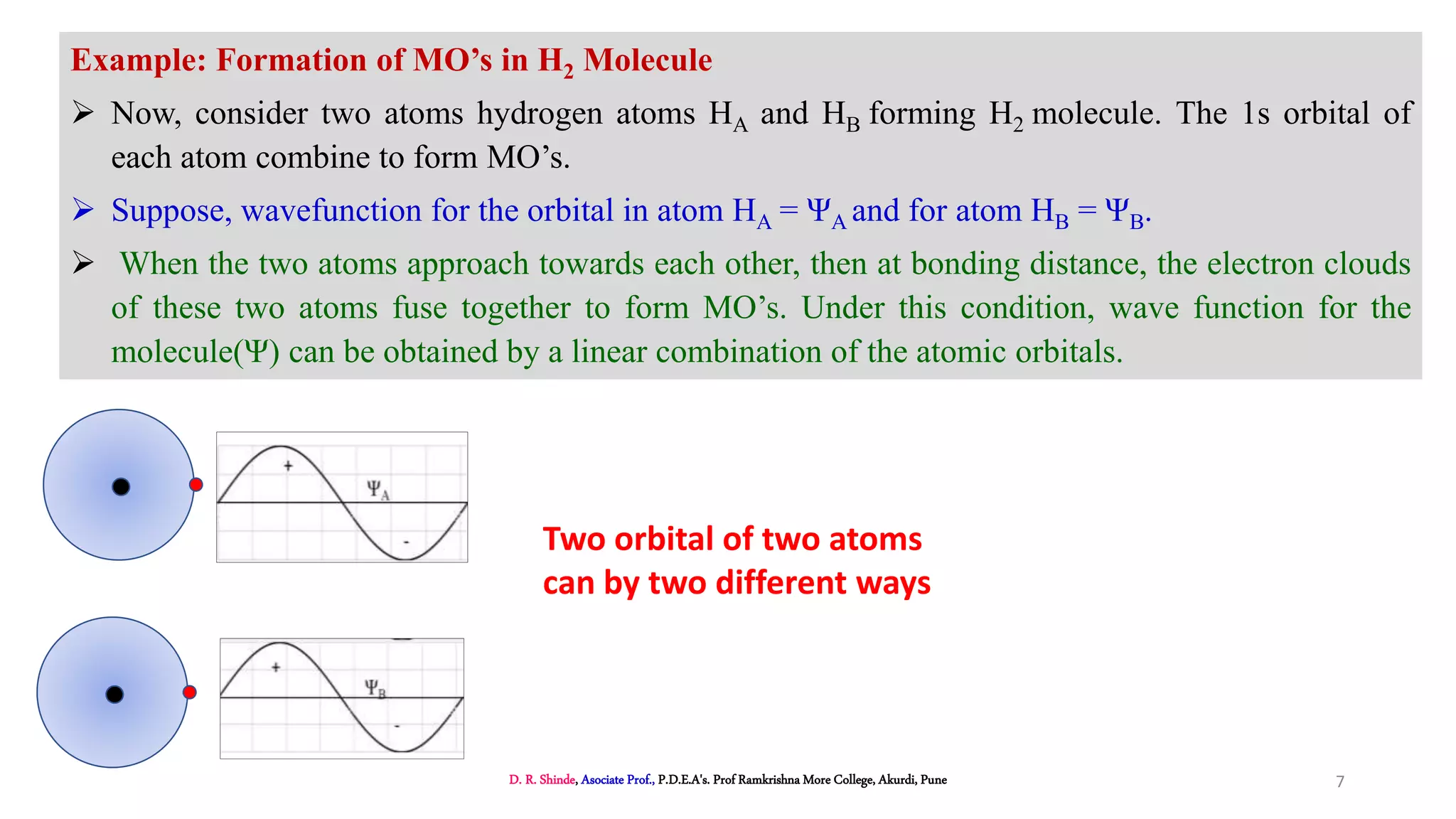
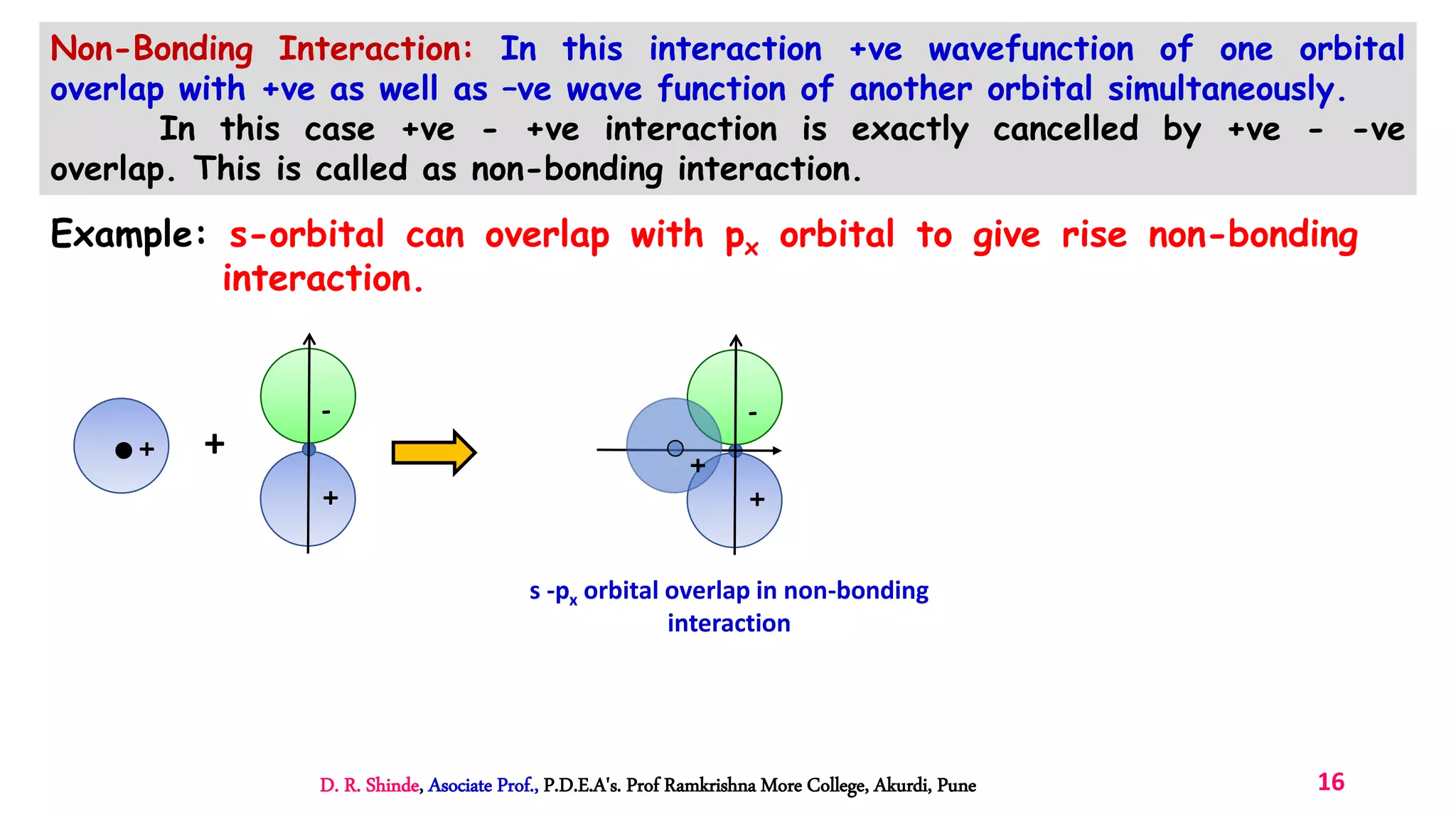
1. The document discusses Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) as an improvement over Valence Bond Theory (VBT) to explain bonding in molecules.
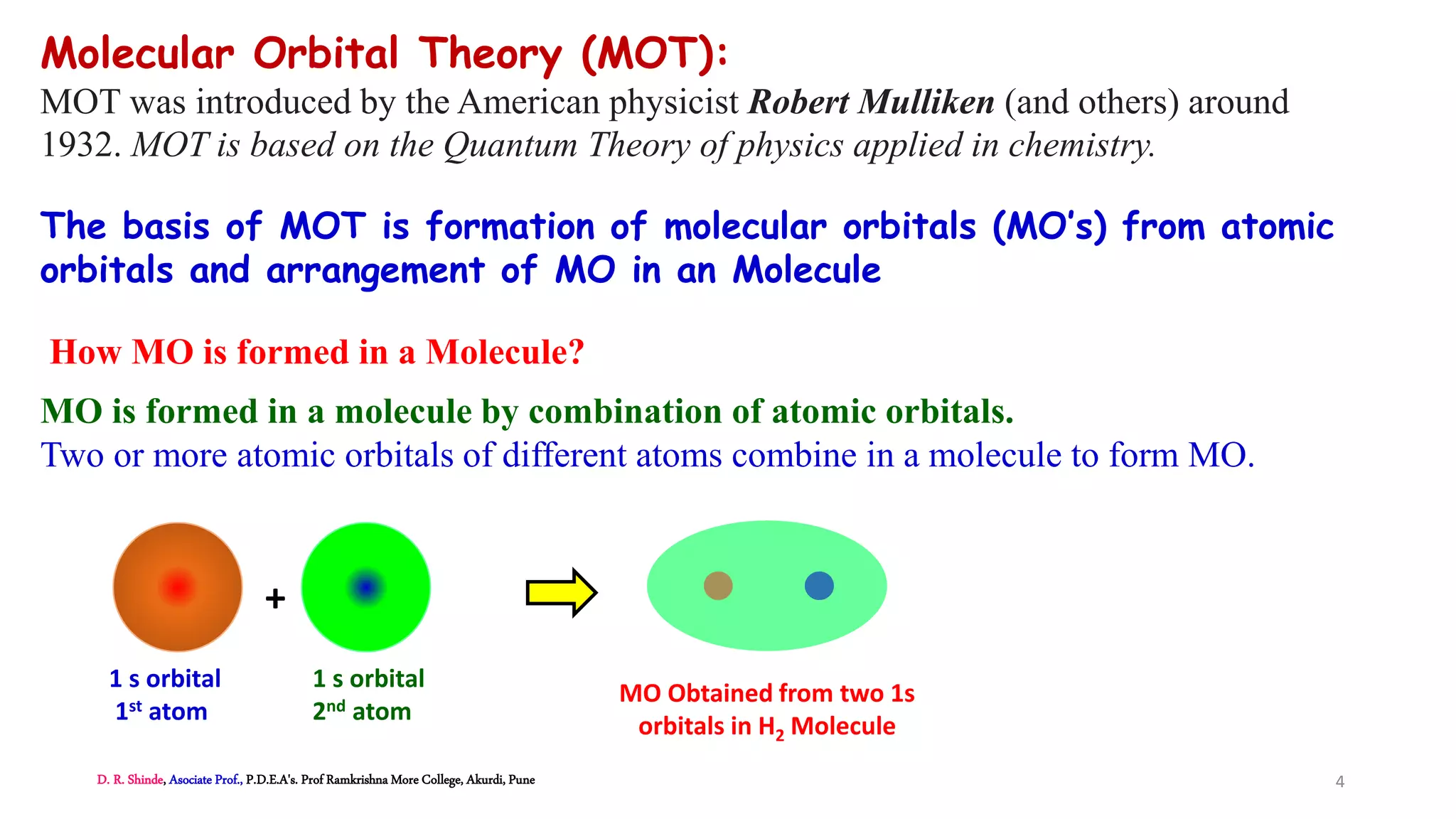
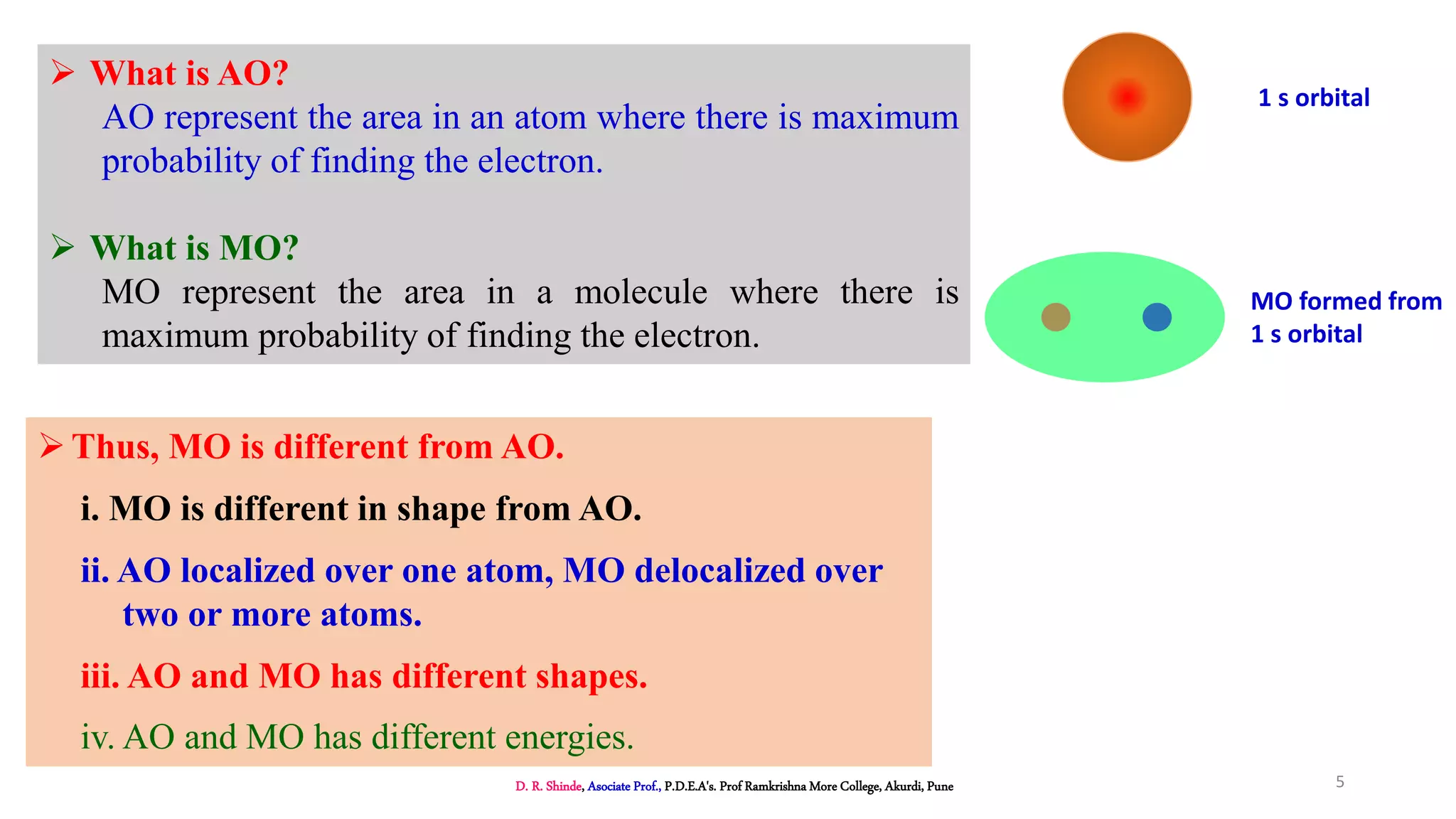
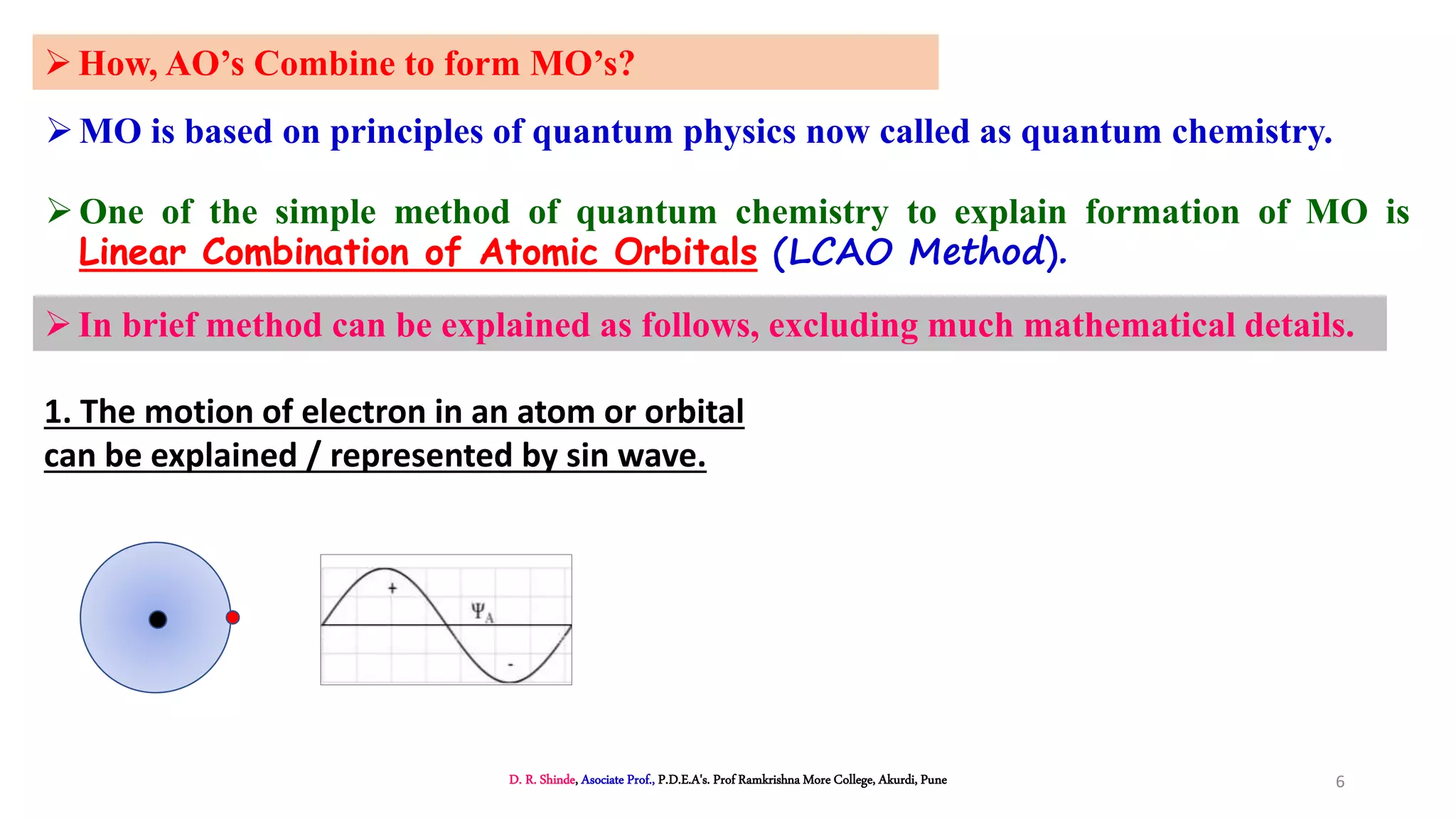
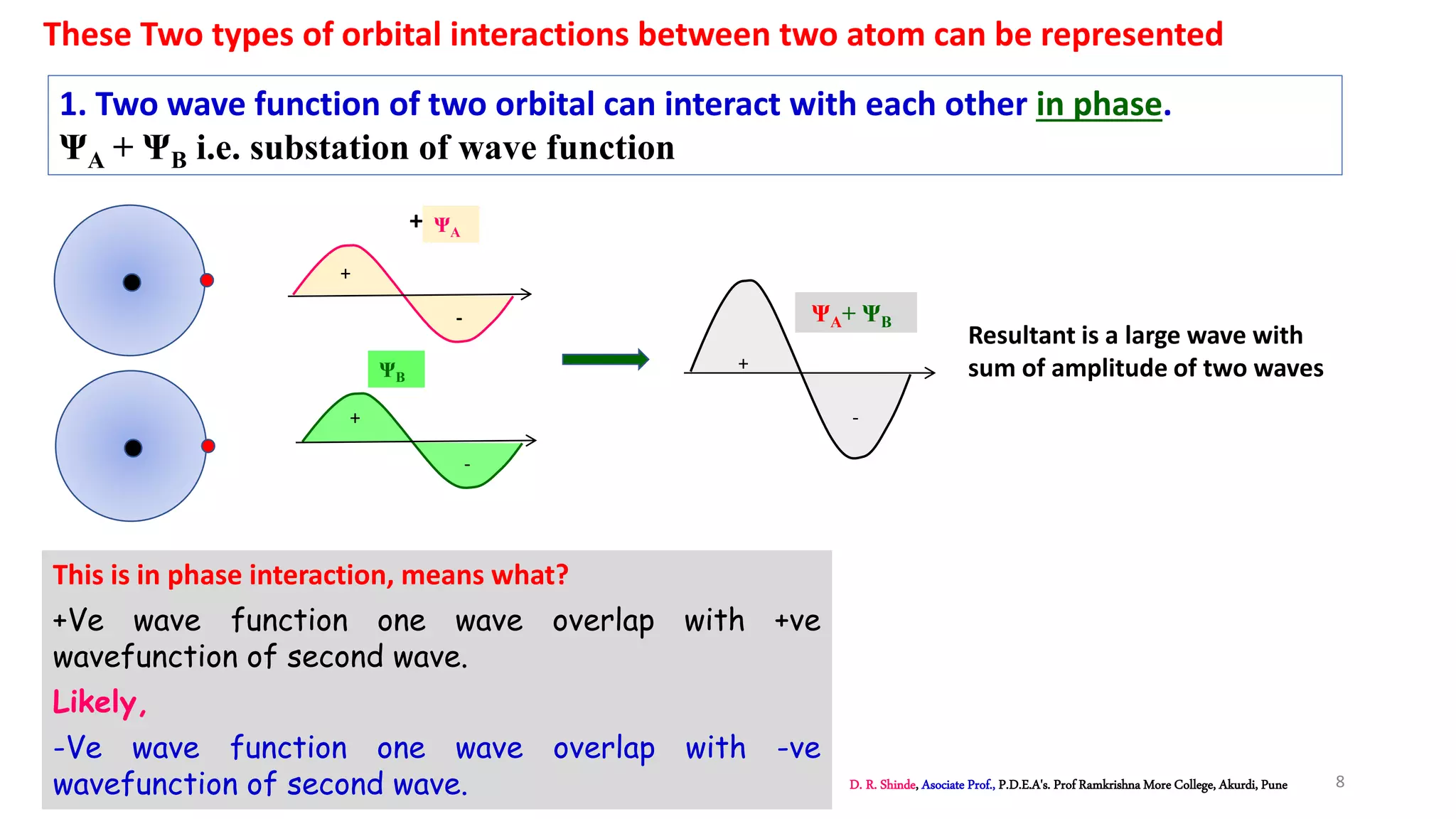
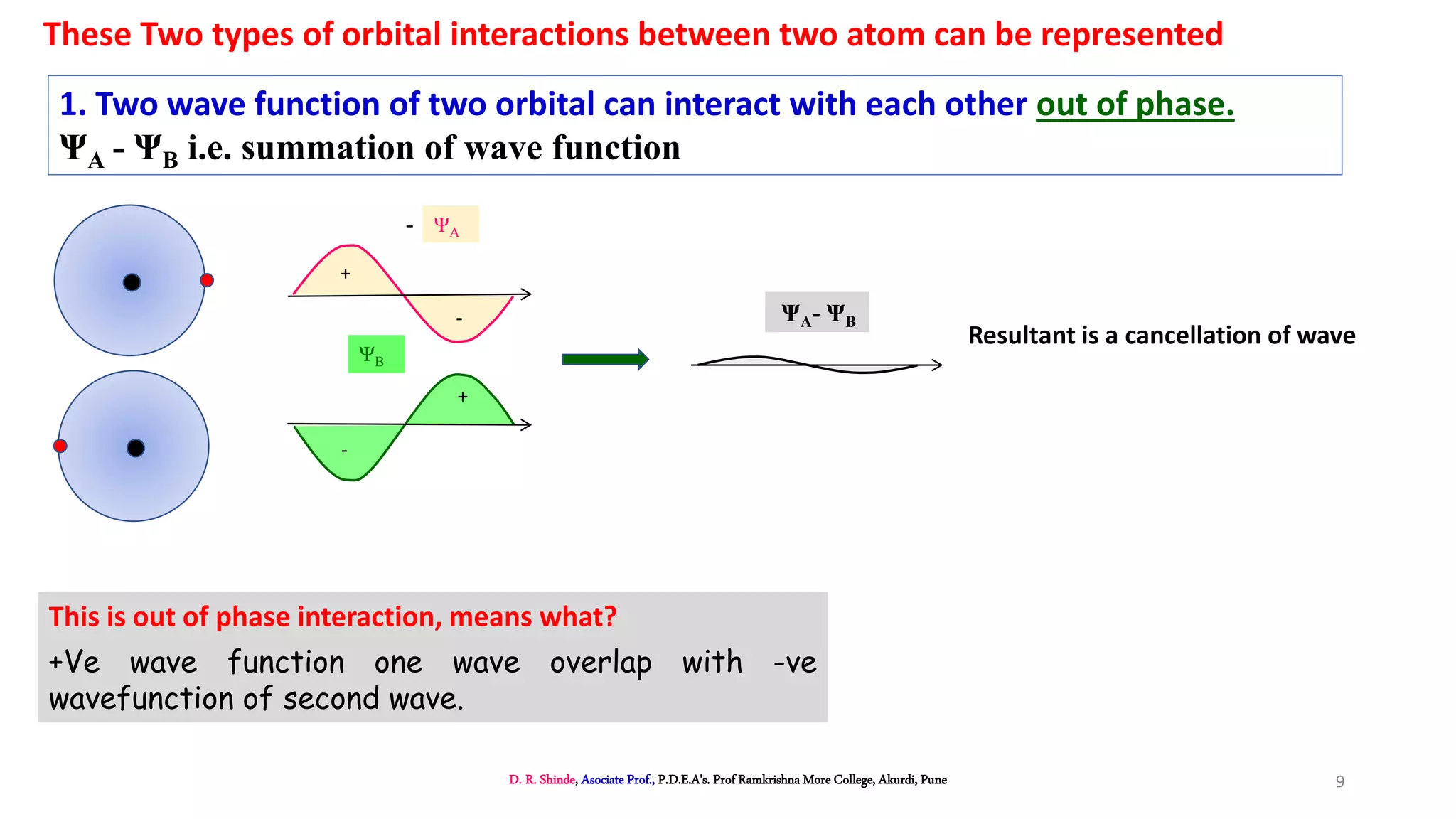
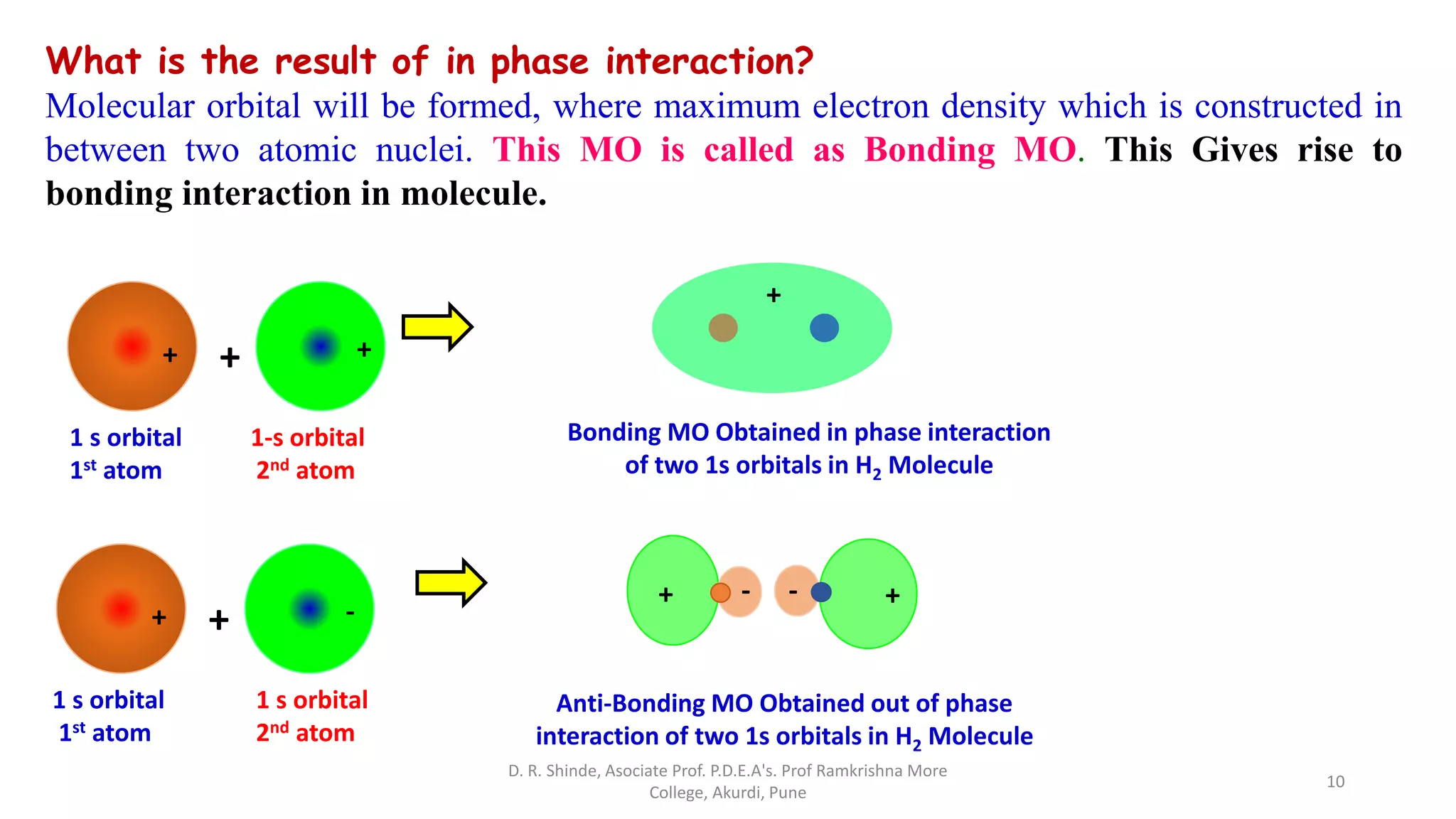
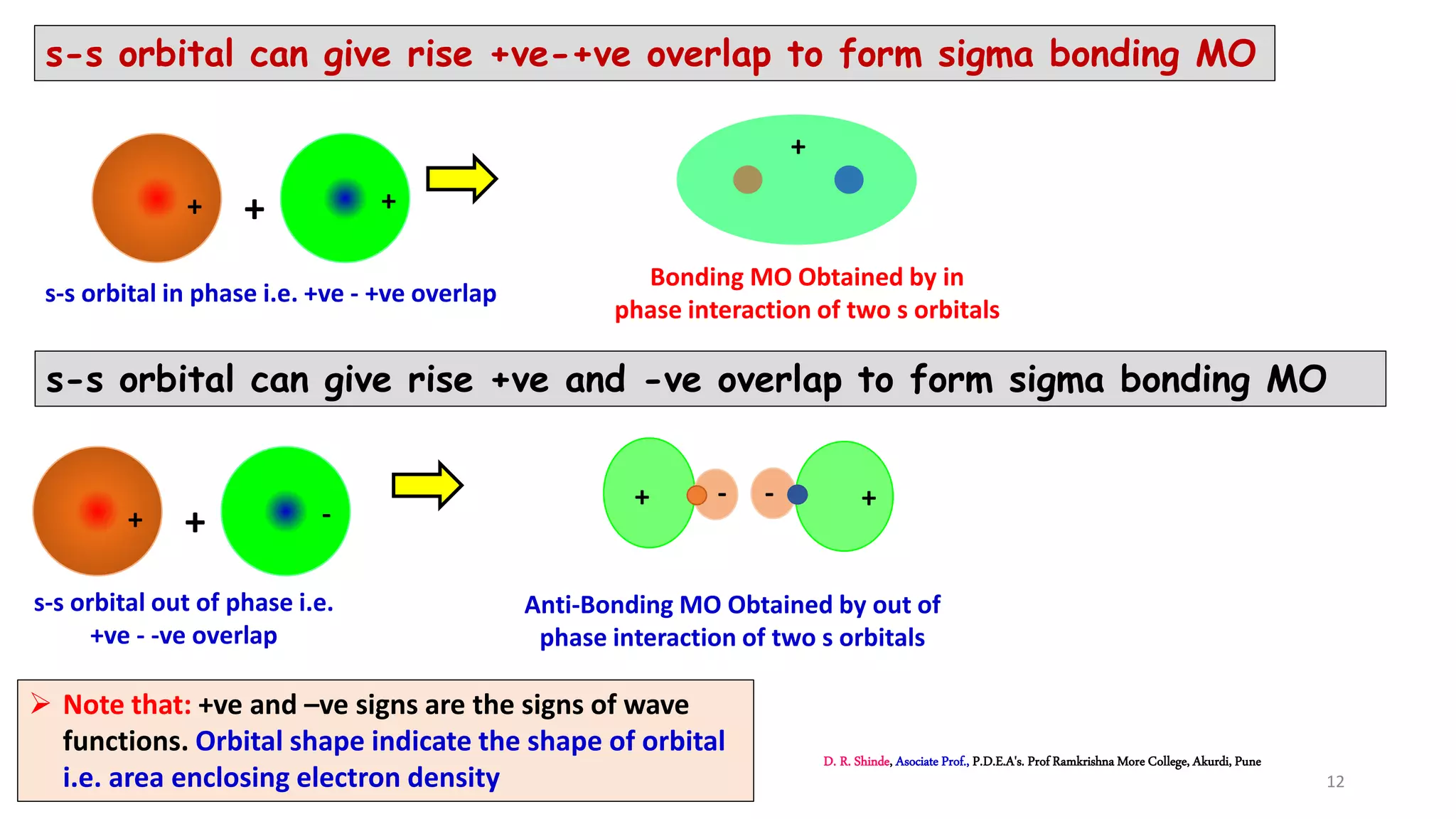
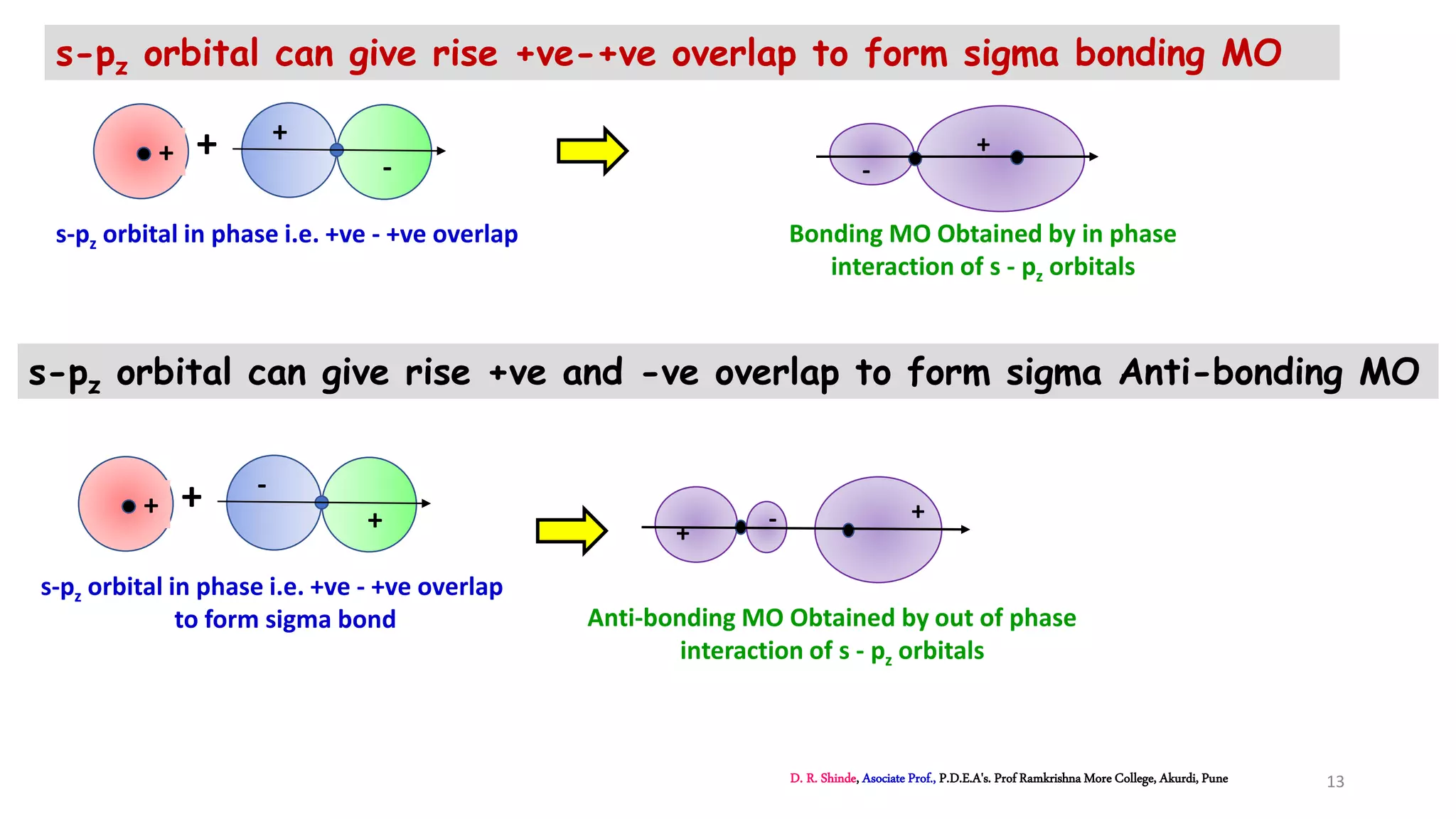
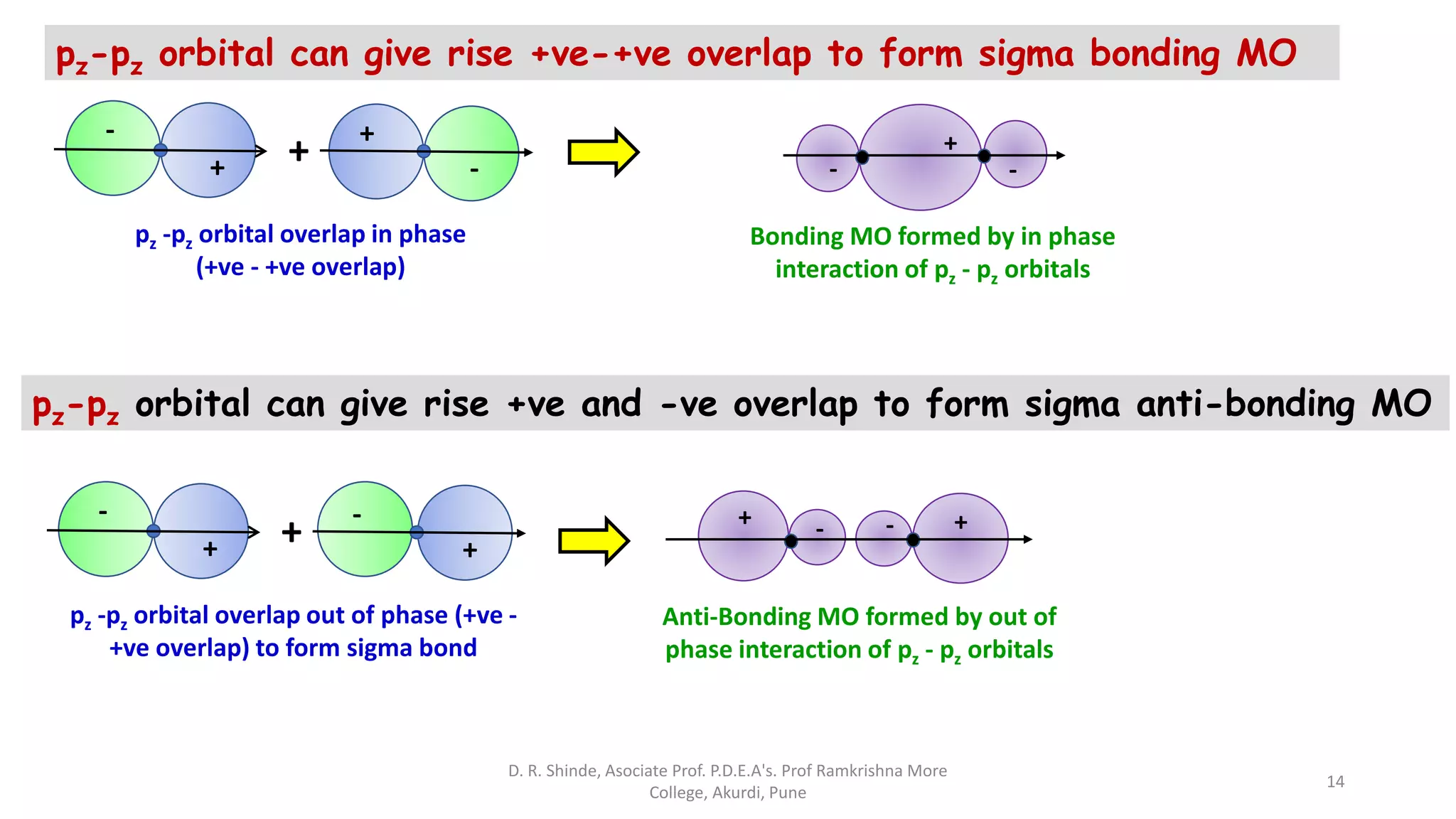
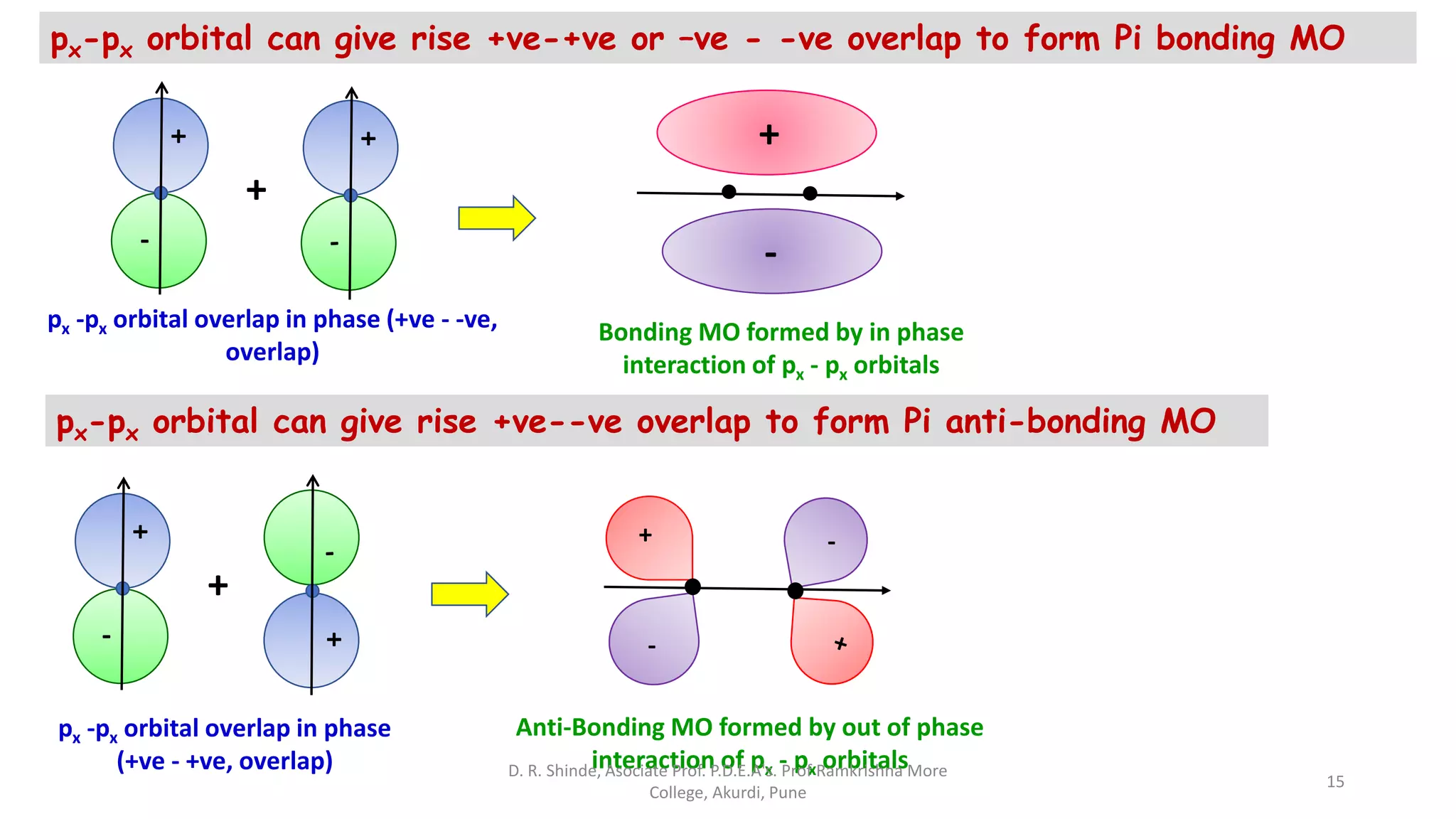
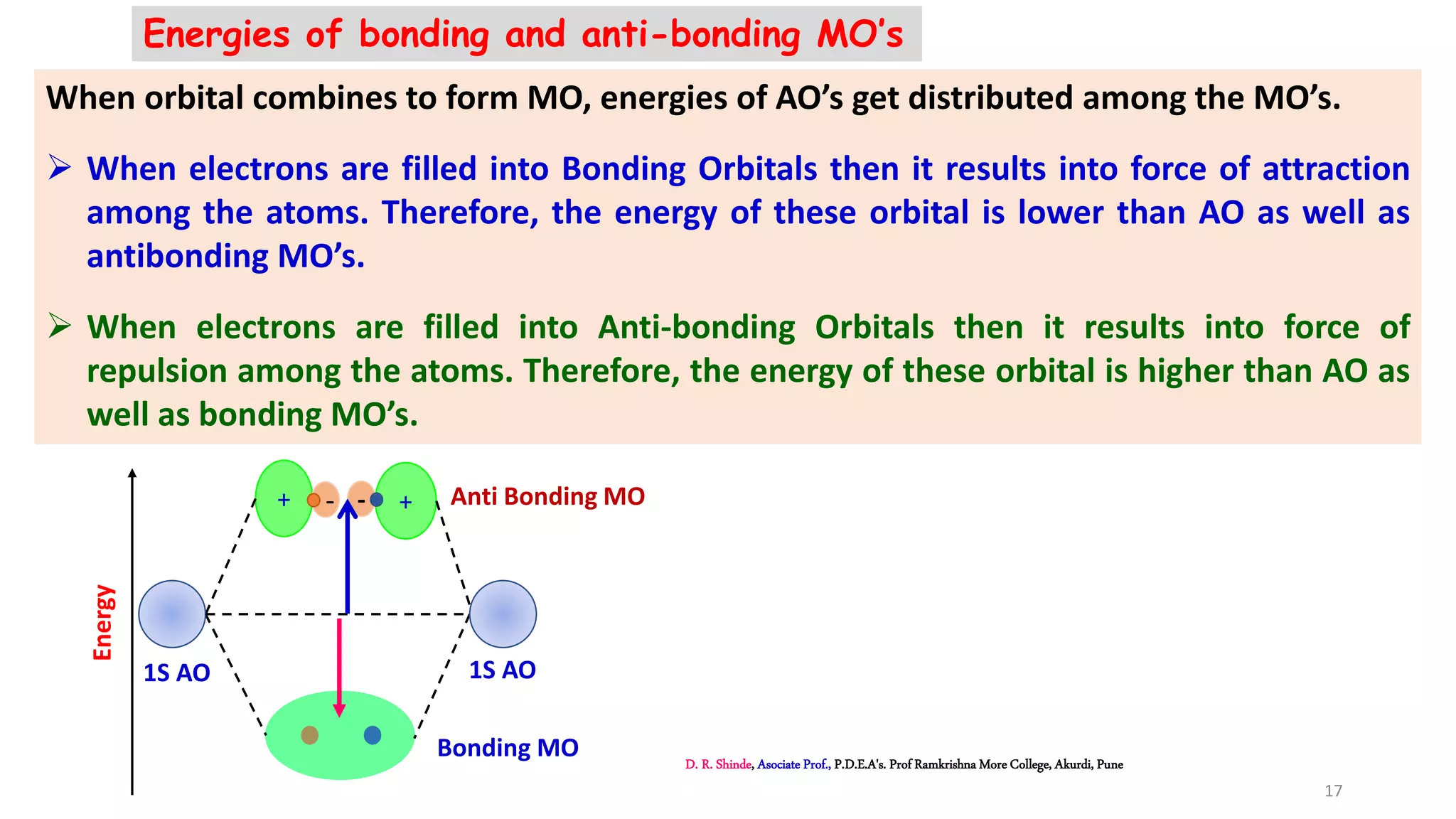
2. MOT proposes that atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals (MOs) through linear combination, resulting in bonding and antibonding MOs.
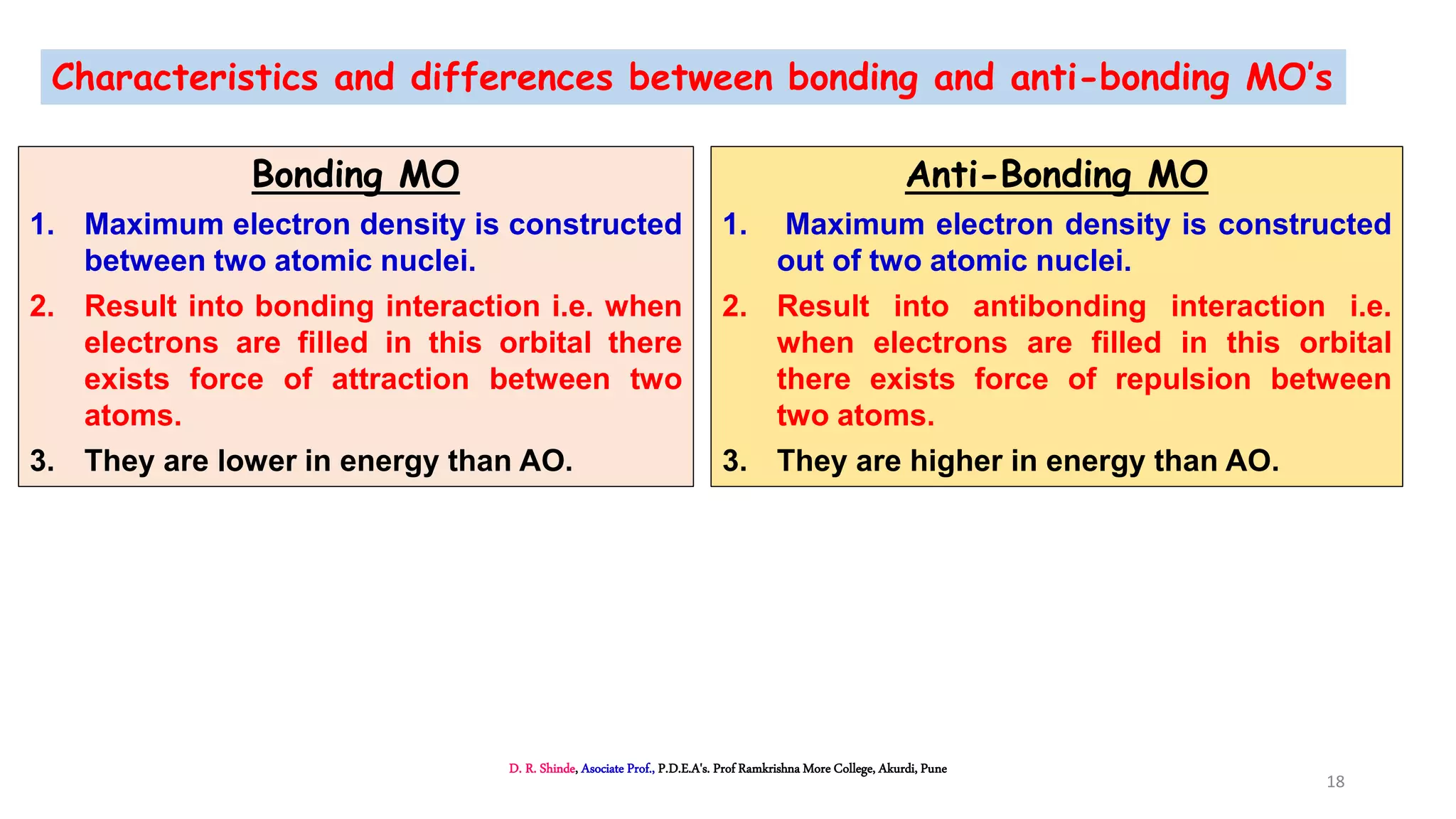
3. Bonding MOs have lower energy and result in attractive forces between atoms, while antibonding MOs have higher energy and result in repulsive forces.

![In this Lecture
we will learn
i. Limitations of VBT
ii. Atomic and Molecular Orbitals [AO’s and MO’s]
iii. Bonding and Antibonding MO’s
iv. Sigma and Pi MO’s and their energies
D. R. Shinde, Asociate Prof., P.D.E.A's. Prof Ramkrishna More College, Akurdi, Pune
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitaltheorypart-1-200805153527/75/Molecular-orbital-theory-part-1-2-2048.jpg)