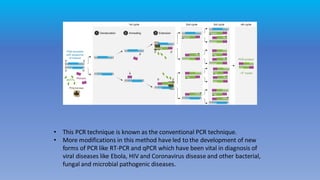
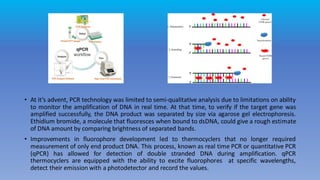
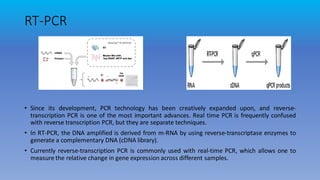
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. It involves cycling between high and low temperatures to separate DNA strands and allow for replication. This allows for targeted amplification of millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) allows for detection and quantification of DNA during amplification through the use of fluorescent probes. Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) first converts RNA to DNA before amplification. PCR techniques like qRT-PCR are currently used for accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 by detecting the SARS-CoV-2 virus from samples.