Embed presentation
Downloaded 66 times








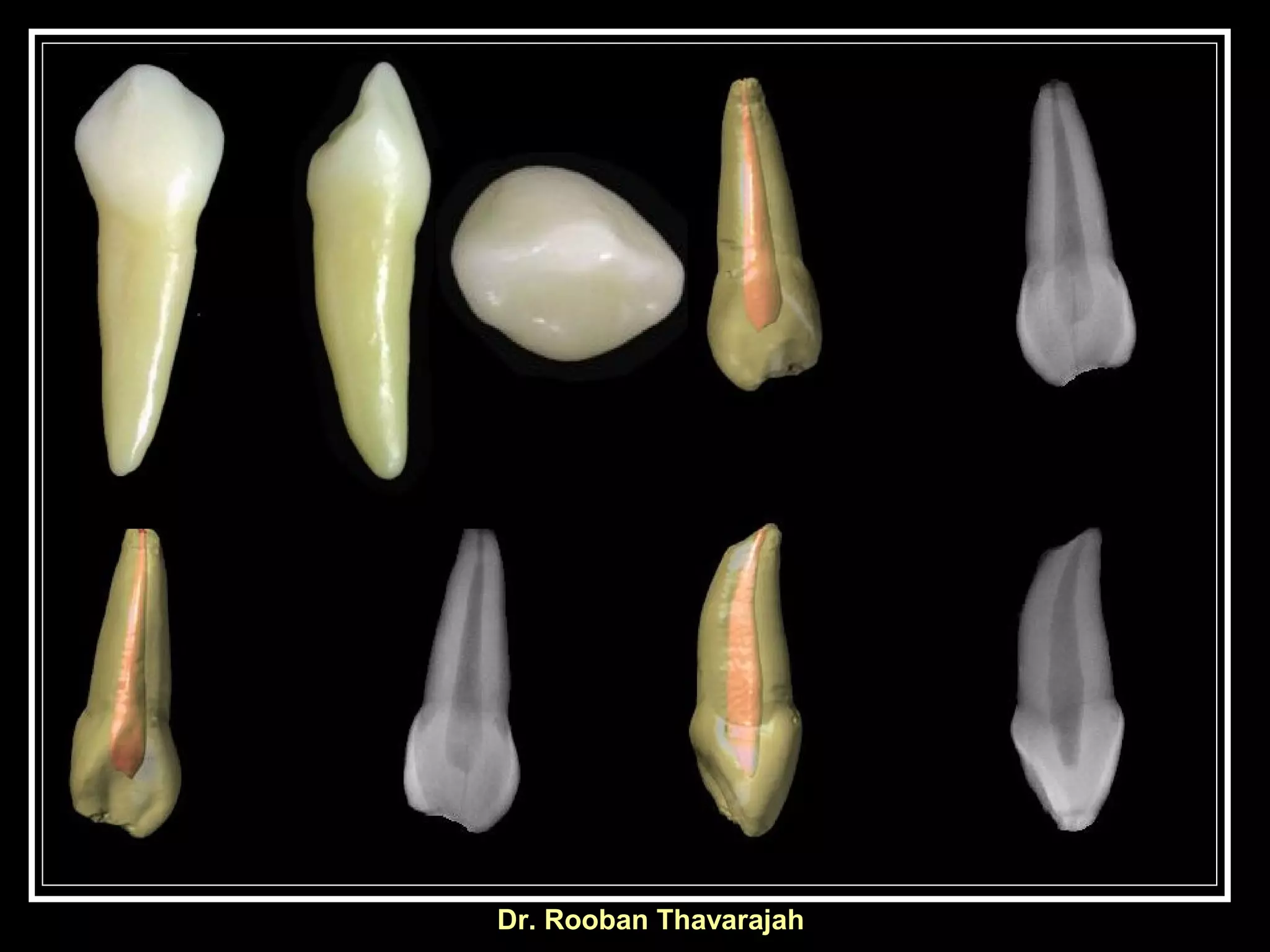

Dr. Rooban Thavarajah's lecture on maxillary canine morphology outlines the distinguishing features of deciduous dentition, emphasizing the crown's dimensions and unique cusp structure. Key points include the tooth's convex surfaces, prominent cingulum, and specific measurements related to mesial and distal slopes. The document also contrasts the morphology with incisors, noting variations in the cervical line and crown height.









