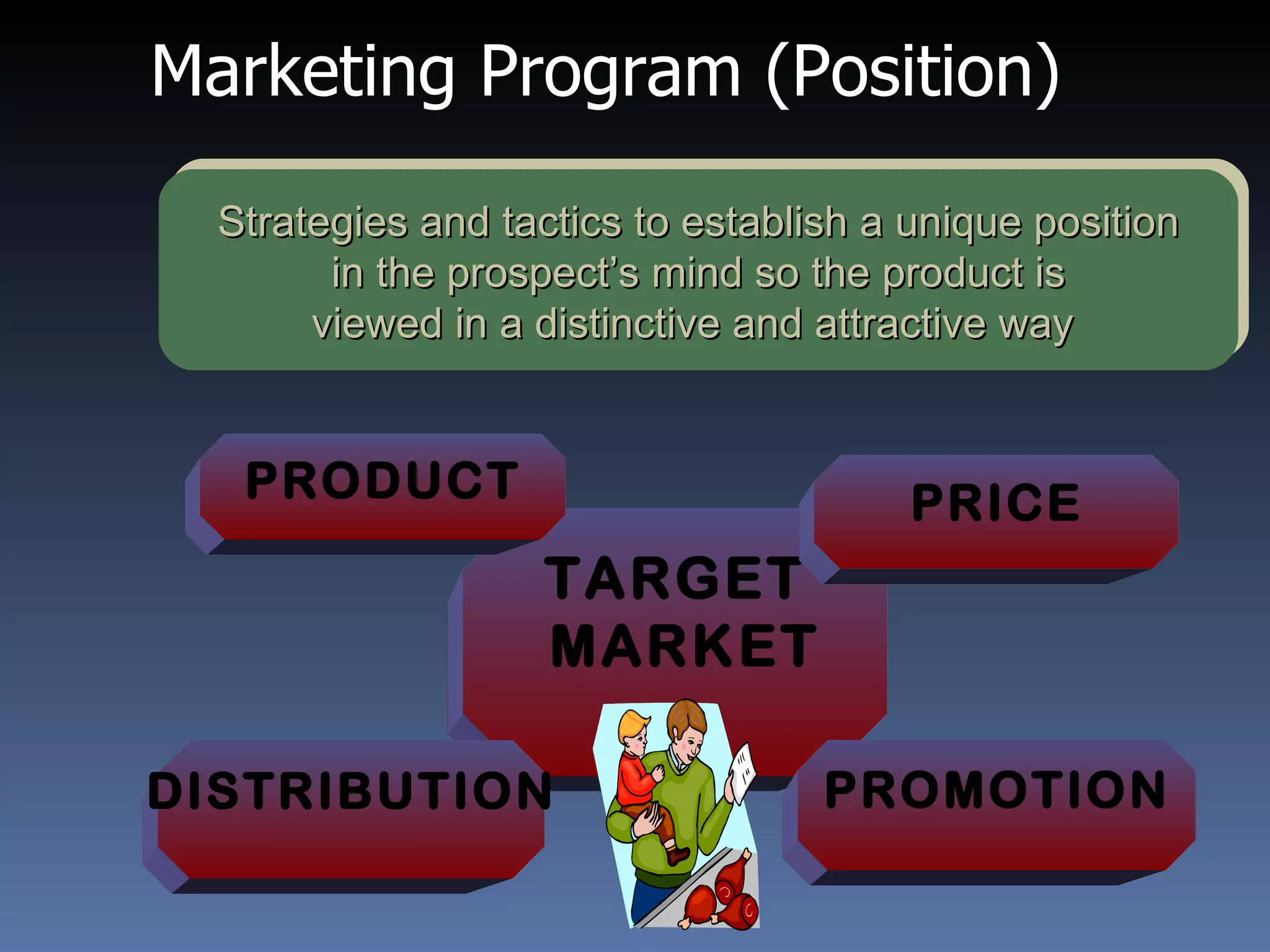
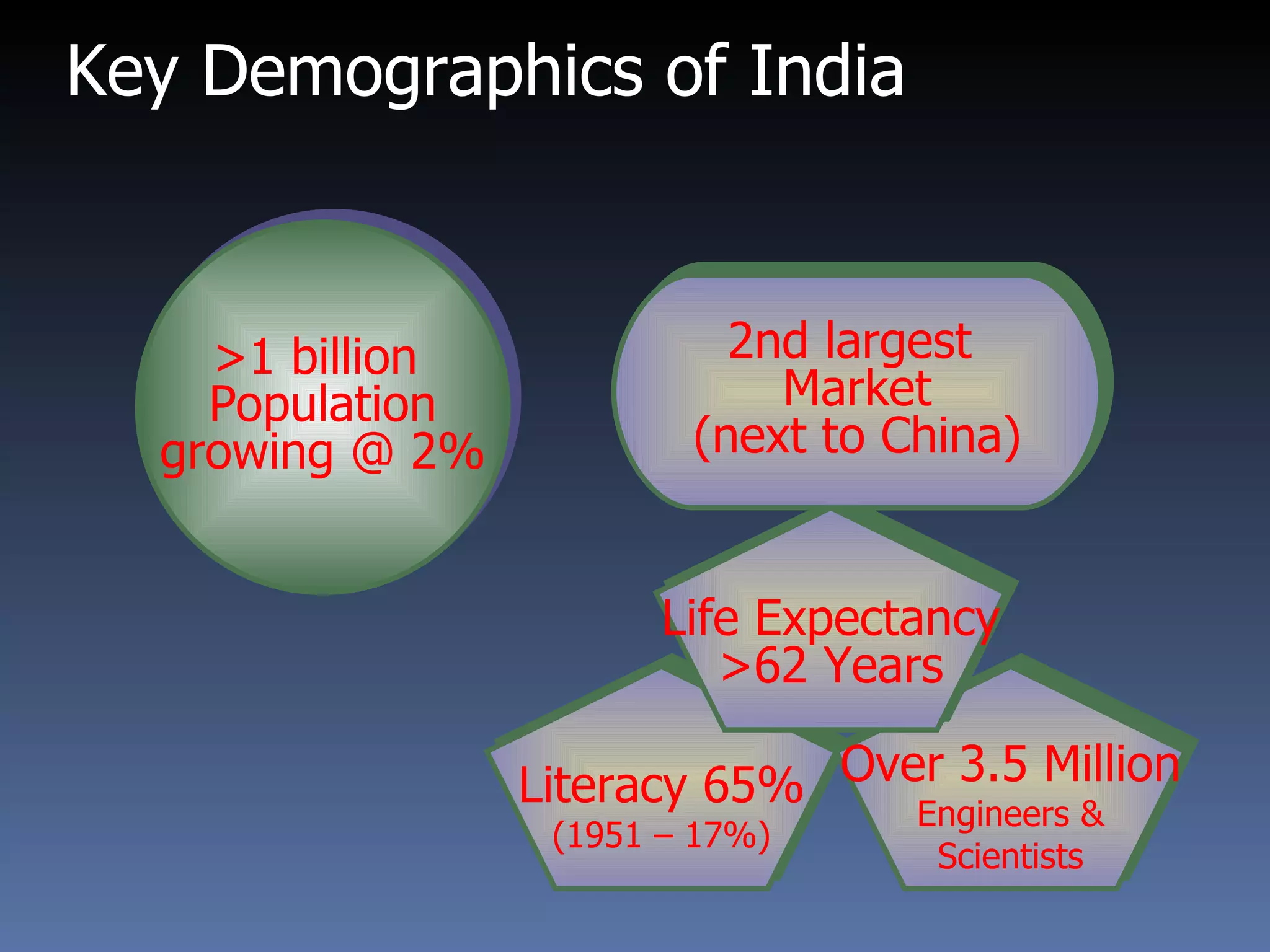
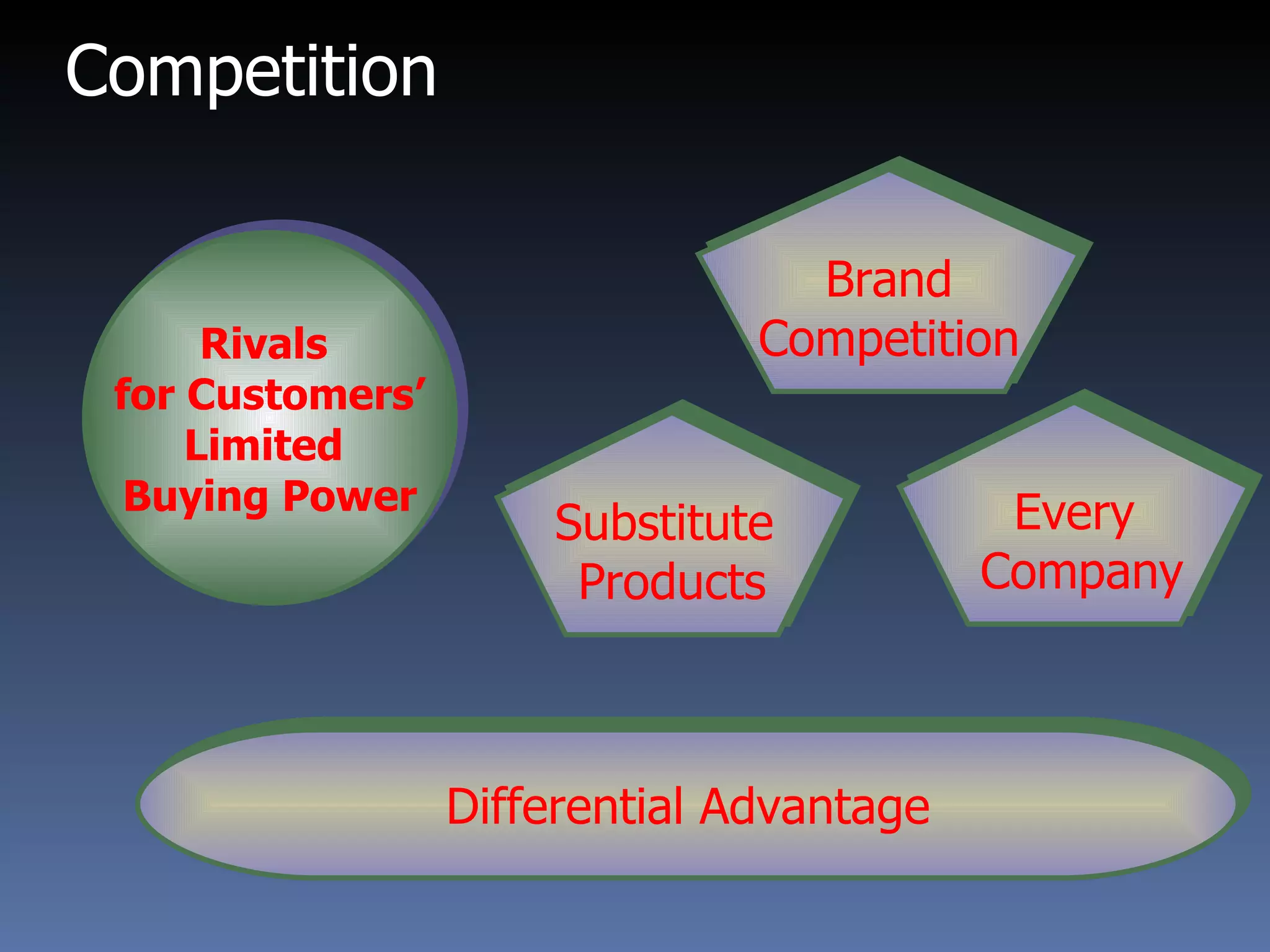
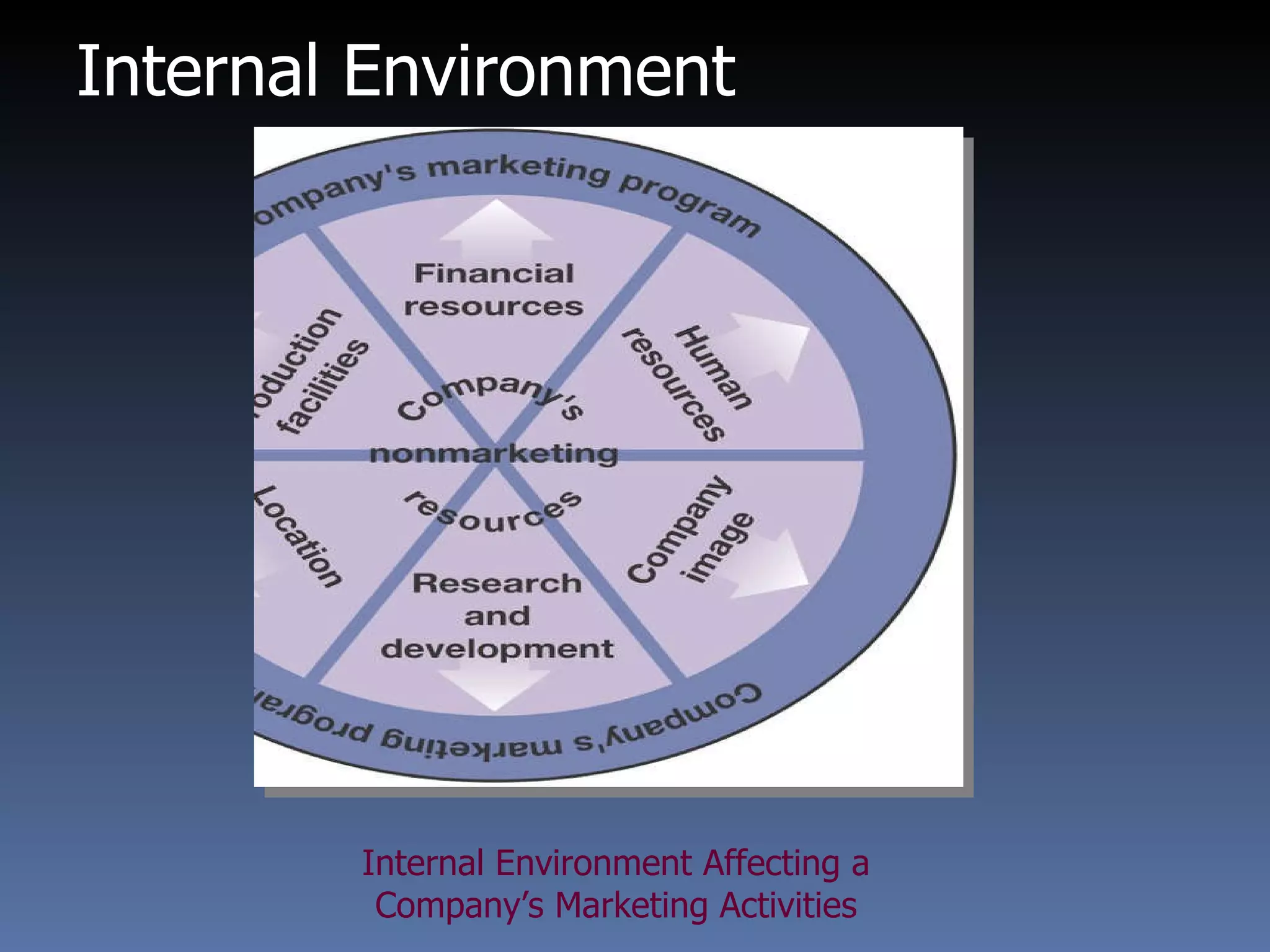
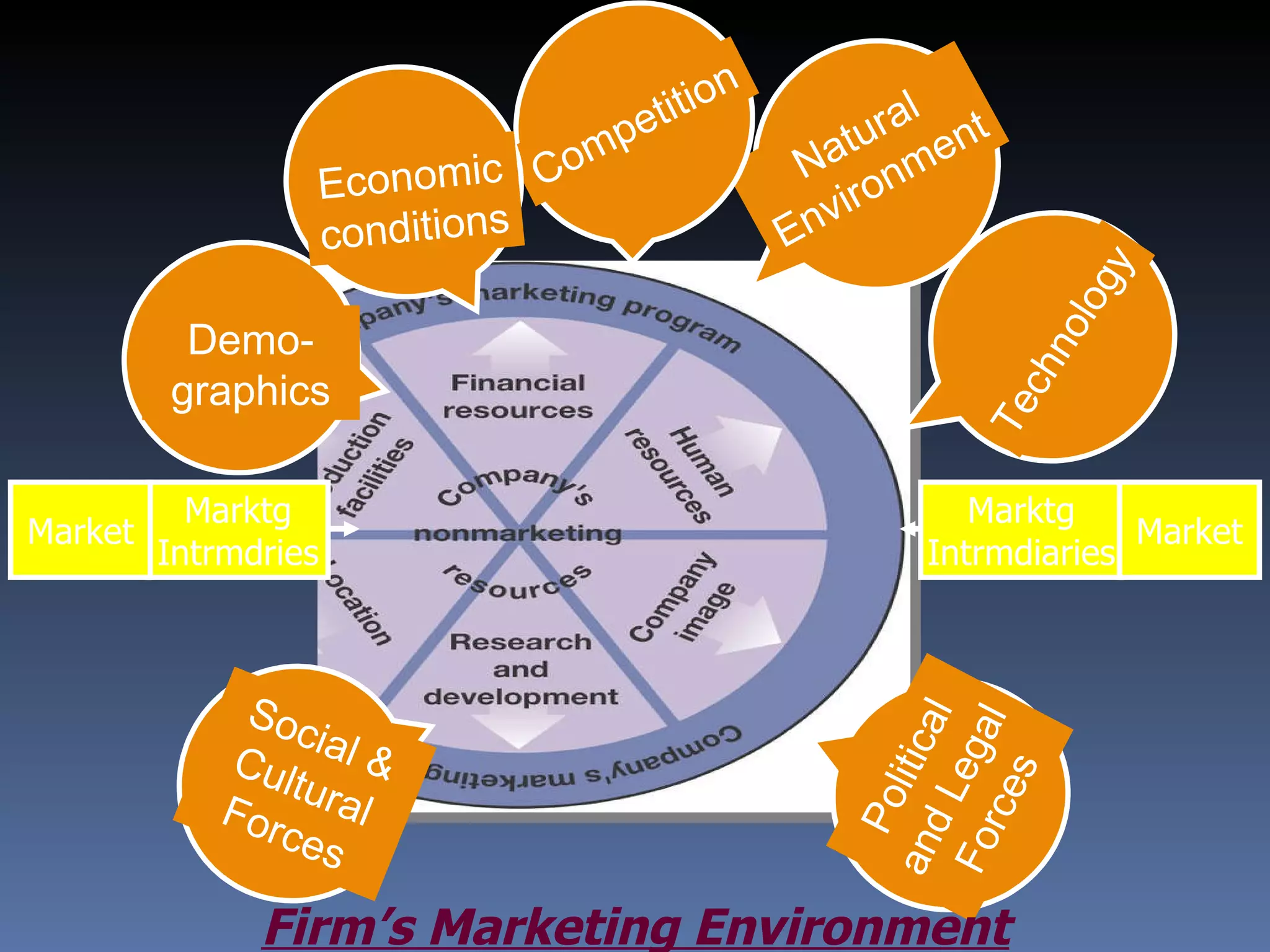
This document provides an overview of international marketing management. It discusses the significance of global markets and the challenges of designing international marketing strategies. Key points covered include:
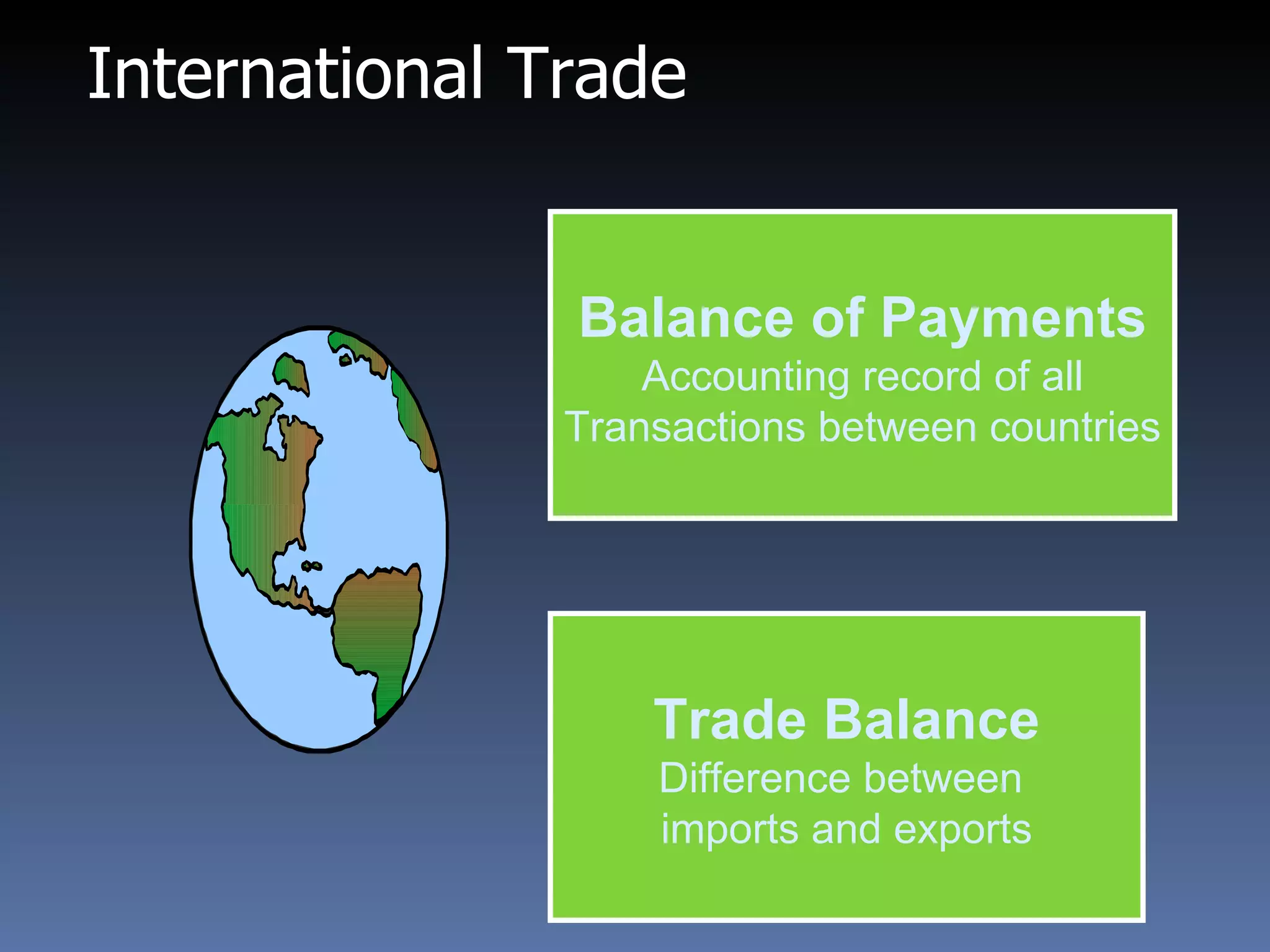
- Reasons for international trade include access to products, comparative advantage, and potential demand in foreign markets.
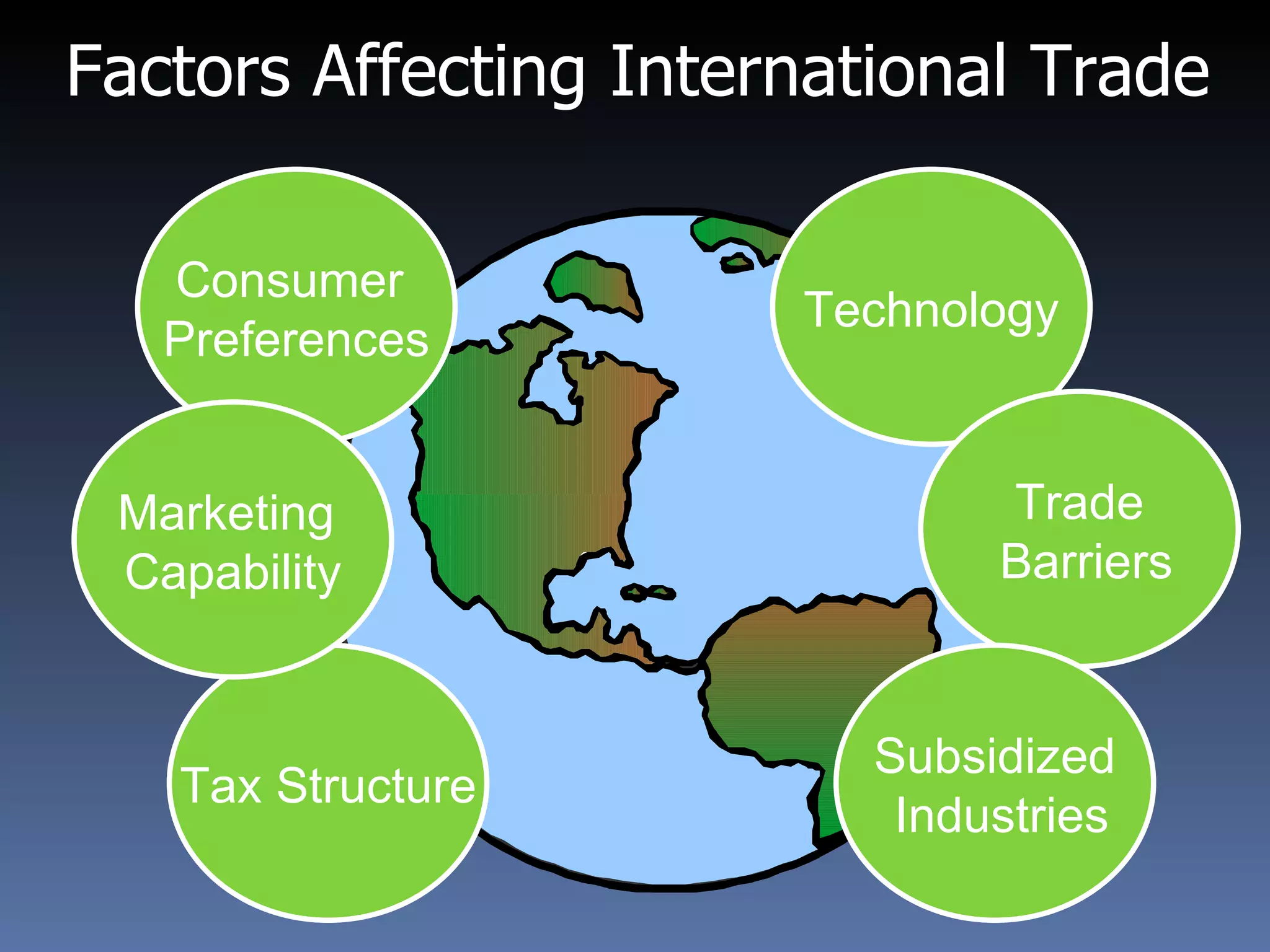
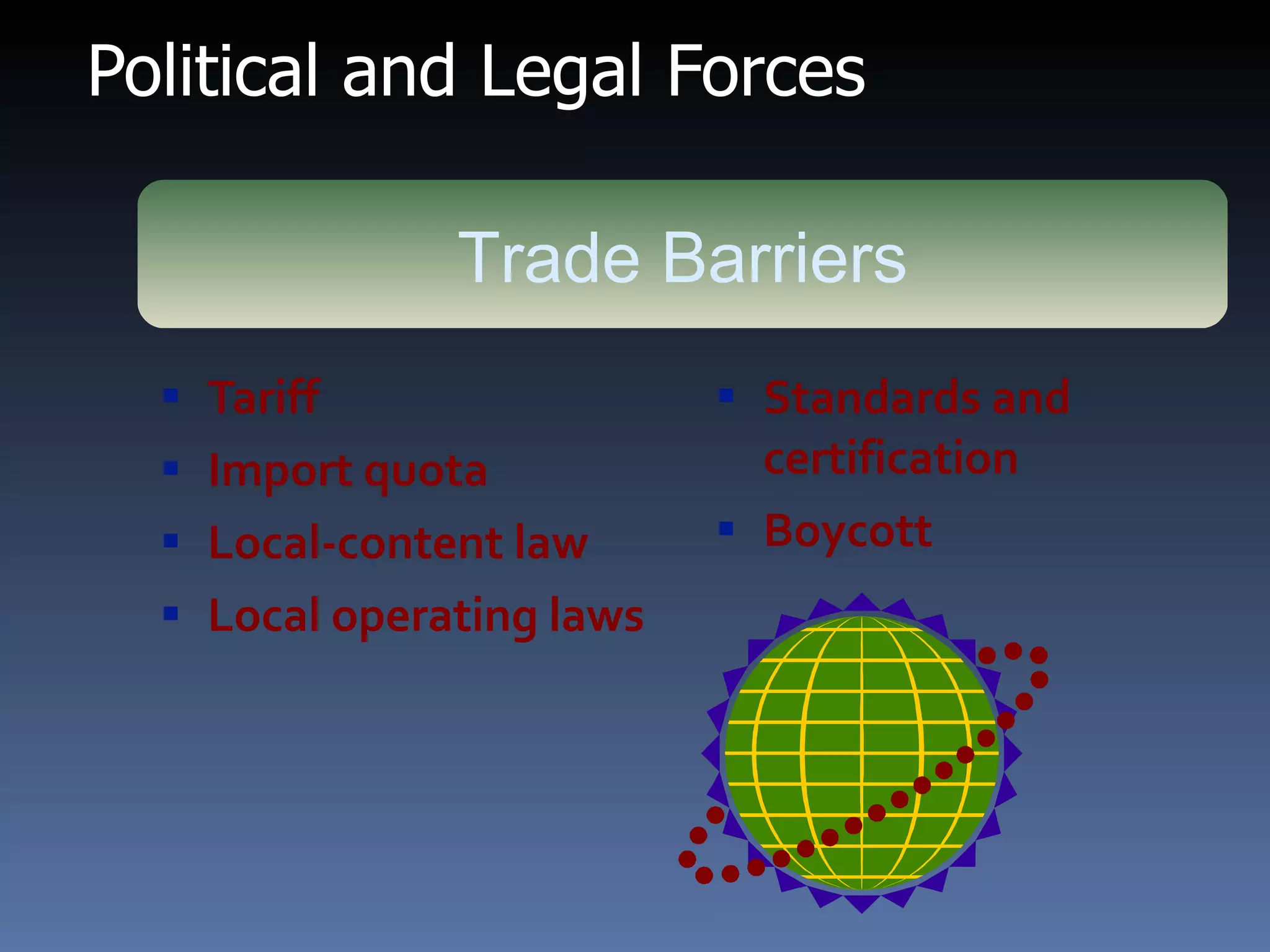
- Factors affecting international trade include technology, consumer preferences, trade barriers, and marketing capability.
- Structures for operating in foreign markets range from low involvement like exporting to high involvement like wholly owned subsidiaries.
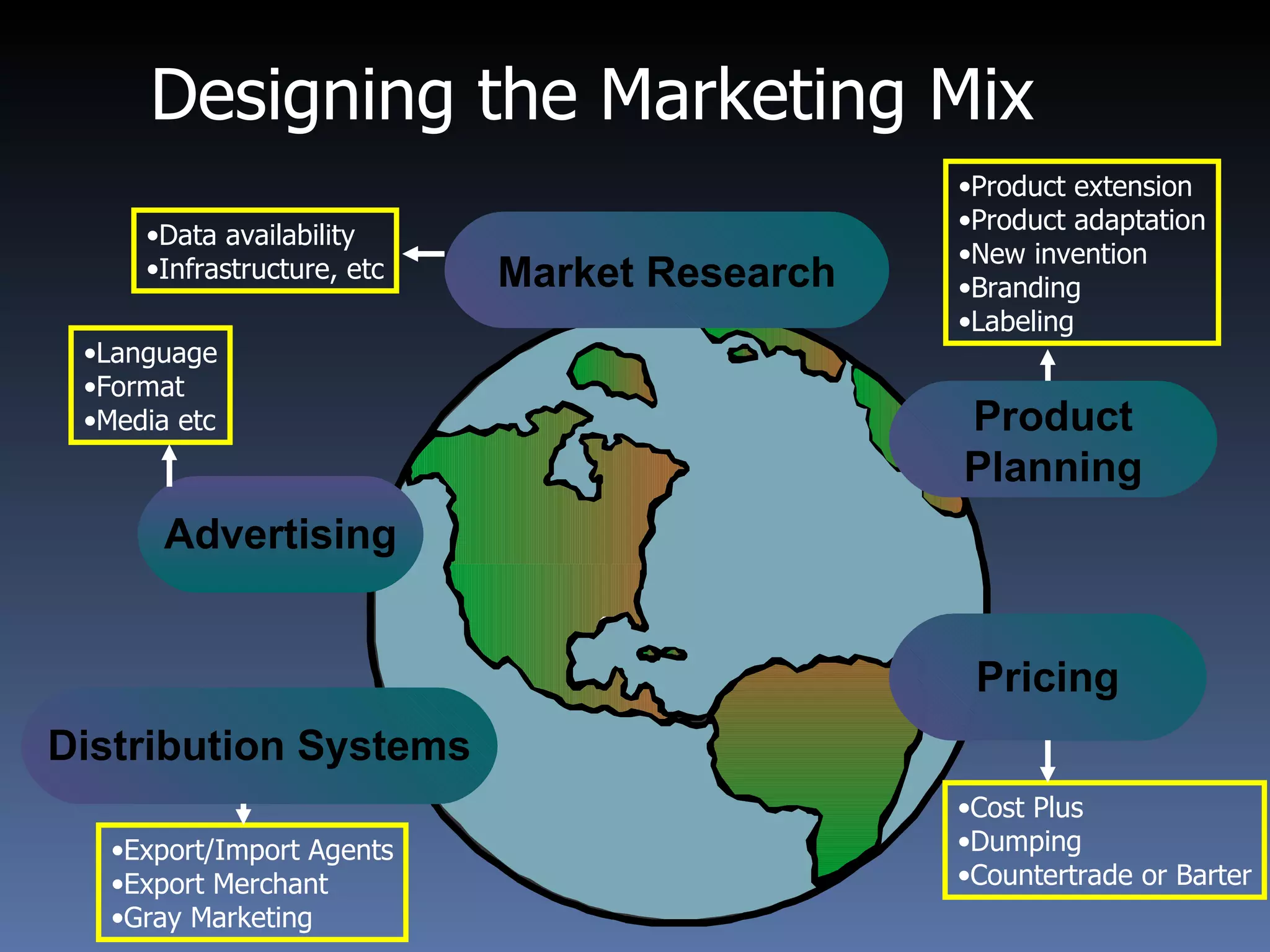
- Designing the international marketing mix requires considering market research, product adaptation, pricing strategies, and promotional adaptations for different countries and cultures.