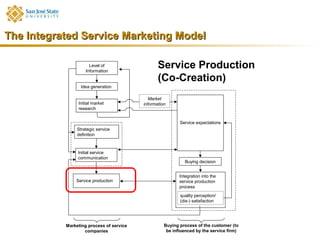
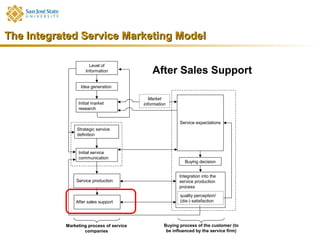
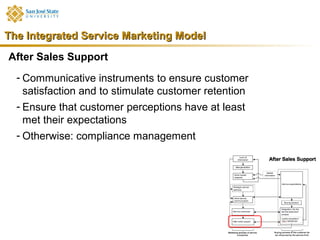
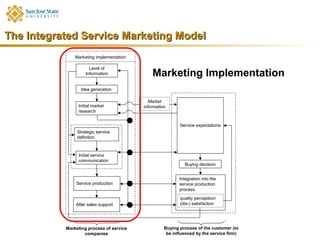
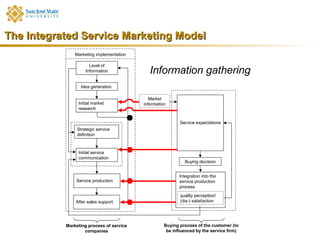
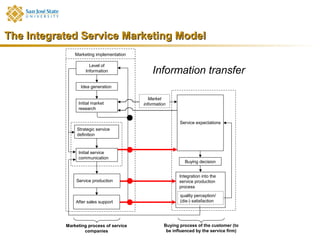
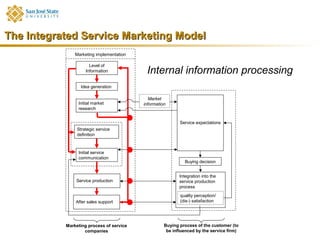
Marketing consists of activities designed to generate exchanges to satisfy human or organizational needs. The evolution of marketing has progressed from a product-orientation to a market-orientation and now emphasizes customer needs and service dominant logic. The goals of marketing are customer satisfaction, stimulation of exchanges and retention, and branding. Service marketing requires closing gaps between expectations and quality using marketing mix instruments while co-creating with customers. Information management is crucial across the integrated service marketing process.