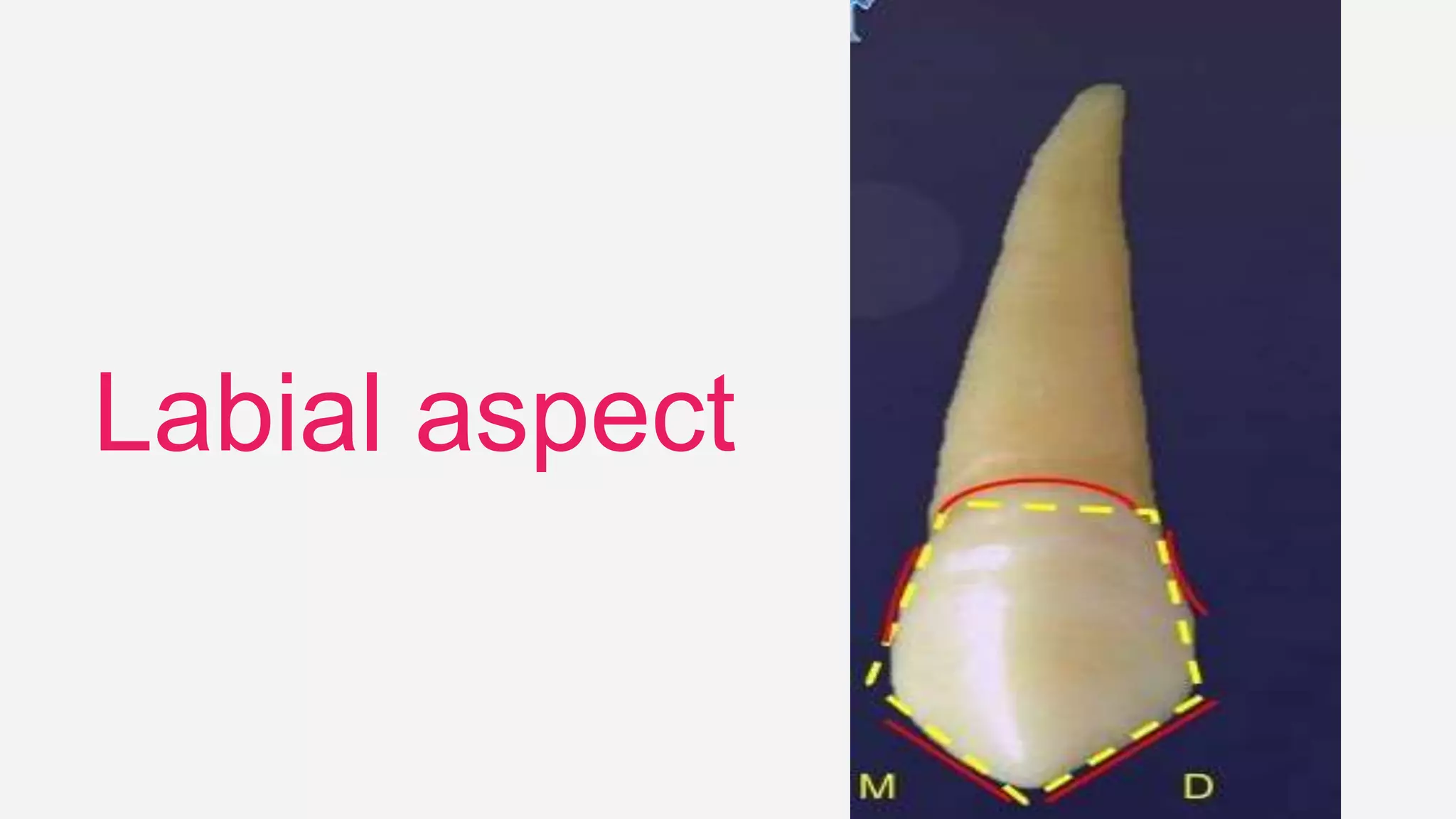
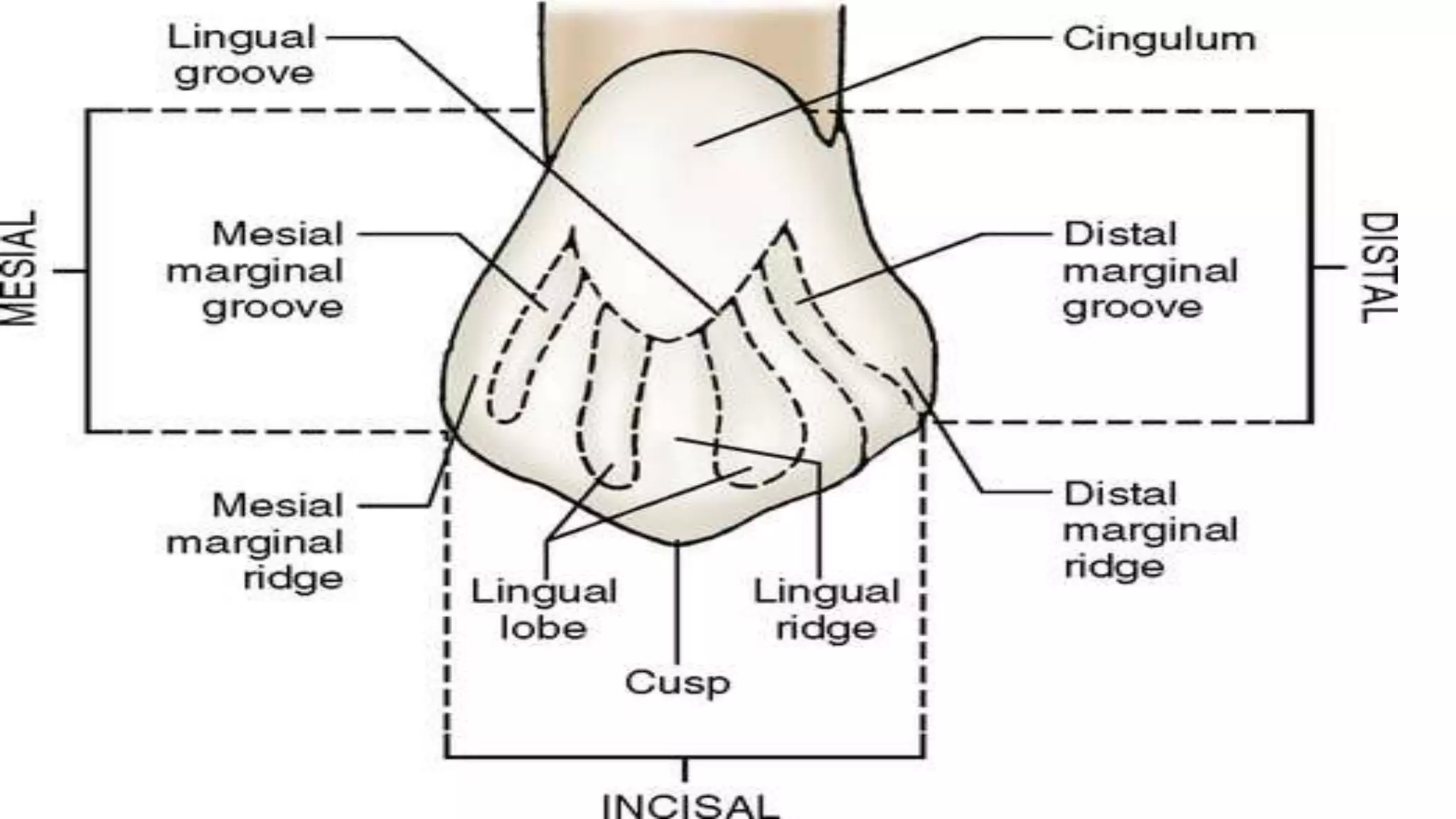
This document provides information about the permanent canine teeth. It describes the anatomy and dimensions of both the maxillary and mandibular canines. The maxillary canine is the longest tooth with a conical root and prominent cusp. It erupts around age 11-12 years. The mandibular canine resembles the maxillary canine but is narrower with slightly shorter roots. Both canines are important for guidance during jaw function and maintaining stability in the dental arch.