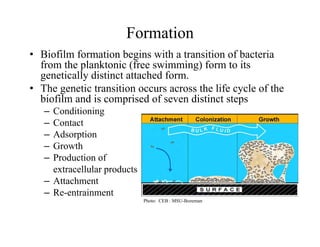
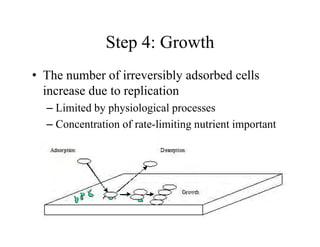
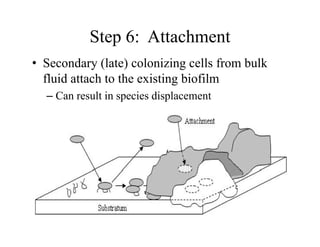
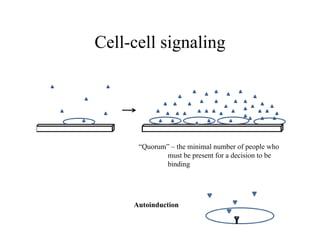
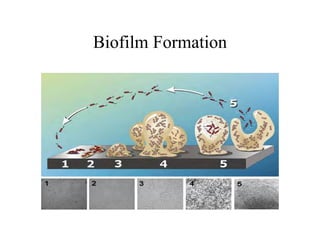
Biofilms are complex communities of microorganisms encased in a self-produced matrix that form on living and non-living surfaces. They are the primary mode of existence for bacteria in aqueous environments. The establishment and maintenance of biofilms is a highly organized, multi-step process involving initial attachment, growth, production of extracellular matrix, and potential later attachment of additional species. Biofilms provide advantages to microorganisms like enhanced nutrient uptake, protection, and social coordination between cells.