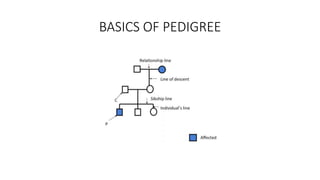
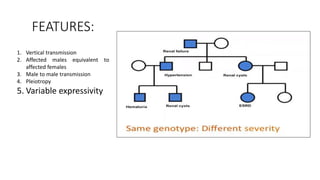
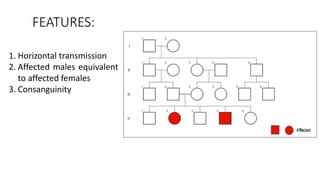
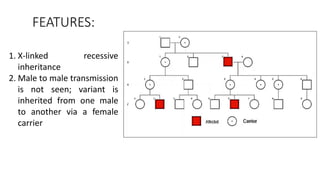
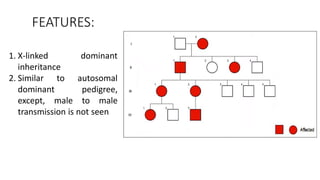
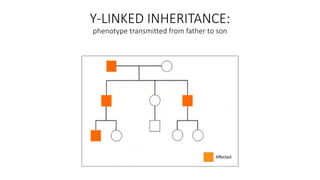
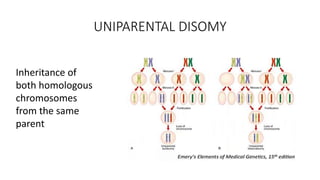
This document discusses various patterns of inheritance including Mendelian patterns like autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked, and Y-linked inheritance. It also covers non-Mendelian inheritance patterns such as mitochondrial, genomic imprinting, unstable repeat expansions, uniparental disomy, mosaicism, and multigenic inheritance. For each pattern of inheritance, the key features are defined.