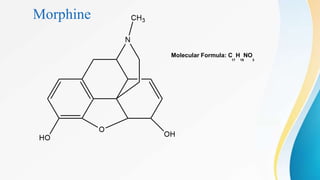
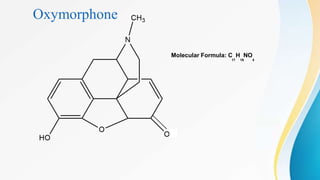
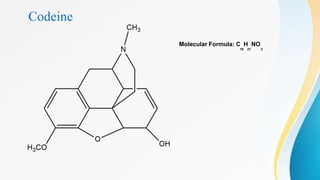
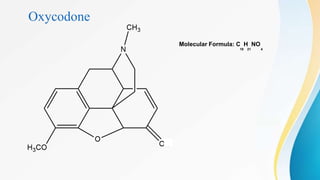
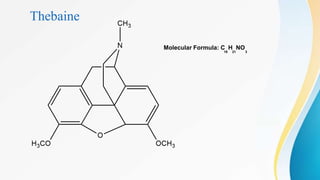
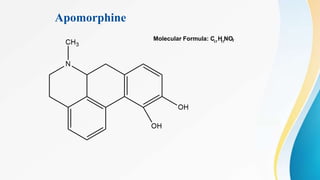
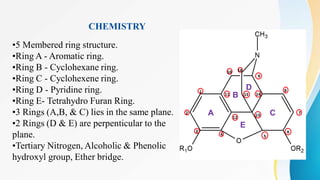
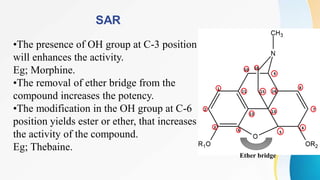
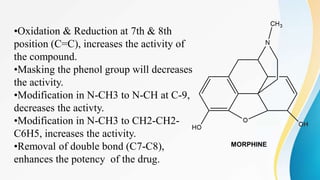
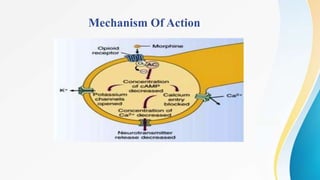
This document discusses drugs that affect the central nervous system, specifically morphine alkaloids. It provides information on morphine, codeine, thebaine, apomorphine, oxycodone, and oxymorphone, including their molecular formulas and brief histories. It also discusses the chemistry, structure-activity relationships, mechanisms of action, and uses of morphine alkaloids. The presentation was given by Aswini Sasidharan of the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry at Grace College of Pharmacy in Palakkad.