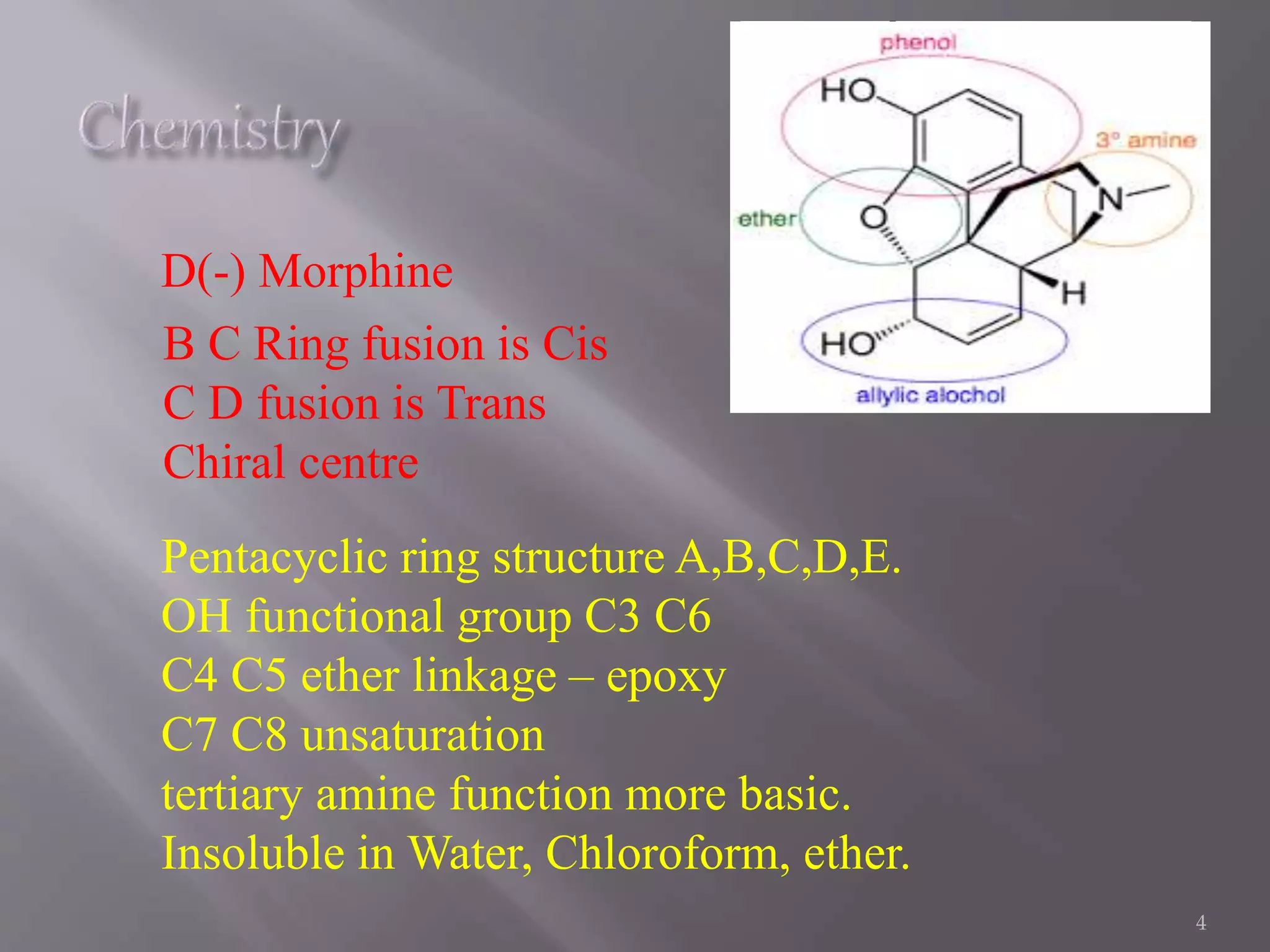
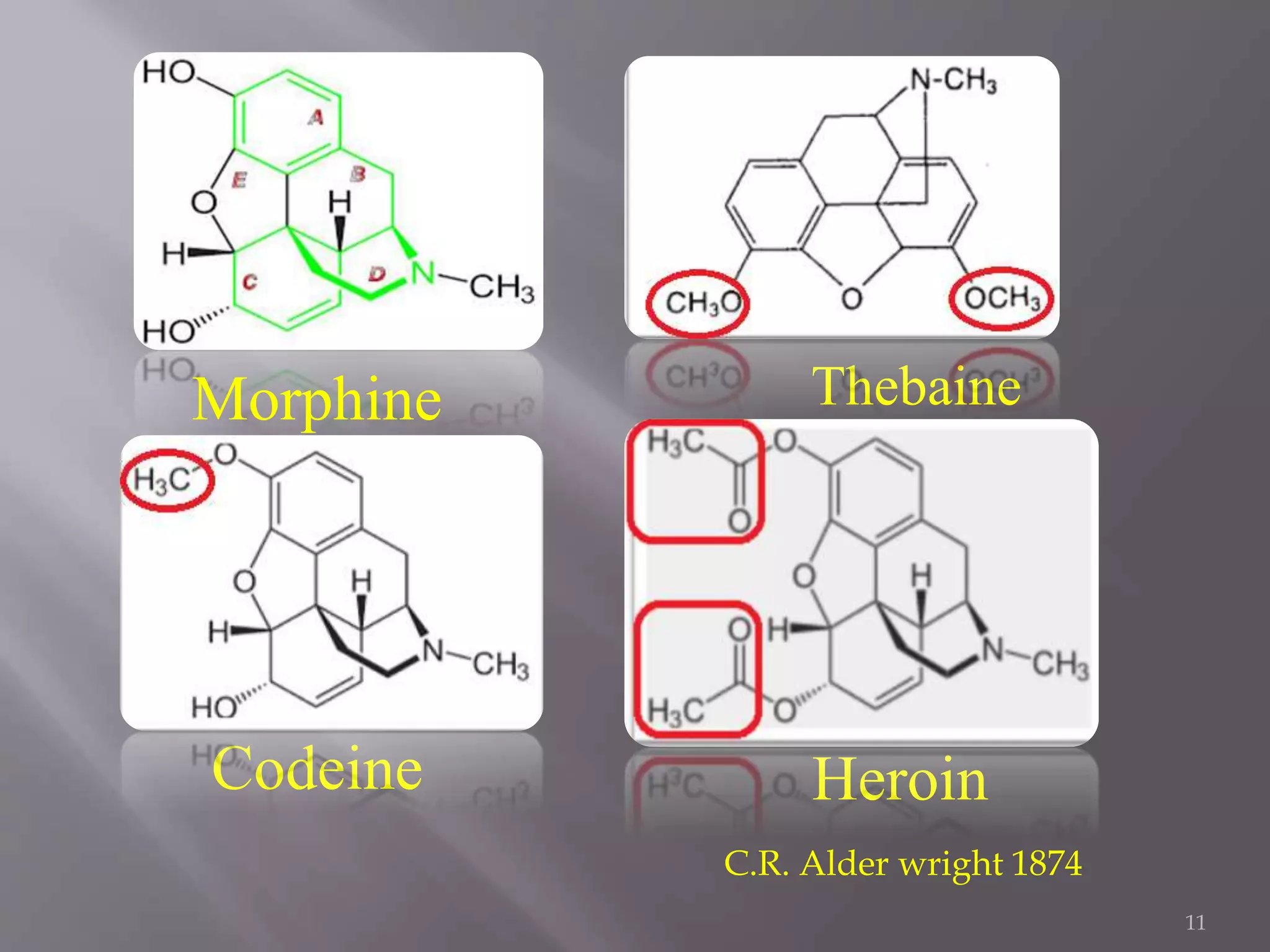
This document discusses the biological source, isolation, and chemical structure of morphine. It was first isolated from the opium poppy Papaver somniferum in 1804. Morphine has a pentacyclic ring structure and is insoluble in water and some organic solvents. It exerts its effects by interacting with opioid receptors in the central nervous system. The document also discusses morphine metabolism and the importance of various functional groups like hydroxyl groups for receptor binding and activity. Finally, it describes approaches to modify the morphine structure by adding or removing rings to synthesize compounds with analgesic activity.