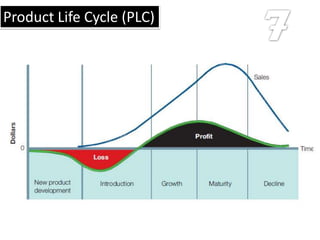
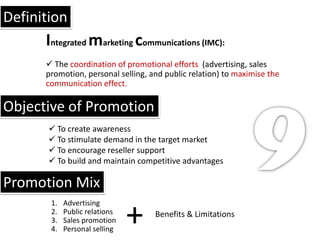
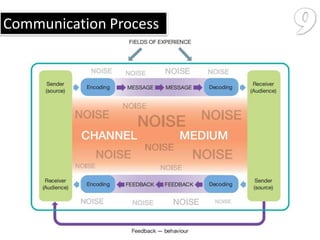
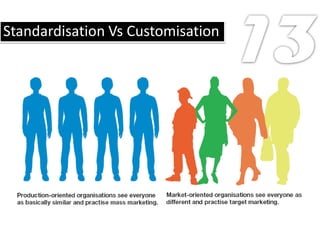
The document defines key marketing concepts:
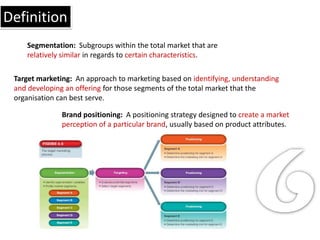
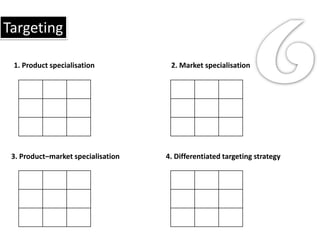
1. Segmentation divides markets into subgroups with similar characteristics. Target marketing develops offerings for specific segments.
2. Brand positioning creates a market perception of a brand based on attributes.
3. Effective segmentation is measurable, accessible, substantial, and practical.