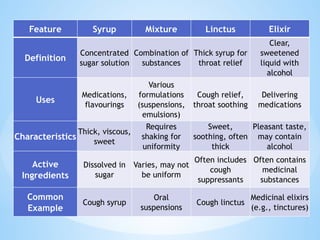
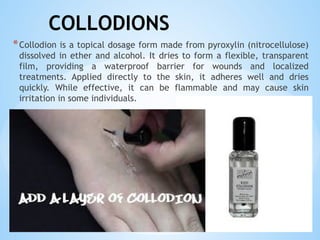
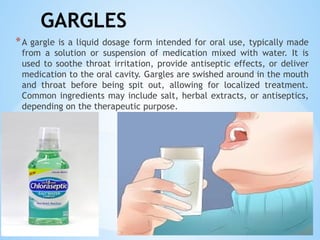
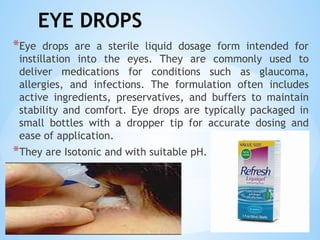
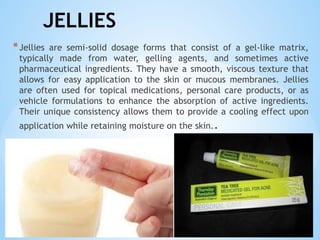
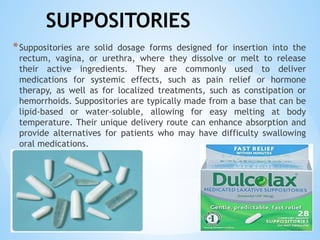
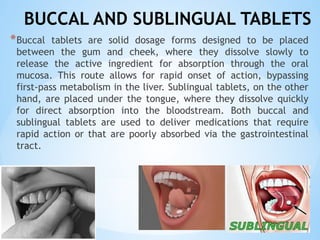
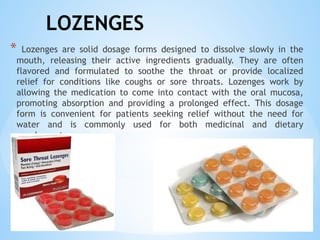
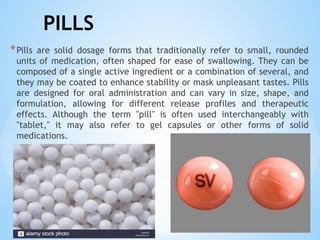
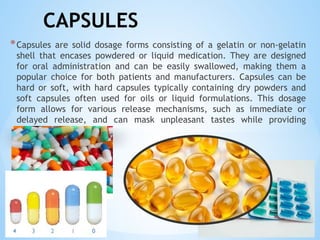
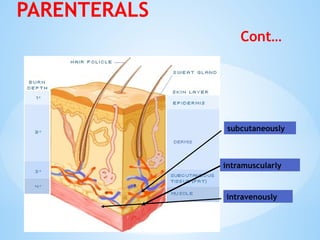
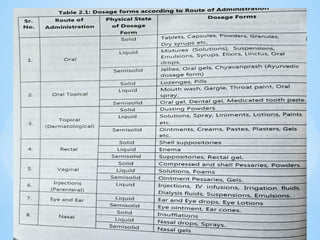
The document outlines the various pharmaceutical dosage forms, emphasizing their classifications based on administration routes, physical forms, and liquid types. Key types discussed include monophasic (like syrups and solutions) and biphasic (like emulsions and suspensions) liquids, as well as semi-solid forms (ointments and creams) and solid forms (tablets and capsules). It details the characteristics, uses, and examples of each dosage form to illustrate their importance in medication delivery.